Abstract
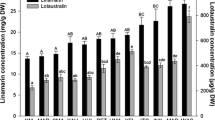
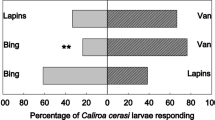
Quantitative experimental results on the antiherbivorous effect of cyanogenesis are rare. In our analyses, we distinguished between the total amount of cyanide-containing compounds stored in a given tissue [cyanogenic potential (HCNp)] and the capacity for release of HCN per unit time (HCNc) from these cyanogenic precursors as a reaction to herbivory. We analyzed the impact of these cyanogenic features on herbivorous insects using different accessions of lima beans (Phaseolus lunatus L.) with different cyanogenic characteristics in their leaves and fourth instars of the generalist herbivore Schistocerca gregaria Forskål (Orthoptera, Acrididae). Young leaves exhibit a higher HCNp and HCNc than mature leaves. This ontogenetic variability of cyanogenesis was valid for all accessions studied. In no-choice bioassays, feeding of S. gregaria was reduced on high cyanogenic lima beans compared with low cyanogenic beans. A HCNp of about 15 μmol cyanide/g leaf (fresh weight) with a corresponding HCNc of about 1 μmol HCN released from leaf material within the first 10 min after complete tissue disintegration appears to be a threshold at which the first repellent effects on S. gregaria were observed. The repellent effect of cyanogenesis increased above these thresholds of HCNp and HCNc. No repellent action of cyanogenesis was observed on plants with lower HCNp and HCNc. These low cyanogenic accessions of P. lunatus were consumed extensively—with dramatic consequences for the herbivore. After consumption, locusts showed severe symptoms of intoxication. Choice assays confirmed the feeding preference of locusts for low over high cyanogenic leaf material of P. lunatus. The bioassays revealed total losses of HCN between 90 and 99% related to the estimated amount of ingested cyanide-containing compounds by the locusts. This general finding was independent of the cyanogenic status (high or low) of the leaf material.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. J. Abbott (1977) ArticleTitleA quantitative association between soil moisture content and the frequency of the cyanogenic form of Lotus corniculatus L. at Birsay, Orkney Heredity 38 397–400
J. P. Baudoin Y. J. Barthelemy V. Ndungo (1991) ArticleTitleVariability of cyanide contents in the primary and secondary genepools of the lima bean, Phaseolus lunatus L. FAO/IBPGR Plant Genet. Resour. Newsl. 85 5–9
E. A. Bernays (1991) ArticleTitleRelationship between deterrence and toxicity of plant secondary compounds for the grasshopper Schistocerca americana J. Chem. Ecol. 17 2519–2526 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XltlKgsA%3D%3D
E. A. Bernays E. M. Chapman E. M. Leather A. R. McCaffery (1977) ArticleTitleThe relationship of Zonocerus variegatus (L.) (Acridoidea: Prygomorphidae) with cassava (Manihot esculenta) Bull. Entomol. Res. 67 391–404
S. Blaise D. Cartier D. Reynaud (1991) ArticleTitleEvolution and differentiation of Lotus corniculatus/Lotus alpinus populations from French south-western Alps. I. Morphologic and cyanogenic variations Evol. Trends Plants 5 137–148
Bokanga, M., Ekanayake, I. J., and Dixon, A. G. O. 1994. Genotype–environment interactions for cyanogenic potential in cassava, pp. 131–140, in M. Bokanga, A. J. A. Essers, N. Poulter, H. Rosling and O. Tewe (eds.). International Workshop on Cassava Safety. Acta Hortic. 375.
L. B. Brattsten J. H. Samuelian K. Y. Long S. A. Kincaid C. K. Evans (1983) ArticleTitleCyanide as feeding stimulant for the southern armyworm, Spodoptera eridania Ecol. Entomol. 8 125–132
P. A. Calatayud B. Rü ParticleLe (1996) ArticleTitleStudy of the nutritional relationships between the cassava mealybug and its host plant Bull. Soc. Zool. Fr. Evol. Zool. 121 391–398
P. A. Calatayud M. Tertuliano B. Rü ParticleLe (1994) ArticleTitleSeasonal variation in secondary compounds in the phloem sap of cassava in relation to plant genotype and infestation by Phenacoccue manihoti (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae) Bull. Entomol. Res. 84 453–459
J. R. Caradus M. B. Forde (1996) ArticleTitleCharacterisation of white clover populations collected from the Caucuses and high altitude regions of eastern Turkey Genet. Resour. Crop Ecol. 43 143–155
J. R. Caradus A. C. Mackay J. F. L. Charlton D. F. Chapman (1990) ArticleTitleGenocology of white clover (Trifolium repens L.) from wet and dry hill country pastures N.Z. J. Agric. Res. 33 377–384
P. D. Coley (1980) ArticleTitleEffects of leaf age and plant life history patterns on herbivory Nature 284 545–546
P. D. Coley (1988) ArticleTitleEffects of plant growth rate and leaf lifetime on the amount and type of anti-herbivore defense Oecologia 74 531–536
P. D. Coley J. P. Bryant F. S. Chapin SuffixIII (1985) ArticleTitleResource availability and plant anti-herbivore defense Science 230 895–899
E. E. Conn (1980) Cyanogenic glycosides E. A. Bell B. V. Charlwood (Eds) Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology. New Series 8 Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York 461–491
G. A. Cooper-Driver T. Swain (1976) ArticleTitleCyanogenic polymorphism in bracken in relation to herbivore predation Nature 260 604. Occurrence Handle1264221
G. A. Cooper-Driver S. Finch T. Swain E. Bernays (1977) ArticleTitleSeasonal variation in secondary plant compounds in relation to the palatability of Pteridium aquilinum Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 5 177–183 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXhvFShsg%3D%3D
J. R. Crush J. R. Caradus (1995) ArticleTitleCyanogenesis potential and iodine concentration in white clover (Trifolium repens L.) cultivars N.Z. J. Agric. Res. 38 309–316 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XktlOisg%3D%3D
D. Debouck (1991) Systematics and morphology A. Schoonhoven Particlevan O. Voysest (Eds) Common Beans: Research for Crop Improvement Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux International Wallingford, UK 55–118
W. M. Ellis R. J. Keymer D. A. Jones (1977a) ArticleTitleThe effect of temperature on the polymorphism of cyanogenesis in Lotus corniculatus L Heredity 38 339–347
H. S. Engler K. C. Spencer L. E. Gilbert (2000) ArticleTitleInsect metabolism: Preventing cyanide release from leaves Nature 406 144–145 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlsVSgu7k%3D Occurrence Handle10910343
P. Feeny (1976) ArticleTitlePlant apparency and chemical defense Recent Adv. Phytochem. 10 1–40 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2sXhvVGrtrw%3D
D. Fischer M. Kogan J. Paxton (1990) ArticleTitleEffect of glyceollin, a soybean phytoalexin on feeding by three phytophagous beetles (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae and Chrysomelidae): Dose versus response Environ. Entomol. 19 1278–1282 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXktVGnsbk%3D
M. Frehner E. E. Conn (1987) ArticleTitleThe linamarin β-glucosidase in Costa Rica wild bean (Phaseolus lunatus L.) is apoplastic Plant Physiol. 84 1296–1300 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXnt1Sgug%3D%3D
R. M. Gleadow I. E. Woodrow (2000a) ArticleTitleTemporal and spatial variation in cyanogenic glycosides in Eucalyptus cladocalyx Tree Physiol. 20 591–598 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjvFSgtbo%3D
R. M. Gleadow I. E. Woodrow (2000b) ArticleTitlePolymorphism in cyanogenic glycoside content and cyanogenic β-glucosidase activity in natural populations of Eucalyptus cladocalyx Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 27 693–699 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnvFSjtw%3D%3D
R. M. Gleadow I. E. Woodrow (2002) ArticleTitleConstraints on effectiveness of cyanogenic glycosides in herbivore defense J. Chem. Ecol. 28 1301–1313 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmsVGmsbs%3D Occurrence Handle12199497
K. J. Hayden I. M. Parker (2002) ArticleTitlePlasticity in cyanogenesis of Trifolium repens L.: inducibility, fitness costs and variable expression Evol. Ecol. Res. 4 155–168
M. Heil (2004) ArticleTitleDirect defense or ecological costs: Responses of herbivorous beetles to volatiles released by wild lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus) J. Chem. Ecol. 30 1289–1295 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXks1aitro%3D Occurrence Handle15303330
W. Hösel E. E. Conn (1982) ArticleTitleThe aglycone specificity of plant β-glucosidases Trends Biochem. Sci. 7 219–221
A. J. Hruska (1988) ArticleTitleCyanogenic glucosides as defence compounds J. Chem. Ecol. 14 2213–2217 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXnt1Cnuw%3D%3D
M. A. Hughes (1991) ArticleTitleThe cyanogenic polymorphism in Trifolium repens L. (white clover) Heredity 66 105–115 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXkvV2jt7o%3D
D. A. Jones (1962) ArticleTitleSelective eating of the acyanogenic form of the plant Lotus corniculatus by various animals Nature 193 1109–1110
D. A. Jones (1966) ArticleTitleOn the polymorphism of cyanogenesis in Lotus corniculatus. I. Selection by animals Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 8 556–567
D. A. Jones (1972) Cyanogenic glycosides and their function J. B. Harborne (Eds) Phytochemical Ecology Academic Press London 103–124
D. A. Jones (1988) Cyanogenesis in animal–plant interactions D. Evered S. Harnett (Eds) Cyanide Compounds in Biology John Wiley & Sons Chichester, UK 151–170
D. A. Jones (1998) ArticleTitleWhy are so many food plants cyanogenic? Phytochemistry 47 155–162 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXislChtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9431670
P. Kakes (1989) ArticleTitleAn analysis of the costs and benefits of the cyanogenic system in Trifolium repens Theor. Appl. Genet. 77 111–118
R. Lieberei (1988) ArticleTitleRelationship of cyanogenic capacity (HCN-c) of the rubber tree Hevea brasiliensis to susceptibility to Microcyclus ulei, the agent causing South American leaf blight J. Phytopathol. 122 54–67 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXltVOrsLw%3D
R. Lieberei A. Schrader B. Biehl K. H. Chee (1983) ArticleTitleEffect of cyanide on Microcyclus ulei cultures J. Rubber Res. Inst. Malays. 31 227–235 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXkvVCmtA%3D%3D
R. Lieberei A. Nahrstedt D. Selmar L. Gasparotto (1986) ArticleTitleThe occurrence of Lotaustralin in the genus Hevea and changes of HCN-potential in developing organs of Hevea brasiliensis Phytochemistry 25 1573–1578 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XltFait7g%3D
R. Lieberei B. Biehl A. Giesemann N. T. V. Junqueira (1989) ArticleTitleCyanogenesis inhibits active defence reactions in plants Plant Physiol. 90 33–36 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXkt1Squro%3D
R. Lieberei H. P. Fock B. Biehl (1996) ArticleTitleCyanogenesis inhibits active defence in plants: Inhibition by gaseous HCN of photosynthetic CO2 fixation and respiration in intact leaves Angew. Bot. 70 230–238 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXhvVKls78%3D
S. Liu D. Norris E. Hartwig M. Xu (1992) ArticleTitleInducible phytoalexins in juvenile soybean genotypes predict soybean looper resistance in the fully developed plants Plant Physiol. 100 1479–1485 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXhvFCqsQ%3D%3D
Loyd, R. and Gray, E. 1970. Amount and distribution of hydrocyanic acid potential during the life cycle of plants of three Sorghum cultivars. Agron. J. 394–397.
A. M. Mainguet A. Louveaux G. Sayed ParticleEL P. Rollin (2000) ArticleTitleAbility of a generalist insect, Schistocerca gregaria, to overcome thioglucoside defense in desert plants: tolerance oradaption? Entomol. Exp. Appl. 94 309–317 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjtVOkuro%3D
J. M. McMahon W. L. B. White R. T. Sayre (1995) ArticleTitleCyanogenesis in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) J. Exp. Bot. 46 731–741 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXntFWksrk%3D
B. L. Møller D. S. Seigler (1999) Biosynthesis of cyanogenic glucosides, cyanolipids and related compounds B. K. Singh (Eds) Plant Amino Acids M. Dekker New York 563–609
D. J. Mowat S. Clawson (1996) ArticleTitleOviposition and hatching of the clover weevil Sitona lepidus Gyll (Coleoptera, Curculionidae) Grass Forage Sci. 51 418–423
A. Nahrstedt (1985) ArticleTitleCyanogenesis and the role of cyanogenic compounds in insects Plant Syst. Evol. 150 35–47 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28Xit1Oh
A. Nahrstedt (1988) Cyanogenic compounds as protecting agents for organisms D. Evered S. Harnett (Eds) Cyanide Compounds in Biology John Wiley & Sons Chichester, UK 131–150
C. A. Patton T. G. Ranney J. D. Burton J. F. Wallenbach (1997) ArticleTitleNatural pest resistance of Prunus taxa to feeding by adult Japanese beetles—role of endogenous allelochemicals in host plant resistance J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 122 668–672
J. E. Poulton (1983) Cyanogenic compounds in plants and their toxic effects R. F. Keeler T. A. Tu (Eds) Handbook of Natural Toxins 1 Marcel Dekker Inc. New York
J. E. Poulton (1988) Localisation and catabolism of cyanogenic glycosides D. Evered S. Harnett (Eds) Cyanide Compounds in Biology. Proceedings of the CIBA Foundation Symposium 140 John Wiley & Sons Chichester, UK 67–91
J. E. Poulton (1990) ArticleTitleCyanogenesis in plants Plant Physiol. 94 401–405 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXmt1Oqtr0%3D
J. E. Poulton C. P. Li (1994) ArticleTitleTissue level compartmentation of (R)-amygdalin and amygdalin hydrolase prevents large-scale cyanogenesis in undamaged Prunus seeds Plant Physiol. 104 29–35 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXht12msbY%3D Occurrence Handle12232058
F. D. Provenza J. A. Pfister C. D. Cheney (1992) ArticleTitleMechanisms of learning in diet selection with reference to phytotoxicosis in herbivores J. Range Manag. 45 36–45
P. J. Schappert J. S. Shore (1999a) ArticleTitleCyanogenesis in Turnera ulmifolia L. (Turneraceae). I. Phenotypic distribution and genetic variation for cyanogenesis on Jamaica Heredity 74 392–404
P. J. Schappert J. S. Shore (1999b) ArticleTitleEffects on cyanogenesis polymorphism in Turnera ulmifolia on Euptoieta hegesia and potential Anolis predators J. Chem. Ecol. 25 1455–1479 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXktlertr0%3D
P. J. Schappert J. S. Shore (1999c) ArticleTitleCyanogenesis, herbivory and plant defense in Turnera ulmifolia on Jamaica Ecoscience 6 511–520
P. J. Schappert J. S. Shore (2000) ArticleTitleCyanogenesis in Turnera ulmifolia L. (Turneraceae). I. Developmental expression, heritability and cost of cyanogenesis Evol. Ecol. Res. 2 337–352
D. S. Seigler (1998) Cyanogenic glycosides and cyanolipids D. S. Seigler (Eds) Plant Secondary Metabolism Kluwer Academic Press Boston 273–296
Selmar, D. 1986. Cyanogenese in Hevea brasiliensis, zwei Wege zur Metabolisierung cyanogener Glycoside. Ph.D. Dissertation. TU Braunschweig, 12–13, 14–15, 63–64, 131–136 (in German).
J. S. Shore C. M. Obrist (1992) ArticleTitleVariation in cyanogenesis within and among populations and species of Turnera series Canaligerae (Turneraceae) Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 20 9–15
L. P. Solomonson (1981) NoChapterTitle B. Vennesland E. E. Conn C. J. Knowles J. Westby F. Wissing (Eds) Cyanide in Biology Academic Press London 11–28
Statistica 6.0. 2001. System Reference by StatSoft, Inc.
E. Swain C. P. Li J. E. Poulton (1992) ArticleTitleTissue and subcellular localization of enzymes catabolizing (R)-amygdalin in mature Prunus serotina seeds Plant Physiol. 100 291–300 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XmtlSitLg%3D
D. B. Tattersal S. Bak P. R. Jones C. E. Olsen J. K. Nielsen M. L. Hansen P. B. HØj B. L. MØller (2001) ArticleTitleResistance to an herbivore through engineered glucoside synthesis Science 293 1826–1828 Occurrence Handle11474068
I. Till (1987) ArticleTitleVariability of expression of cyanogenesis in white clover (Trifolium repens L.) Heredity 59 265–271
S. S. Thayer E. E. Conn (1981) ArticleTitleSubcellular localization of dhurrin β-glucosidase and hydroxynitrilase in the mesophyll cells of Sorghum leaf blades Plant Physiol. 67 617.
N. Underwood (1999) ArticleTitleThe influence of plant and herbivore characteristics on the interaction between induced resistance and herbivore population dynamics Am. Nat. 153 282–294
N. Underwood W. Morris K. Gross J. R. I. Lockwood (2000) ArticleTitleInduced resistance to Mexican bean beetles in soybeans: Variation among genotypes and lack of correlation with constitutive resistance Oecologia 122 83–89
J. Vetter (2000) ArticleTitlePlant cyanogenic glycosides Toxicon 38 11–36 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXns1Glur0%3D Occurrence Handle10669009
M. Zagrobelny S. Bak A. V. Rasmussen B. JØrgensen C. M. Naumann B. L. MØller (2004) ArticleTitleCyanogenic glucosides and plant–insect interactions Phytochemistry 65 293–306 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXmvFGnug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle14751300
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Dr. David S. Seigler for fruitful discussions. We also thank the “Institut für Pflanzengenetik und Kulturpflanzenforschung” in Gatersleben for providing the seed material of our experimental plants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ballhorn, D.J., Lieberei, R. & Ganzhorn, J.U. Plant Cyanogenesis of Phaseolus lunatus and its Relevance for Herbivore–Plant Interaction: The Importance of Quantitative Data. J Chem Ecol 31, 1445–1473 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-005-5791-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-005-5791-2