Abstract
Purpose
Most work–life research focuses on the spillover of the nuclear family to the workplace, offering little insight into how other family relationships and friendships can spill over to affect employees’ organizational attachment. Past research has also overlooked the role of relationship quality and the mechanisms underlying these life-to-work spillover effects. Addressing these shortcomings, we integrate the systemic model of community attachment with job embeddedness theory to develop a model of community relational embeddedness and then use this model to examine how nonwork relationships connect people to their workplaces.
Design/Methodology/Approach
We used survey data from a national sample of 2025 accounting professionals and tested mediation hypotheses using structural equation modeling.
Findings
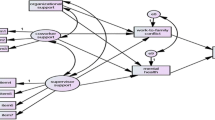
Employees’ relationships with friends and family predicted their attachment to their communities, which in turn predicted their workplace turnover intentions. Supporting our theoretical model, bonds with friends and family predicted moving intentions, and community fit and sacrifice mediated these effects. Community fit and sacrifice also predicted work turnover intentions indirectly through moving intentions. Tests also revealed that, surprisingly, friendships had a stronger impact on community attachment than family.
Implications
Employees are connected to their organizations through an array of close community relationships that extend beyond the nuclear family (i.e., spouse, children). Organizations can enhance employees’ workplace attachment by recognizing the role of friends and offering work–life programs that use a broad conceptualization of family (e.g., adult siblings, parents).
Originality/Value
Our study illustrates the importance of community relationships to workplace attachment, and the need to incorporate relational quality, nonnuclear family, and friendships in future research.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, R. (1992). Is happiness a home in the suburbs? The influence of urban versus suburban neighborhoods on psychological health. Journal of Community Psychology, 20, 353–372.
Allen, L., Long, P., & Perdue, R. (1991). Relational patterns between community dimensions and global measures of community satisfaction. Journal of Rural Studies, 7, 331–338.
Baldridge, D. C., Eddleston, K. A., & Veiga, J. F. (2006). Saying no to being uprooted: The impact of family and gender on willingness to relocate. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 79, 131–149.
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1995). The need to belong: Desire for interpersonal attachments as a fundamental human motivation. Psychological Bulletin, 117, 497–529.
Beggs, J. J., Hurlbert, J. S., & Haines, V. A. (1996). Community attachment in a rural setting: A refinement and empirical test of the systemic model. Rural Sociology, 61, 407–426.
Belot, M., & Ermisch, J. (2009). Friendship ties and geographical mobility: Evidence from Great Britain. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series A (Statistics in Society), 172, 427–442.
Bengtson, V. L. (2001). Beyond the nuclear family: The increasing importance of multigenerational bonds. Journal of Marriage and Family, 63, 1–16.
Bernerth, J. B., & Aguinis, H. (2016). A critical review and best-practice recommendations for control variable usage. Personnel Psychology, 69, 229–283.
Blegen, M. A., Mueller, C. W., & Price, J. L. (1988). Measurement of kinship responsibility for organizational research. Journal of Applied Psychology, 73, 402–409.
Bollen, K. A. (2007). Interpretational confounding is due to misspecification, not to type of indicator: Comment on Howell, Breivik, and Wilcox (2007). Psychological Methods, 12, 219–228.
Bollen, K. A., & Bauldry, S. (2011). Three Cs in measurement models: Causal indicators, composite indicators, and covariates. Psychological Methods, 16, 265–284.
Buckner, J. C. (1988). The development of an instrument to measure neighborhood cohesion. American Journal of Community Psychology, 16, 771–791.
Cammann, C., Fichman, M., Jenkins, D., & Klesh, J. (1983). Assessing the attitudes and perceptions of organizational members. In S. Seashore, E. Lawler, P. Mirvis, & C. Cammann (Eds.), Assessing organizational change: A guide to methods, measures and practices (pp. 71–138). New York: Wiley.
Carmeli, A., & Gittell, J. H. (2009). High-quality relationships, psychological safety, and learning from failures in work organizations. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 30, 709–729.
Casper, W. J., Eby, L. T., Bordeaux, C., Lockwood, A., & Lambert, D. (2007). A review of research methods in IO/OB work–family research. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92, 28–43.
Conway, J. M., & Lance, C. E. (2010). What reviewers should expect from authors regarding common method bias in organizational research. Journal of Business and Psychology, 25, 325–334.
Cross, S. E., & Madson, L. (1997). Models of the self: Self-construals and gender. Psychological Bulletin, 122, 5–37.
Crossley, C. D., Bennett, R. J., Jex, S. M., & Burnfield, J. L. (2007). Development of a global measure of job embeddedness and integration into a traditional model of voluntary turnover. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92, 1031–1042.
Crowe, J. (2010). Community attachment and satisfaction: The role of a community’s social network structure. Journal of Community Psychology, 38, 622–644.
DaVanzo, J. S., & Morrison, P. A. (1981). Return and other sequences of migration in the United States. Demography, 18, 85–101.
De Jong, G. F., & Gardner, R. W. (Eds.). (1981). Migration decision making: Multidisciplinary approaches to microlevel studies in developed and developing countries. New York: Pergamon.
Diamantopoulos, A. (2011). Incorporating formative measures into covariance-based structural equation models. MIS Quarterly, 35, 335–358.
Dutton, J. E., & Ragins, B. R. (Eds.). (2007). Exploring positive relationships at work: Building a theoretical and research foundation. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Eby, L. T., & Allen, T. D. (Eds.). (2012). Personal relationships: The effect on employee attitudes, behavior, and well-being. New York: Routledge.
Eby, L. T., Casper, W. J., Lockwood, A., Bordeaux, C., & Brinley, A. (2005). Work and family research in IO/OB: Content analysis and review of the literature (1980–2002). Journal of Vocational Behavior, 66, 124–197.
Eby, L. T., & Russell, J. E. (2000). Predictors of employee willingness to relocate for the firm. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 57, 42–61.
Fehr, B. (1996). Friendship processes. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Feldman, D. C., Ng, T. W., & Vogel, R. M. (2012). Off-the-job embeddedness: A reconceptualization and agenda for future research. In J. J. Martocchio, A. Joshi, & H. Liao (Eds.), Research in personnel and human resources management (Vol. 31, pp. 209–251). Bingley: Emerald.
Flaherty, J., & Brown, R. B. (2010). A multilevel systemic model of community attachment: Assessing the relative importance of the community and individual levels. American Journal of Sociology, 116, 503–542.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. Journal of Marketing Research, 18, 382–388.
Freeberg, A. L., & Stein, C. H. (1996). Felt obligation towards parents in Mexican-American and Anglo-American young adults. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 13, 457–471.
Gillespie, B. J., Lever, J., Frederick, D., & Royce, T. (2015). Close adult friendships, gender, and the life cycle. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 32, 709–736.
Greenhaus, J. H., & Powell, G. N. (2006). When work and family are allies: A theory of work–family enrichment. Academy of Management Review, 31, 72–92.
Greenhaus, J. H., & Powell, G. N. (2012). The family-relatedness of work decisions: A framework and agenda for theory and research. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 80, 246–255.
Guest, A. M., & Lee, B. A. (1983). Sentiment and evaluation as ecological variables. Sociological Perspectives, 26, 159–184.
Gusfield, J. R. (1975). Community: A critical response. New York: Harper & Row.
Hidalgo, M. C., & Hernández, B. (2001). Place attachment: Conceptual and empirical questions. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 21, 273–281.
Homans, G. C. (1951). The human group. New York: Routledge.
House, J. S., Umberson, D., & Landis, K. R. (1988). Structures and processes of social support. Annual Review of Sociology, 14, 293–318.
Hu, L., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 6, 1–55.
Jiang, K., Liu, D., McKay, P. F., Lee, T. W., & Mitchell, T. R. (2012). When and how is job embeddedness predictive of turnover? A meta-analytic investigation. Journal of Applied Psychology, 97, 1077–1096.
Johnson, R. E., Rosen, C. C., & Chang, C. H. (2011). To aggregate or not to aggregate: Steps for developing and validating higher-order multidimensional constructs. Journal of Business and Psychology, 26, 241–248.
Kasarda, J. D., & Janowitz, M. (1974). Community attachment in mass society. American Sociological Review, 39, 328–339.
Kiazad, K., Holtom, B. C., Hom, P. W., & Newman, A. (2015). Job embeddedness: A multifoci theoretical extension. Journal of Applied Psychology, 3, 641–659.
Kraimer, M. L., Shaffer, M. A., Harrison, D. A., & Ren, H. (2012). No place like home? An identity strain perspective on repatriate turnover. Academy of Management Journal, 55, 399–420.
Laschober, T. C., Allen, T. D., & Eby, L. T. (2012). Negative nonwork relational exchanges and links to employees’ work attitudes, work behaviors, and well-being. In L. T. Eby & T. D. Allen (Eds.), Personal relationships: The effect on employee attitudes, behavior, and well-being (pp. 325–348). New York: Routledge.
Lawton, L., Silverstein, M., & Bengtson, V. (1994). Affection, social contact, and geographic distance between adult children and their parents. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 56, 57–68.
Lee, T. W., Burch, T. C., & Mitchell, T. R. (2014). The story of why we stay: A review of job embeddedness. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 1, 1–18.
Lee, T. R., Mancini, J. A., & Maxwell, J. W. (1990). Sibling relationships in adulthood: Contact patterns and motivations. Journal of Marriage and Family, 52, 431–440.
Lee, T. W., Mitchell, T. R., Sablynski, C. J., Burton, J. P., & Holtom, B. C. (2004). The effects of job embeddedness on organizational citizenship, job performance, volitional absences, and voluntary turnover. Academy of Management Journal, 47, 711–722.
Lee, B. A., Oropesa, R. S., & Kanan, J. W. (1994). Neighborhood context and residential mobility. Demography, 31, 249–270.
Lieberman, M. D. (2013). Social: Why our brains are wired to connect. New York: Crown.
Low, S. M., & Altman, I. (1992). Place attachment: A conceptual inquiry. In I. Altman & S. M. Low (Eds.), Place attachment (pp. 1–12). New York: Plenum Press.
Lu, M. (2011). Analyzing migration decision making: Relationships between residential satisfaction, mobility intentions, and moving behavior. Environment and Planning A, 30, 1473–1495.
MacKenzie, S. B., Podsakoff, P. M., & Jarvis, C. B. (2005). The problem of measurement model misspecification in behavioral and organizational research and some recommended solutions. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90, 710–730.
MacKinnon, D. P., Lockwood, C. M., Hoffman, J. M., West, S. G., & Sheets, V. (2002). A comparison of methods to test mediation and other intervening variable effects. Psychological Methods, 7, 83–104.
Mai, K. M., Ellis, A. P., Christian, J. S., & Porter, C. O. (2016). Examining the effects of turnover intentions on organizational citizenship behaviors and deviance behaviors: A psychological contract approach. Journal of Applied Psychology,. doi:10.1037/apl0000115.
Mesch, G. S., & Manor, O. (1998). Social ties, environmental perception, and local attachment. Environment and Behavior, 30, 504–519.
Mindel, C. H. (1980). Extended familism among urban Mexican Americans, Anglos, and Blacks. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 2, 21–34.
Mitchell, T. R., Holtom, B. C., Lee, T. W., Sablynski, C. J., & Erez, M. (2001). Why people stay: Using job embeddedness to predict voluntary turnover. Academy of Management Journal, 44, 1102–1121.
Ng, T. W., & Feldman, D. C. (2014). Community embeddedness and work outcomes: The mediating role of organizational embeddedness. Human Relations, 67, 71–103.
Özbilgin, M. F., Beauregard, T. A., Tatli, A., & Bell, M. P. (2011). Work–life, diversity and intersectionality: A critical review and research agenda. International Journal of Management Reviews, 13, 177–198.
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2012). Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annual Review of Psychology, 65, 539–569.
Procidano, M. E., & Heller, K. (1983). Measures of perceived social support from friends and from family: Three validation studies. American Journal of Community Psychology, 11, 1–24.
Puddifoot, J. E. (2003). Exploring “personal” and “shared” sense of community identity in Durham city, England. Journal of Community Psychology, 31, 87–106.
Ragins, B. R., Gonzalez, J. A., Ehrhardt, K., & Singh, R. (2012). Crossing the threshold: The spillover of community racial diversity and diversity climate to the workplace. Personnel Psychology, 65, 755–787.
Ragins, B. R., Lyness, K., Williams, L., & Winkel, D. (2014). Life spillovers: The spillover of fear of home foreclosure to the workplace. Personnel Psychology, 67, 763–800.
Ramesh, A., & Gelfand, M. J. (2010). Will they stay or will they go? The role of job embeddedness in predicting turnover in individualistic and collectivistic cultures. Journal of Applied Psychology, 95, 807–823.
Raymond, C. M., Brown, G., & Weber, D. (2010). The measurement of place attachment: Personal, community, and environmental connections. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 30, 422–434.
Roberson, Q., Ryan, A. M. & Ragins, B. R. (in press). The evolution and future of diversity at work. Journal of Applied Psychology.
Sampson, R. J. (1988). Local friendship ties and community attachment in mass society: A multilevel systemic model. American Sociological Review, 53, 766–779.
Scannell, L., & Gifford, R. (2010). Defining place attachment: A tripartite organizing framework. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 30, 1–10.
Sellers, R. M., Smith, M. A., Nicole Shelton, J., Rowley, S. A., & Chavous, T. M. (1998). Multidimensional model of racial identity: A reconceptualization of African American racial identity. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 2, 18–39.
Siemsen, E., Roth, A., & Oliveira, P. (2010). Common method bias in regression models with linear, quadratic, and interaction effects. Organizational Research Methods, 13, 456–476.
Spector, P. E., & Brannick, M. T. (2011). Methodological urban legends: The misuse of statistical control variables. Organizational Research Methods, 14, 287–305.
Stephens, J. P., Heaphy, E. D., Carmeli, A., Spreitzer, G. M., & Dutton, J. E. (2013). Relationship quality and virtuousness: Emotional carrying capacity as a source of individual and team resilience. The Journal of Applied Behavioral Science, 9, 13–41.
Swartz, T. T. (2009). Intergenerational family relations in adulthood: Patterns, variations, and implications in the contemporary United States. Annual Review of Sociology, 35, 191–212.
Tharenou, P., & Caulfield, N. (2010). Will I stay or will I go? Explaining repatriation by self-initiated expatriates. Academy of Management Journal, 53, 1009–1028.
Ulrich-Schad, J. D., Henly, M., & Safford, T. G. (2013). The role of community assessments, place, and the great recession in the migration intentions of rural Americans. Rural Sociology, 78, 371–398.
Voydanoff, P. (2001). Incorporating community into work and family research: A review of basic relationships. Human Relations, 54, 1609–1637.
Voydanoff, P. (2014). Work, family, and community: Exploring interconnections (2nd ed.). New York: Psychology Press.
Wellman, B., & Wortley, S. (1990). Different strokes from different folks: Community ties and social support. American Journal of Sociology, 96, 558–588.
Williams, L. J., Hartman, N., & Cavazotte, F. (2010). Method variance and marker variables: A review and comprehensive CFA marker technique. Organizational Research Methods, 13, 477–514.
Wiseman, J. P. (1986). Friendship: Bonds and binds in a voluntary relationship. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 3, 191–211.
Zhang, M., Fried, D. D., & Griffeth, R. W. (2012). A review of job embeddedness: Conceptual, measurement issues, and directions for future research. Human Resource Management Review, 22, 220–231.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonzalez, J.A., Ragins, B.R., Ehrhardt, K. et al. Friends and Family: The Role of Relationships in Community and Workplace Attachment. J Bus Psychol 33, 89–104 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10869-016-9476-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10869-016-9476-3