Abstract
Background
Interleukin-21 (IL-21) is critical in the development of autoimmune diseases. The role of IL-21 in the pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) remains unknown.
Materials and Methods
We examined the expression of IL-21, IL-17, and interferon (IFN)-γ in ITP patients and controls by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and flow cytometry. Detection of specific anti-platelet GPIIb/IIIa and/or GPIb/IX autoantibodies was measured by modified monoclonal antibody specific immobilization of platelet antigens.
Results
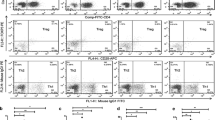
IL-21 was expressed on both CD3+CD8− T cells and CD3+CD8+ T cells by flow cytometry. Plasma IL-21 level and the percentage of CD3+CD8−IL-21+ T cells and CD3+CD8+IL-21+ T cells were significantly elevated in ITP patients compared to controls. The percentage of CD3+CD8−IL-17+ T (Th17), CD3+CD8−IFN-γ+ T (Th1), and CD3+CD8+IFN-γ+ T (Tc1) cells also significantly increased in ITP patients. Moreover, we found a significant positive correlation between CD3+CD8−IL-21+ T cells and Th17 cells. In addition, a positive correlation between CD3+CD8−IL-21+ T cells and Th1 cells was also found.
Conclusion
Together, our results indicated a possible role of IL-21 in ITP patients correlated to Th17 and Th1 cells, and blockade of IL-21 may be a reasonable therapeutic strategy for ITP especially those with active disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stasi R, Evangelista ML, Stipa E, Buccisano F, Venditti A, Amadori S. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: current concepts in pathophysiology and management. Thromb Haemost. 2008;99:4–13.
Ogawara H, Handa H, Morita K, Hayakawa M, Kojima J, Amagai H, et al. High Th1⁄Th2 ratio in patients with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Eur J Haematol. 2003;71:283–8.
Panitsas FP, Theodoropoulou M, Kouraklis A, Karakantza M, Theodorou GL, Zoumbos NC, et al. Adult chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) is the manifestation of a type-1 polarized immune response. Blood. 2004;103:2645–7.
Liu B, Zhao H, Poon MC, Han Z, Gu D, Xu M, et al. Abnormality of CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cell in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Eur J Haematol. 2007;78:139–43.
Yu J, Heck S, Patel V, Levan J, Yu Y, Bussel JB, et al. Defective circulating CD25 regulatory T cells in patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2008;112:1325–8.
Olsson B, Andersson PO, Jernås M, Jacobsson S, Carlsson B, Carlsson LM, et al. T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity toward platelets in chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nat Med. 2003;9:1123–4.
Zhao C, Li X, Zhang F, Wang L, Peng J, Hou M. Increased cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity predominant in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura without platelet autoantibodies. Haematologica. 2008;93:1428–30.
Spolski R, Leonard WL. Interleukin-21: basic biology and implications for cancer and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;26:57–79.
Parrish-Novak J, Dillon SR, Nelson A, Hammond A, Sprecher C, Gross JA, et al. Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature. 2000;408:57–63.
Davis ID, Skak K, Smyth MJ, Kristjansen PE, Miller DM, Sivakumar PV. Interleukin-21 signaling: functions in cancer and autoimmunity. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:6926–32.
Young DA, Hegen M, Ma HL, Whitters MJ, Albert LM, Lowe L, et al. Blockade of the interleukin-21/interleukin-21 receptor pathway ameliorates disease in animal models of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1152–63.
Herber D, Brown TP, Liang S, Young DA, Collins M, Dunussi-Joannopoulos K. IL-21 has a pathogenic role in a lupus-prone mouse model and its blockade with IL-21R:Fc reduces disease progression. J Immunol. 2007;178:3822–30.
Fina D, Sarra M, Fantini MC, Rizzo A, Caruso R, Caprioli F, et al. Regulation of gut inflammation and th17 cell response by interleukin-21. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1038–48.
Mitoma H, Horiuchi T, Kimoto Y, Tsukamoto H, Uchino A, Tamimoto Y, et al. Decreased expression of interleukin-21 receptor on peripheral B lymphocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Mol Med. 2005;16:609–15.
Andersson AK, Feldmann M, Brennan FM. Neutralizing IL-21 and IL-15 inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine production in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand Immunol. 2008;68:103–11.
Distler JH, Jüngel A, Kowal-Bielecka O, Michel BA, Gay RE, Sprott H, et al. Expression of interleukin-21 receptor in epidermis from patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:856–64.
Rodeghiero F, Stasi R, Gernsheimer T, Michel M, Provan D, Arnold DM, et al. Standardization of terminology, definitions and outcome criteria in immune thrombocytopenic purpura of adults and children: report from an international working group. Blood. 2009;113:2386–93.
Hou M, Peng J, Shi Y, Zhang C, Qin P, Zhao C, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) for the treatment of steroid-resistant idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Eur J Haematol. 2003;70:353–7.
Spolski R, Leonard WJ. The Yin and Yang of interleukin-21 in allergy, autoimmunity and cancer. Curr Opin Immunol. 2008;20:295–301.
Nurieva R, Yang XO, Martinez G, Zhang Y, Panopoulos AD, Ma L, et al. Essential autocrine regulation by IL-21 in the generation of inflammatory T cells. Nature. 2007;448:480–3.
Korn T, Bettelli E, Gao W, Awasthi A, Jäger A, Strom TB, et al. IL-21 initiates an alternative pathway to induce proinflammatory T(H)17 cells. Nature. 2007;448:484–7.
Fina D. Role of interleukin-21 in inflammation and allergy. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2007;6:63–8.
Strengel M, Sareneva T, Foste D, Julkunen I, Matikainen S. IL-21 up-regulates the expression of genes associated with innate immunity and Th1 responses. J Immunol. 2002;169:3600–5.
Monteleone G, Monteleone I, Fina D, Vavassori P, Del Vecchio Blanco G, Caruso R, et al. Interleukin-21 enhances T-helper cell type I signaling and interferon-gamma production in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:687–94.
Fina D, Sarra M, Caruso R, Del Vecchio Blanco G, Pallone F, MacDonald T, et al. Interleukin-21 contributes to the mucosal T helper Cell type 1 response in celiac disease. Gut. 2008;57:887–92.
Wurster AL, Rodgers VL, Satoskar AR, Whitters MJ, Young DA, Collins M, et al. Interleukin 21 is a T helper (Th) cell 2 cytokine that specifically inhibits the differentiation of naive Th cells into interferon g-producing Th1 cells. J Exp Med. 2002;196:969–77.
Fröhlich A, Marsland BJ, Sonderegger I, Kurrer M, Hodge MR, Harris NL. IL-21 receptor signaling is integral to the development of Th2 effector responses in vivo. Blood. 2007;109:2023–31.
Zhou L, Ivanov II, Spolski R, Min R, Shenderov K, Egawa T. IL-6 programs T(H)-17 cell differentiation by promoting sequential engagement of the IL-21 and IL-23 pathways. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:967–74.
Sonderegger I, Kisielow J, Meier R, King C, Kopf M. IL-21 and IL-21R are not required for development of Th17 cells and autoimmunity in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38:1833–8.
Coquet JM, Chakravarti S, Smyth MJ, Godfrey DI. Cutting edge: IL-21 is not essential for Th17 differentiation or experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2008;180:7097–101.
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation (30600680, 30471941, 30770922, 30470742, 30570779, 30600259, 30628015, and 30300312), 973 Project (2006CB503800), Key Clinical Research Project of Chinese Ministry of Health (2007–2009), Research Project of National Public Fare (200802031), Cultivation Fund of the Key Scientific and Technical Innovation Project, Ministry of Education of China (NO704030), the Shandong Technological Development Project (BS2009SW014, 2005BS03022 and 2005GG4202018), Taishan Scholar Foundation, and the SRF for ROCS, SEM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Ma, D., Zhang, J. et al. Elevated Interleukin-21 Correlated to Th17 and Th1 Cells in Patients with Immune Thrombocytopenia. J Clin Immunol 30, 253–259 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-009-9353-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-009-9353-1