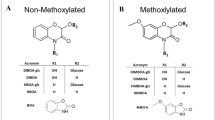
Abstract
A recent greenhouse study revealed a significant reduction of germination and growth of redroot pigweed (Amaranthus retroflexus) and common purslane (Portulaca oleracea) by rye mulch, whereas velvetleaf (Abutilon theophrasti) and common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album) were not suppressed. Since BOA detoxification by metabolic alteration may influence the relation between the benzoxazinoid content of the soil mulch and weed suppression, we tested the dynamics in BOA detoxification in different plant organs of three and 10-day-old seedlings of four warm season weeds incubated with five BOA concentrations (4, 20, 40, 80, and 200 μmol g−1 fresh weight). In addition, germination and length of 3-day-old seedlings were measured after exposure to 0, 0.3, 1.5, 3, 6, and 15 μmol BOA. Finally, we tested the influence of the MDR translocator inhibitors verapamil, nifedipine, and the GST inhibitor ethycrynic acid on BOA accumulation and detoxification activity. Due to BOA-detoxification, all weeds were able to grow in environments with low BOA contents. At higher contents, Abutilon theophrasti and Chenopodium album had a better chance to survive because of highly active mechanisms that avoided the uptake of BOA (A. theophrasti) and of efficient detoxification activities in youngest seedlings (C. album). The interpretation of all of the data gave the following sequence of increasing sensitivity: A. theophrasti <<< C. album << P. oleracea ≤ A. retroflexus. The results were in agreement with recent findings of the suppression of these weeds by rye mulches and their benzoxazinoid contents. Our studies demonstrate for the first time that the detoxification of BOA influences the survival of certain weeds in environments enriched with this allelochemical. Therefore, detoxification processes affect the potential for weed suppression by soil allelochemicals in sustainable weed management.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awasthi, S., Srivastava, S. K., Ahmad, F., Ahmad, H., and Ansari, G. A. 1993. Interactions of glutathione S-transferase-π with ethacrynic acid and its glutathione conjugate. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1164:173–178.
Baerson, S. R., Sanchez-Moreiras, A. M., Pedrol-Bonjoch, N., Schulz, M., Kagan, I. A., Agarwal, A. K., Reigosa, M. J., and Duke, S. O. 2005. Detoxification and transcriptome response in Arabidopsis seedlings exposed to the allelochemical benzoxazolin-2(3H)-one. J. Biol. Chem. 280:21867–21881.
Barnes, J. P. and Putnam, A. R. 1987. Role of benzoxazinones in allelopathy by rye (Secale cereale L.). J. Chem. Ecol. 56:1788–1800.
Batish, D. R., Singh, H. P., Setia, N., Kaur, S., and Kohli, R. K. 2006. 2-Benzoxazolinone (BOA) induced oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation and changes in some antioxidant enzyme activities in mung bean (Phaseolus aureus). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 44:819–827.
Belz, R. G. and Hurle, K. 2004. A novel laboratory screening bioassay for crop seedling allelopathy. J. Chem. Ecol. 30:481–485.
Burgos, N. R., Talbert, R. E., and Mattice, J. D. 1999. Cultivar and age differences in the production of allelochemicals by Secale cereale. Weed Sci. 47:481–485.
Chase, W. R., Nair, M. G., and Putnam, A. R. 1991. 2,2’-oxo-1,1’-azobenzene: selective toxicity of rye (Secale cereale L.) allelochemicals to weed and crop species: II. J. Chem. Ecol. 17:9–19.
Conte, S. S. and Lloyed, A. M. 2011. Exploring multiple drug and herbicide resistance in plants-spotlight on transporter proteins. Plant Sci. 180:196–203.
Dixon, D. P., Skipsey, M., and Edward, R. 2010. Roles for glutathione transferases in plant secondary metabolism. Phytochemistry 71:338–350.
Frey, M., Chomet, P., Glawischnig, E., Stettner, C., Grün, S., Winklmair, A., Eisenreich, W., Bacher, A., Meerley, R. B., Briggs, S. P., Simcox, K., and Gierl, A. 1997. Analysis of a chemical plant defense mechanism in grasses. Science 277:696–699.
Frey, M., Schullehner, K., Dick, R., Fiesselmann, A., and Gierl, A. 2009. Benzoxazinoid biosynthesis, a model for evolution of secondary metabolic pathways in plants. Phytochemistry 70:1645–1651.
Gavazzi, C., Schulz, M., Marocco, A., and Tabaglio, V. 2010. Sustainable weed control by allelochemicals from rye cover crops from greenhouse to field evidence. Allelopathy J. 25:259–274.
Gierl, A. and Frey, M. 2001. Evolution of benzoxazinone biosynthesis and indole production in maize. Planta 213:493–498.
Glawischnig, E., Grün, S., Frey, M., and Gierl, A. 1999. Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase of DIBOA biosynthesis: specificity and conservation among grasses. Phytochemistry 50:925–930.
Hofmann, D., Knop, M., Hao, H., Hennig, L., Sicker, D., and Schulz, M. 2006. Glucosides from MBOA and BOA detoxification by Zea mays and Portulaca oleracea. J. Nat. Prod. 69:34–37.
Hussain, M. I. and Reigosa, M. J. 2011. Allelochemical stress inhibits growth, leaf water relations, PSII photochemistry, non-photochemical fluorescence quenching, and heat energy dissipation in three C3 perennial species. J. Exp. Bot. 62:4533–4545.
Hussain, M. I., Gonzalez, L., and Reigosa, M. J. 2008. Germination and growth response of four plant species towards different allelochemicals and herbicides. Allelopathy J. 22:101–110.
Ito, H. and Gray, W. M. 2006. A gain-of-function mutation in the Arabidopsis pleiotropic drug resistance transporter PDR9 confers resistance to auxinic herbicides. Plant Physiol. 142:63–74.
Jonczyk, R., Schmidt, H., Osterrieder, A., Fisselmann, A., Schullehner, K., Haslbeck, M., Sicker, D., Hofmann, D., Yalpani, N., and Simmons, C. 2008. Elucidation of the final reactions of DIMBOA-glucoside biosynthesis in maize: characterization of Bx6 and Bx7. Plant Physiol. 146:1053–1063.
Kuroda, T. and Tsuchiya, T. 2009. Multidrug efflux transporters in the MATE family. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1794:763–768.
Liebman, M. and Sundberg, D. N. 2006. Seed mass affects the susceptibility of weed and crop species to phytotoxins extracted from red clover shoots. Weed Sci. 54:340–345.
Loyola-Vargas, V. M., Broeckling, C. D., Badri, D., and Vivanco, J. M. 2006. Effects of transporters on the secretion of phytochemicals by the roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 225:301–310.
Macias, A. F., Marin, D., Oliveros-Bastidas, A., Castellano, D., Simonet, A. M., and Molinillo, J. M. G. 2005. Structure-activity relationships (SAR) studies of benzoxazinones, their degradation products and analogues. Phytotoxicity on standard target species (STS). J Agric Food Chem 53:538–548.
Macias, A. F., Marin, D., Oliveros-Bastidas, A., Castellano, D., Simonet, A. M., and Molinillo, J. M. G. 2006. Structure-activity relationships (SAR) studies of benzoxazinones, their degradation products and analogues. Phytotoxicity on problematic weeds Avena fatua L. and Lolium rigidum Gaud. J Agric Food Chem 54:1040–1048.
Maron, L. G., Pineros, M. A., Guimaraes, C. T., Magalhaes, J. V., Pleiman, J. K., Mao, C. Z., Shaff, J., Belicias, S. N. J., and Kochian, L. V. 2010. Two functionally distinct members of the MATE (multi drug and toxic compound extrusion) family of transporters potentially underlie two major aluminium tolerance QTLs in maize. Plant J. 61:728–740.
Moriyama, Y., Hiasa, M., Matsumoto, T., and Omote, H. 2008. Multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE)-type proteins as anchor transporters for the excretion of metabolic waste products and xenobiotics. Xenobiot. 38:1107–1118.
Putnam, A. R. and Defrank, J. 1983. Use of phytotoxic plant residues for selective weed control. Crop Prot. 2:173–181.
Reberg-Horton, S. C., Burton, J. D., Danehower, D. A., Ma, G., Monks, D. W., Murphy, J. P., Ranells, N. N., Williamson, D. J., and Creamer, N. G. 2005. Changes over time in the allelochemical content of ten cultivars of rye (Secale cereale L.). J. Chem. Ecol. 31:179–193.
Rice, C. P., Park, Y. B., Adam, F., Abdul-Baki, A. A., and Teasdale, J. R. 2005. Hydroxamic acid content and toxicity of rye at selected growth stages. J. Chem. Ecol. 31:1887–1905.
Sanchez-Moreiras, A. M. and Reigosa, M. J. 2005. Whole plant response of lettuce after root exposure to BOA (2(3H)-benzoxazoninone). J. Chem. Ecol. 31:2689–703.
Sanchez-Moreiras, A. M., Oliveros-Bastidas, A., and Reigosa, M. J. 2010. Reduced photosynthetic activity is directly correlated with 2-(3H)-benzoxazolinone accumulation in lettuce leaves. J. Chem. Ecol. 36:205–209.
Schullehner, K., Dick, R., Vitzthum, F., Schwab, W., Brandt, W., Frey, F., and Gierl, A. 2008. Benzoxazinoid biosynthesis in dicot plants. Phytochemistry 69:2668–2677.
Schulz, M. and Wieland, I. 1999. Variations in metabolism of BOA among species in various field communities - biochemical evidence for co-evolutionary processes in plant communities? Chemoecology 9:133–141.
Schulz, M., Knop, M., Kant, S., Sicker, D., Voloshchuk, N., and Gryganski, A. 2006. Detoxification of allelochemicals - the case of benzoxazolin-2(3H)-one (BOA), pp. 157–170, in M. J. Reigosa, N. Pedro, and L. Gonzales (eds.), Allelopathy: a physiological process with ecological implications. Springer, Dordrecht.
Shilling, D. G., Liebl, R. A., and Worsham, A. D. 1985. The Chemistry of Allelopathy: Biochemical Interactions among Plants, pp. 243–271, in A. C. Thompson (ed.), Chapter, Rye and Wheat Mulch: The Suppression of Certain Broad-leaved Weeds and the Isolation and Identification of Phytotoxins. Am Chem Society, Washington.
Sicker, D. and Schulz, M. 2002. Benzoxazinones in plants: Occurrence, synthetic access, and biological activity. Studies Nat. Prod. Chem. 27:185–232.
Sicker, D., Frey, M., Schulz, M., and Gierl, A. 2000. Role of natural benzoxazinones in the survival strategies of plants, pp. 319–346, in K. W. Jeong (ed.), International Review of Cytology - A Survey of Cell Biology Vol. 198. Academic, San Diego.
Sicker, D., Schneider, B., Hennig, L., Knop, M., and Schulz, M. 2001. Glucoside carbamate from benzoxazolin-2(3H)-one detoxification in extracts and exudates of corn roots. Phytochemistry 58:819–825.
Sicker, D., Hao, H., and Schulz, M. 2004. Benzoxazolin-2-(3H)-ones. Generation, effects and detoxification in the competition among plants, pp. 77–102, in F. A. Macias, J. C. G. Galindo, J. M. G. Molinillo, and H. G. Cutler (eds.), Recent Advances on Allelopathy Vol. II. CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Simmons, C. R., Fridlender, M., Navarro, P. A., and Yalpani, N. 2003. A maize defense-inducible gene is a major facilitator superfamily member related to bacterial multidrug resistance efflux antiporters. Plant. Mol. Biol. 52:433–446.
Singh, H. P., Batish, D. R., Kaur, S., Setia, N., and Kohli, R. K. 2005. Effects of 2-benzoxazolinone on the germination, early growth and morphogenetic response of mung bean (Phaseolus aureus). Ann. Appl. Biol. 147:267–274.
Tabaglio, V. and Gavazzi, C. 2006. Effects of rye mulch on maize summer weeds (in Italian). Inf. Agr. 62:37–40.
Tabaglio, V., Gavazzi, C., Schulz, M., and Marocco, A. 2008. Alternative weed control using the allelopathic effect of natural benzoxazinoids from rye mulch. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 28:397–401.
von Rad, U., Hüttl, R., Lottspeich, F., Gierl, A., and Frey, M. 2001. Two glucosyltransferases involved in detoxification of benzoxazinoids in maize. Plant J. 28:633–642.
Weidenhamer, J. D., Morton, T. C., and Romeo, J. T. 1987. Solution volume and seed number: Often overlooked factors in allelopathic bioassays. J. Chem. Ecol. 13:1481–1491.
Wieland, I., Kluge, M., Schneider, B., Schmidt, J., Sicker, D., and Schulz, M. 1998. 3-ß-D-Glucopyranosyl-benzoxazolin-2(3H)-one - a detoxification product of benzoxazolinone in oat roots. Phytochemistry 49:719–722.
Wieland, I., Friebe, A., Kluge, M., Sicker, D. and Schulz, M. 1999. Detoxification of 2-(3H)-benzoxazolinone in higher plants, pp. 47–56, in F.A. Macias, J.C.G. Galindo, J.M.G. Molinillo and H.G. Cutler (eds.). Recent Advances in Allelopathy. A Science for the Future. Universidad Cadiz (E).
Yao, S., Lan, H., and Zhang, F. 2010. Variation of seed heteromorphism in Chenopodium album and the effects of salinity stress on the descendants. Ann. Bot. 105:1015–1025.
Yuan, J., Tranel, P. J., and Stewart Jr., C. N. 2006. Non-target-site herbicide resistance: a family business. Trends Plant Sci 12:6–13.
Zasada, I. A., Rice, C. P., and Meyer, S. L. F. 2007. Improving the use of rye (Secale cereale) for nematode management: potential to select cultivars based on Meloidogyne incognita host status and benzoxazinoid content. Nematology 9:53–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schulz, M., Marocco, A. & Tabaglio, V. BOA Detoxification of Four Summer Weeds during Germination and Seedling Growth. J Chem Ecol 38, 933–946 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-012-0136-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-012-0136-4