Abstract
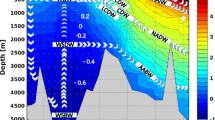
Although the circulation of intermediate water masses in the eastern North Atlantic remains poorly defined, the presence of fresher intermediate waters, the Sub-Artic (SAIW) and the Antarctic Intermediate Water (AAIW), as well the saline intermediate Mediterranean Water (MW), has been tracked using biogeochemical properties. Here we assess the hydrographic and chemical structures of intermediate waters along the western Portuguese margin by examining the vertical distributions and property-property plots of chemical tracers (oxygen and nutrients). AAIW was traced by low oxygen and high nutrients, while SAIW was recognized by low nutrients. The Mediterranean Water (MW) undercurrent is shown to spread towards the eastern flank of Gorringe bank. Concurrently, the fresher waters gained salt by direct incorporation of MW, while this water was enriched in nutrients on its way northward and westward owing, to a great extent, to the entrainment of an AAIW branch. The distributions of nutrients and apparent oxygen utilization are discussed in terms of regional ocean circulation. Our analysis suggests a circulation pattern of the various intermediate waters along the western Portuguese margin: MW extends all over the area, but its presence is more pronounced around cape St. Vincent; SAIW apparently moves southward, reaching the Gorringe bank region, and AAIW flows northward along the coast and around the bank.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambar, I. and M. R. Howe (1979): Observations of Mediterranean outflow. I. Mixing in the Mediterranean outflow. Deep-Sea Res., 26A, 535–554.
Ambar, I., N. Serra, M. J. Brogueira, G. Cabeçadas, F. Abrantes, P. Freitas, C. Gonçalves and N. Gonzalez (2002): Physical, chemical and sedimentological aspects of the Mediterranean Outflow off Iberia. Deep-Sea Res., II, 49, 4163–4177.
Ambe, M. (1978): Note of the experience in the preparation of CSK standard solutions and the ICES-SCORE intercalibration experiment, 1969–1970. Mar. Chem., 6, 171–178.
Aminot, A. and R. Kerouel (2004): Dissolved organic carbon nitrogen and phosphorus in the N-E Atlantic and N-W Mediterranean with particular reference to non-refractory fractions and degradation. Deep-Sea Res., I, 51, 1975–1999.
Arhan, M. (1990): The North Atlantic Current and Subarctic Intermediate Water. J. Mar. Res., 48, 109–144.
Broecker, W. S. (1974): “NO” a conservative water-mass tracer. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 23, 100–107.
Broecker, W. S. and T.-H. Peng (1982): Tracers in the Sea. Eldigo Press, Palisades, NY, 690 pp.
Broecker, W. S., T. Takahashi and T. Takahashi (1985): Sources and flow patterns of deep-ocean waters as deduced from potential temperature, salinity, and initial phosphate concentration. J. Geophys. Res., 90, 6925–6939.
Brogueira, M. J., G. Cabeçadas and C. Gonçalves (2004): Chemical resolution of a meddy emerging off southern Portugal. Cont. Shelf Res., 24, 1651–1657.
Cabeçadas, G., M. J. Brogueira and C. Gonçalves (2002): The chemistry of Mediterranean outflow and its interactions with surrounding waters. Deep-Sea Res., II, 49, 4263–4270.
Cabeçadas, G., M. J. Brogueira and C. Gonçalves (2003): Intermediate water masses off south-southwest Portugal: Chemical tracers. J. Mar. Res., 61, 539–552.
Carrit, D. E. and J. H. Carpenter (1966): Comparison and evaluation of currently employed modifications of the Winkler method for determining oxygen in seawater. A NASCO re port. J. Mar. Res., 24, 286–318.
Coelho, H. and R. Santos (2003): Enhanced primary production over seamounts: a numerical study. 4o Simpósio sobre a Margem Ibérico Atlântica, 3 pp.
Coste, B., P. Le Corre and H. J. Minas (1988): Re-evaluation of the nutrient exchanges in the Strait of Gibraltar. Deep-Sea Res., 35, 767–775.
Fiekas, V., J. Elken, T. J. Muller, A. Aitsam and W. Zenk (1992): A view of the Canary basin thermocline circulation in winter. J. Geophys. Res., 97, 12,495–12,510.
Harvey, J. and M. Arhan (1988): The water masses of the central North Atlantic in 1983–84. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 18, 1855–1875.
Hinrichsen, H. H. and M. Tomczak (1993): Optimum multiparameter analysis of the water mass structure in the western North Atlantic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res., 98, 10,155–10,169.
Irigoien, X., O. Fiksen, U. Cotano, A. Uriarte, P. Alvarez, H. Arrizabalaga, G. Boyra, M. Santos, Y. Sagarminaga, P. Otheguy, E. Etxebeste, L. Zarauz, Artetxe and L. Motos (2007): Could Biscay Bay Anchovy recruit through a spatial loophole? Prog. Oceanogr., 74, 132–148.
Kase, R. H. and W. Zenk (1987): Reconstructed Mediterranean salt lens trajectories. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 17, 158–163.
Koutsikopoulos, C. and B. Le Cann (1996): Physical processes and hydrological structures related to the Bay of Biscay anchovy. Scient. Mar., 60(Supl. 2), 9–19.
Minas, H. J., B. Coste, P. Le Corre, M. Minas and P. Raimbault (1991): Biological and geochemical signatures associated with the water circulation through the Strait of Gibraltar and in the western Alboran Sea. J. Geophys. Res., 96, 8755–8771.
Pérez, F. F., C. G. Castro, X. A. Álvarez-Salgado and A. F. Ríos (2001): Coupling between the Iberian basin-scale circulation and the Portugal boundary current system: a chemical study. Deep-Sea Res., I, 48, 1519–1533.
Pingree, R. and B. Le Cann (1990): Structure, strength and seasonality of the slope currents in the Bay of Biscay region. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc., 70, 857–885.
Pollard, R. T., J. F. Read, N. P. Holliday and H. Leach (2004): Water masses and circulation pathways through the Iceland Basin during Vivaldi 1996. J. Geophys. Res., 109, CO4004.
Ríos, A. F., F. Fraga and F. F. Pérez (1989): Estimation of coefficients for the calculation of “NO”, “PO” and “CO”, starting from elemental composition of natural phytoplankton. Scient. Mar., 53, 779–784.
Serra, N. and I. Ambar (2002): Eddy generation in the Mediterranean Undercurrent. Deep-Sea Res., II, 49, 4225–4243.
UNESCO (1981): Background papers and supporting data on the Practical Salinity Scale 1978. UNESCO Tech. Paper Mar. Sci., 37, 1–144.
van Aken, H. (2000): The hydrography of the mid-latitude Northeast Atlantic Ocean. II: The intermediate water masses. Deep-Sea Res., I, 47, 789–824.
Zenk, W. (1970): On temperature and salinity structure of the Mediterranean water in the N.E. Atlantic. Deep-Sea Res., 17, 627–632.
Zenk, W. and L. Armi (1990): The complex spreading pattern of Mediterranean Water off the Portuguese continental slope. Deep-Sea Res., 37, 1805–1823.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cabeçadas, G., José Brogueira, M., Gelena Cavaco, M. et al. Chemical signature of intermediate water masses along western Portuguese margin. J Oceanogr 66, 201–210 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-010-0018-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-010-0018-8