Abstract
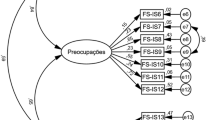
The purpose of this study was to translate the Feeding/Swallowing Impact Survey (FS-IS) into Turkish and to test its reliability and validity in caregivers of children with cerebral palsy (CP). Caregivers accompanying the 117 children with CP who were referred for an instrumental swallowing evaluation were included in the study. The FS-IS was translated from English into Turkish by using the forward, backward, forward translation method. Parents completed the Turkish version of the Feeding/Swallowing Impact Survey (T-FS-IS) which has 3 subscales including daily activities, worry and feeding difficulties. Swallowing function was assessed with Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study, and penetration and aspiration severity was determined according to the Penetration-Aspiration Scale (PAS). The internal consistency, test-retest reliability, construct validity, and discriminant validity of the T-FS-IS were investigated. Internal consistency was excellent with Cronbach alphas all above 0.8 (Total score = 0.99, daily activities = 0.98, worries = 0.98, and feeding difficulties = 0.96). The Intraclass correlation coefficient was 0.93, demonstrating excellent test-retest reliability. All three subscales of the T-FS-IS including daily activities, worry, and feeding difficulties as well as the total score significantly correlated with the PAS scores. Caregivers whose children had aspiration reported worse scores in the T-FS-IS total and its subscales compared with caregivers whose children without airway aspiration according to PAS (p < 0.01). The T-FS-IS is a reliable and valid instrument for measuring the impact of swallowing disorders on caregivers of children with CP. It can be used in clinical practice and research. Clinical trial number: NCT03005093.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arvedson, J. C. (2008). Assessment of pediatric dysphagia and feeding disorders: clinical and instrumental approaches. Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 14(2), 118–127.
Beaton, D. E., Bombardier, C., Guillemin, F., & Ferraz, M. B. (2000). Guidelines for the process of crosscultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine, 25(24), 3186–3191.
Cockerill, H., van den Engel-Hoek, L., & Harding, C. (2016). Assessing children’s swallowing: parent and professional perceptions. Tizard Learning Disability Review, 21(3), 117–125.
Erasmus, C. E., van Hulst, K., Rotteveel, J. J., Willemsen, M. A., & Jongerius, P. H. (2012). Clinical practice: swallowing problems in cerebral palsy. European Journal of Pediatrics, 171(3), 409–414.
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A. G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 175–191.
Fracchia, M. S., Diercks, G., Yamasaki, A., Hersh, C., Hardy, S., Hartnick, M., & Hartnick, C. (2017). Assessment of the feeding Swallowing Impact Survey as a quality of life measure in children with laryngeal cleft before and after repair. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology, 99, 73–77.
Frost, M. H., Reeve, B. B., Liepa, A. M., Stauffer, J. W., Hays, R. D., & Mayo/FDA Patient-Reported Outcomes Consensus Meeting Group. (2007). What is sufficient evidence the reliability and validity of patient-reported outcome measures? Value in Health, 10(Suppl 2), 94–105.
George, D., & Mallery, P. (2003). SPSS for Windows step by step: A simple guide and reference. Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Harding, C., & Halai, V. (2009). Providing dysphagia training for carers of children who have profound and multiple learning disabilities. British Journal of Developmental Disabilities, 55(1), 33–47.
Kovar, K. J. (1997). Nutrition assessment and management in pediatric dysphagia. Seminars in Speech and Language, 18(1), 39–50.
Lefton-Greif, M. A., & Arvedson, J. C. (2016). Pediatric feeding/swallowing: Yesterday, today, and tomorrow. Seminars in Speech and Language, 37(4), 298–309.
Lefton-Greif, M. A., Okelo, S. O., Wright, J. M., Collaco, J. M., McGrath-Morrow, S. A., & Eakin, M. N. (2014). Impact of children's feeding/swallowing problems: validation of a new caregiver instrument. Dysphagia, 29(6), 671–677.
Liley, A. J., & Manthorpe, J. (2003). The impact of home enteral tube feeding in everyday life: a qualitative study. Health & Social Care in the Community, 11(5), 415–422.
Logemann, J. A. (1998). Evaluation of swallowing disorders. In J. A. Logemann (Ed.), Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders (pp. 139–168). Austin: Pro-ed.
Matsuo, K., & Palmer, J. B. (2008). Anatomy and physiology of feeding and swallowing – Normal and abnormal. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics of North America, 19(4), 691–707.
Mukaka, M. M. (2012). Statistics corner: a guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Medical Journal, 24, 69–71.
Nund, R.L., Scarinci, N.A., Cartmill, B., Ward, E.C. (2015). Dysphagia and the family, seminars in dysphagia. Renee Speyer (Ed.), InTech, https://doi.org/10.5772/60856. Available from: https://www.intechopen.com/books/seminars-in-dysphagia/dysphagia-and-the-family.
Parkes, J., Hill, N., Platt, M. J., & Donnelly, C. (2010). Oromotor dysfunction and communication impairments in children with cerebral palsy: a register study. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 52(12), 1113–1119.
Raina, P., O’Donnell, M., Rosenbaum, P., Brehaut, J., Walter, S. D., Russell, D., et al. (2005). The health and well-being of caregivers of children with cerebral palsy. Pediatrics, 115, e626–e636.
Rodenburg, R., Meijer, A. M., Dekovic, M., & Aldenkamp, A. P. (2007). Parents of children with enduring epilepsy: predictors of parenting stress and parenting. Epilepsy and Behavior, 11(2), 197–207.
Rosenbek, J. C., Robbins, J. A., Roecker, E. B., Coyle, J. L., & Wood, J. L. (1996). A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia, 11, 93–98.
Wallander, J. L., & Varni, J. W. (1998). Effects of pediatric chronic physical disorders on child and family adjustment. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 39(1), 29–46.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the caregivers and children who participated in the study. The authors declared that this study has received no financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the parents who participated in this study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serel Arslan, S., Kılınç, H.E., Yaşaroğlu, Ö.F. et al. Reliability and Validity of the Turkish Version of the Feeding/Swallowing Impact Survey. J Dev Phys Disabil 30, 723–733 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10882-018-9615-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10882-018-9615-z