Abstract
Background
BAFF (B-cell activating factor of the tumor necrosis factor family) and APRIL (a proliferation-inducing ligand) are two of the major survival factors for B cells. Many studies have shown that BAFF levels were elevated in MS patients. However, whether the levels of CSF BAFF/APRIL increased in NMO patients was still unclear.
Objective
To measure the CSF BAFF and APRIL concentration of in NMO patients, and explore their relationship with disease activity in NMO.
Methods
CSF BAFF and APRIL was measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in NMO (n = 22), MS (n = 18) patients and controls (n = 14).
Results
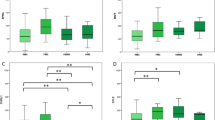
Concentration of BAFF and APRIL in NMO patients were significantly higher than MS and controls. CSF BAFF and APRIL levels in controls were also lower than MS. Both NMO and MS revealed an increased disease disability with increased CSF BAFF. CSF APRIL was associated with EDSS scores in NMO, but not found in MS.
Conclusions
BAFF/APRIL system considered important for aggressive B cells and T-cell responses, and may stimulates B cells and T cell activation in acute relapse of NMO and MS. In NMO patients, CSF BAFF and APRIL may be key factors of B cell immune response and reflect disease severity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lennon VA, Wingerchuk DM, Kryzer TJ, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Fujihara K, Nakashima I, Weinshenker BG. A serum autoantibody marker of neuromyelitis optica: distinction frommultiple sclerosis. Lancet. 2004;364:2106–12.
McKeon A, Pittock SJ. Neuromyelitis optica and the evolving spectrum of water channel autoimmunity: a new direction. Eur J Neurol. 2009;16(4):433–5.
Sellner J, Boggild M, Clanet M, Hintzen RQ, Illes Z, Montalban X, Du Pasquier RA, Polman CH, Sorensen PS, Hemmer B. EFNS guidelines on diagnosis and management of neuromyelitis optica. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(8):1019–32.
Wu GF, Alvarez E. The immunopathophysiology of multiple sclerosis. Neurol Clin. 2011;29(2):257–78.
Archelos JJ, Storch MK, Hartung HP. The role of B cells and autoantibodies in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2000;47:694–706.
Meinl E, Derfuss T, Krumbholz M, Pröbstel AK, Hohlfeld R. Humoral autoimmunity in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 2011;306:180–2.
Vaknin-Dembinsky A, Brill L, Orpaz N, Abramsky O, Karussis D. Preferential increase of B-cell activating factor in the cerebrospinal fluid of neuromyelitis optica in a white population. Mult Scler. 2010;16(12):1453–7.
Chan KH, Ramsden DB, Yu YL, Kwok KH, Chu AC, Ho PW, Kwan JS, Lee R, Lim E, Kung MH, Ho SL. Neuromyelitis optica-IgG in idiopathic inflammatory demyelinating disorders amongst Hong Kong Chinese. Eur J Neurol. 2009;16(3):310–6.
Mackay F, Silveira PA, Brink R. B cells and the BAFF/APRIL axis: fast forward on autoimmunity and signaling. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007;19:327–36.
Schneider P. The role of APRIL and BAFF in lymphocyte activation. Curr Opin Immunol. 2005;17:282–9.
Cheema GS, Roschke V, Hilbert DM, Stohl W. Elevated serum B lymphocyte stimulator levels in patients with systemic immune-based rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:1313–9.
Farina C, Aloisi F, Meinl E. Astrocytes are active players in cerebral innate immunity. Trends Immunol. 2007;28:138–45.
Thangarajh M, Gomes A, Masterman T, Hillert J, Hjelmstrom P. Expression of B-cell-activating factor of the TNF family (BAFF) and its receptors in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 2004;152:183–90.
Krumbholz M, Faber H, Steinmeyer F, Hoffmann LA, Kümpfel T, Pellkofer H, Derfuss T, Ionescu C, Starck M, Hafner C, Hohlfeld R, Meinl E. Interferon-beta increases BAFF levels in multiple sclerosis: implica-tions for B cell autoimmunity. Brain. 2008;131:1455–63.
Piazza F, DiFrancesco JC, Fusco ML, Corti D, Pirovano L, Frigeni B, Mattavelli L, Andreoni S, Frigo M, Ferrarese C, Tredici G, Cavaletti G. Cerebrospinal fluid levels of BAFF and APRIL in untreated multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 2010;220:104–7.
Wingerchuk DM, Lennon VA, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, Weinshenker BG. Revised diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica. Neurology. 2006;66:1485–9.
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B, Clanet M, Cohen JA, Filippi M, Fujihara K, Havrdova E, Hutchinson M, Kappos L, Lublin FD, Montalban X, O'Connor P, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Thompson AJ, Waubant E, Weinshenker B, Wolinsky JS. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol. 2011;69:292–302.
Ng LG, Mackay CR, Mackay F. The BAFF/APRIL system: life beyond B lymphocytes. Mol Immunol. 2005;42:763–72.
Mukhopadhyay A, Ni J, Zhai Y, Yu GL, Aggarwal BB. Identification and characterization of a novel cytokine, THANK, a TNF homologue that activates apoptosis, nuclear factor-kappaB, and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:15978–81.
Shu HB, Hu WH, Johnson H. TALL-1 is a novel member of the TNF family that is down-regulated by mitogens. J Leukoc Biol. 1999;65:680–3.
Eilertsen GO, Van Ghelue M, Strand H, Nossent JC. Increased levels of BAFF in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus are associated with acute-phase reactants, independent of BAFF genetics: a case-control study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011;Oct 8. PubMed PMID: 21984763.
Vadacca M, Margiotta D, Sambataro D, Buzzulini F, Lo Vullo M, Rigon A, Afeltra A. BAFF/APRIL pathway in Sjögren syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus: relationship with chronic inflammation and disease activity. Reumatismo. 2011;62:259–65.
Ragheb S, Li Y, Simon K, VanHaerents S, Galimberti D, De Riz M, Fenoglio C, Scarpini E, Lisak R. Multiple sclerosis: BAFF and CXCL13 in cerebrospinal fluid. Mult Scler. 2011;17:819–29.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no.81171126).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Honghao Wang, Kai Wang, Xiaonan Zhong and Wei Qiu contributed equally to the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Wang, K., Zhong, X. et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid BAFF and APRIL Levels in Neuromyelitis Optica and Multiple Sclerosis Patients During Relapse. J Clin Immunol 32, 1007–1011 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9709-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-012-9709-9