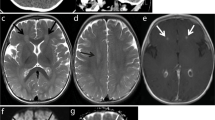
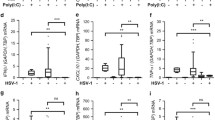
Abstract
Purpose
Enterovirus A71 (EV71) causes a broad spectrum of childhood diseases, ranging from asymptomatic infection or self-limited hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) to life-threatening encephalitis. The molecular mechanisms underlying these different clinical presentations remain unknown. We hypothesized that EV71 encephalitis in children might reflect an intrinsic host single-gene defect of antiviral immunity. We searched for mutations in the toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) gene. Such mutations have already been identified in children with herpes simplex virus encephalitis (HSE).
Methods
We sequenced TLR3 and assessed the impact of the mutations identified. We tested dermal fibroblasts from a patient with EV71 encephalitis and a TLR3 mutation and other patients with known genetic defects of TLR3 or related genes, assessing the response of these cells to TLR3 agonist poly(I:C) stimulation and EV71 infection.
Results
Three children with EV71 encephalitis were heterozygous for rare mutations—TLR3 W769X, E211K, and R867Q—all of which were shown to affect TLR3 function. Furthermore, fibroblasts from the patient heterozygous for the W769X mutation displayed an impaired, but not abolished, response to poly(I:C). We found that TLR3-deficient and TLR3-heterozygous W769X fibroblasts were highly susceptible to EV71 infection.
Conclusions
Autosomal dominant TLR3 deficiency may underlie severe EV71 infection with encephalitis. Human TLR3 immunity is essential to protect the central nervous system against HSV-1 and EV71. Children with severe EV71 infections, such as encephalitis in particular, should be tested for inborn errors of TLR3 immunity.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and supplementary information.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Change history
11 April 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-022-01259-9
References
Jacques J, Moret H, Minette D, Leveque N, Jovenin N, Deslee G, Lebargy F, Motte J, Andreoletti L. Epidemiological, molecular, and clinical features of enterovirus respiratory infections in French children between 1999 and 2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46(1):206–13.
Ho M, Chen ER, Hsu KH, Twu SJ, Chen KT, Tsai SF, Wang JR, Shih SR. An epidemic of enterovirus 71 infection in Taiwan. Taiwan Enterovirus Epidemic Working Group. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(13):929–35.
Chang LY. Enterovirus 71 in Taiwan. Pediatr Neonatol. 2008;49(4):103–12.
Huang CC, Liu CC, Chang YC, Chen CY, Wang ST, Yeh TF. Neurologic complications in children with enterovirus 71 infection. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(13):936–42.
Chang LY, Lin HY, Gau SS, Lu CY, Hsia SH, Huang YC, et al. Enterovirus A71 neurologic complications and long-term sequelae. J Biomed Sci. 2019;26(1):57.
Zhang SY, Herman M, Ciancanelli MJ. Perez de Diego R, Sancho-Shimizu V, Abel L, Casanova JL: TLR3 immunity to infection in mice and humans. Curr Opin Immunol. 2013;25(1):19–33.
Sancho-Shimizu V. Perez de Diego R, Jouanguy E, Zhang SY, Casanova JL: Inborn errors of anti-viral interferon immunity in humans. Curr Opin Virol. 2011;1(6):487–96.
Zhang SY, Jouanguy E, Ugolini S, Smahi A, Elain G, Romero P, Segal D, Sancho-Shimizu V, Lorenzo L, Puel A, et al. TLR3 deficiency in patients with herpes simplex encephalitis. Science. 2007;317(5844):1522–7.
Guo Y, Audry M, Ciancanelli M, Alsina L, Azevedo J, Herman M, Anguiano E, Sancho-Shimizu V, Lorenzo L, Pauwels E, et al. Herpes simplex virus encephalitis in a patient with complete TLR3 deficiency: TLR3 is otherwise redundant in protective immunity. J Exp Med. 2011;208(10):2083–98.
Lim HK, Seppanen M, Hautala T, Ciancanelli MJ, Itan Y, Lafaille FG, Dell W, Lorenzo L, Byun M, Pauwels E, et al. TLR3 deficiency in herpes simplex encephalitis: high allelic heterogeneity and recurrence risk. Neurology. 2014;83(21):1888–97.
Casrouge A, Zhang SY, Eidenschenk C, Jouanguy E, Puel A, Yang K, Alcais A, Picard C, Mahfoufi N, Nicolas N, et al. Herpes simplex virus encephalitis in human UNC-93B deficiency. Science. 2006;314(5797):308–12.
Herman M, Ciancanelli M, Ou YH, Lorenzo L, Klaudel-Dreszler M, Pauwels E, Sancho-Shimizu V, Perez de Diego R, Abhyankar A, Israelsson E, et al. Heterozygous TBK1 mutations impair TLR3 immunity and underlie herpes simplex encephalitis of childhood. J Exp Med. 2012;209(9):1567–82.
Perez de Diego R, Sancho-Shimizu V, Lorenzo L, Puel A, Plancoulaine S, Picard C, Herman M, Cardon A, Durandy A, Bustamante J, et al. Human TRAF3 adaptor molecule deficiency leads to impaired Toll-like receptor 3 response and susceptibility to herpes simplex encephalitis. Immunity. 2010;33(3):400–11.
Sancho-Shimizu V, Perez de Diego R, Lorenzo L, Halwani R, Alangari A, Israelsson E, Fabrega S, Cardon A, Maluenda J, Tatematsu M, et al. Herpes simplex encephalitis in children with autosomal recessive and dominant TRIF deficiency. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(12):4889–902.
Andersen LL, Mork N, Reinert LS, Kofod-Olsen E, Narita R, Jorgensen SE, Skipper KA, Honing K, Gad HH, Ostergaard L, et al. Functional IRF3 deficiency in a patient with herpes simplex encephalitis. J Exp Med. 2015;212(9):1371–9.
Gorbea C, Makar KA, Pauschinger M, Pratt G, Bersola JL, Varela J, David RM, Banks L, Huang CH, Li H, et al. A role for Toll-like receptor 3 variants in host susceptibility to enteroviral myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(30):23208–23.
Belkaya S, Kontorovich AR, Byun M, Mulero-Navarro S, Bajolle F, Cobat A, Josowitz R, Itan Y, Quint R, Lorenzo L, et al. Autosomal recessive cardiomyopathy presenting as acute myocarditis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;69(13):1653–65.
Lim HK, Huang SXL, Chen J, Kerner G, Gilliaux O, Bastard P, Dobbs K, Hernandez N, Goudin N, Hasek ML, et al. Severe influenza pneumonitis in children with inherited TLR3 deficiency. J Exp Med. 2019;216(9):2038–56.
Sun Y, Leaman DW. Ectopic expression of Toll-like receptor-3 (TLR-3) overcomes the double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) signaling defects of P2.1 cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2004;24(6):350–61.
Stojdl DF, Lichty BD, tenOever BR, Paterson JM, Power AT, Knowles S, Marius R, Reynard J, Poliquin L, Atkins H, et al. VSV strains with defects in their ability to shutdown innate immunity are potent systemic anti-cancer agents. Cancer Cell. 2003;4(4):263–75.
Oshiumi H, Matsumoto M, Funami K, Akazawa T, Seya T. TICAM-1, an adaptor molecule that participates in Toll-like receptor 3-mediated interferon-beta induction. Nat Immunol. 2003;4(2):161–7.
Garcia-Cattaneo A, Gobert FX, Muller M, Toscano F, Flores M, Lescure A, Del Nery E, Benaroch P. Cleavage of toll-like receptor 3 by cathepsins B and H is essential for signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109(23):9053–8.
Sironi M, Peri AM, Cagliani R, Forni D, Riva S, Biasin M, et al. TLR3 mutations in adult patients with herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus encephalitis. J Infect Dis. 2017;215(9):1430–4.
Liang F, Glans H, Enoksson SL, Kolios AGA, Lore K, Nilsson J. Recurrent herpes zoster ophthalmicus in a patient with a novel Toll-like receptor 3 variant linked to compromised activation capacity in fibroblasts. J Infect Dis. 2020;221(8):1295–303.
McMinn PC. Recent advances in the molecular epidemiology and control of human enterovirus 71 infection. Curr Opin Virol. 2012;2(2):199–205.
Zhang X, Xu H, Chen X, Li X, Wang X, Ding S, Zhang R, Liu L, He C, Zhuang L, et al. Association of functional polymorphisms in the MxA gene with susceptibility to enterovirus 71 infection. Hum Genet. 2014;133(2):187–97.
Chang LY, Chang IS, Chen WJ, Huang YC, Chen GW, Shih SR, Juang JL, Shih HM, Hsiung CA, Lin TY, et al. HLA-A33 is associated with susceptibility to enterovirus 71 infection. Pediatrics. 2008;122(6):1271–6.
Yang J, Zhao N, Su NL, Sun JL, Lv TG, Chen ZB. Association of interleukin 10 and interferon gamma gene polymorphisms with enterovirus 71 encephalitis in patients with hand, foot and mouth disease. Scand J Infect Dis. 2012;44(6):465–9.
Chopra JS, Sawhney IMS, Dhand UK, Prabhakar S, Naik S, Sehgal S. Neurological complications of acute haemorrhagic conjunctivitis. J Neurol Sci. 1986;73(2):177–91.
Casanova JL, Abel L. The genetic theory of infectious diseases: a brief history and selected illustrations. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2013;14:215–43.
Bsibsi M, Ravid R, Gveric D, van Noort JM. Broad expression of toll-like receptors in the human central nervous system. J Neuropath Exp Neurol. 2002;61(11):1013–21.
Chang SC, Lin JY, Lo LY, Li ML, Shih SR. Diverse apoptotic pathways in enterovirus 71-infected cells. J Neurovirol. 2004;10(6):338–49.
Wang YF, Chou CT, Lei HY, Liu CC, Wang SM, Yan JJ, Su IJ, Wang JR, Yeh TM, Chen SH, et al. A mouse-adapted enterovirus 71 strain causes neurological disease in mice after oral infection. J Virol. 2004;78(15):7916–24.
Lafaille FG, Pessach IM, Zhang SY, Ciancanelli MJ, Herman M, Abhyankar A, Ying SW, Keros S, Goldstein PA, Mostoslavsky G, et al. Impaired intrinsic immunity to HSV-1 in human iPSC-derived TLR3-deficient CNS cells. Nature. 2012;491(7426):769–73.
Lafaille FG, Ciancanelli MJ, Studer L, Smith G, Notarangelo L, Casanova JL, Zhang SY. Deciphering human cell-autonomous anti-HSV-1 immunity in the central nervous system. Front Immunol. 2015;6:208.
Kuo RL, Kao LT, Lin SJ, Wang RY, Shih SR. MDA5 plays a crucial role in enterovirus 71 RNA-mediated IRF3 activation. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e63431.
Lei X, Xiao X, Xue Q, Jin Q, He B, Wang J. Cleavage of interferon regulatory factor 7 by enterovirus 71 3C suppresses cellular responses. J Virol. 2013;87(3):1690–8.
Lu J, Yi L, Zhao J, Yu J, Chen Y, Lin MC, Kung HF, He ML. Enterovirus 71 disrupts interferon signaling by reducing the level of interferon receptor 1. J Virol. 2012;86(7):3767–76.
Wang B, Xi X, Lei X, Zhang X, Cui S, Wang J, Jin Q, Zhao Z. Enterovirus 71 protease 2Apro targets MAVS to inhibit anti-viral type I interferon responses. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(3):e1003231.
Negishi H, Osawa T, Ogami K, Ouyang X, Sakaguchi S, Koshiba R, Yanai H, Seko Y, Shitara H, Bishop K, et al. A critical link between toll-like receptor 3 and type II interferon signaling pathways in antiviral innate immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(51):20446–51.
Lei X, Sun Z, Liu X, Jin Q, He B, Wang J. Cleavage of the adaptor protein TRIF by enterovirus 71 3C inhibits antiviral responses mediated by Toll-like receptor 3. J Virol. 2011;85(17):8811–8.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and their families for participating in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (CMRPG3F1211, CMRPD190621, and 1A0681) and the National Science Council in Taiwan (NSC-98–2320-B-182–040-MY2 and MOST 110-2327-B-006-004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Cheng-Lung Ku and Shen-Ying Zhang conceived and designed the experiments; Chen-Yen Kuo, Hye-Kyung Lim, Chia-Chi Lo, and Jing-Ya Ding conducted the research; Chia-Chi Lo, Chen-Yen Kuo, and Cheng-Lung Ku analyzed data and wrote the manuscript; Chen-Yen Kuo, Shao-Hsuan Hsia, Jainn-Jim Lin, Tzou-Yien Lin, and Loan-Ying Chang provided patient samples and history; Jie Chen provided experiment help during the process of revision; Rei-Lin Kuo, Shen-Ying Zhang, and Jean-Laurent Casanova provided experiment support and expertise. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The study was conducted with approval from the Institutional Review Board of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (IRB number: 201100792B0).
Consent to Participate
All patients provided written informed consent approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital. Blood samples and skin biopsy specimens were obtained from patients and their relatives, with written informed consent, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuo, CY., Ku, CL., Lim, HK. et al. Life-Threatening Enterovirus 71 Encephalitis in Unrelated Children with Autosomal Dominant TLR3 Deficiency. J Clin Immunol 42, 606–617 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-021-01170-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-021-01170-9