Abstract
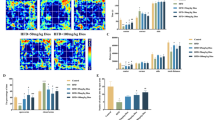
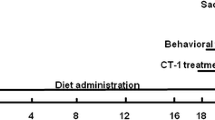
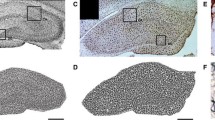
High-fat diet-induced metabolic changes are not restricted to the onset of cardiovascular diseases, but also include effects on brain functions related to learning and memory. This study aimed to evaluate mitochondrial markers and function, as well as cognitive function, in a rat model of metabolic dysfunction. Eight-week-old male Wistar rats were subjected to either a control diet or a two-hit protocol combining a high fat diet (HFD) with the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor L-NAME in the drinking water. HFD plus L-NAME induced obesity, hypertension, and increased serum cholesterol. These rats exhibited bioenergetic dysfunction in the hippocampus, characterized by decreased oxygen (O2) consumption related to ATP production, with no changes in H2O2 production. Furthermore, OPA1 protein expression was upregulated in the hippocampus of HFD + L-NAME rats, with no alterations in other morphology-related proteins. Consistently, HFD + L-NAME rats showed disruption of performance in the Morris Water Maze Reference Memory test. The neocortex did not exhibit either bioenergetic changes or alterations in H2O2 production. Calcium uptake rate and retention capacity in the neocortex of HFD + L-NAME rats were not altered. Our results indicate that hippocampal mitochondrial bioenergetic function is disturbed in rats exposed to a HFD plus L-NAME, thus disrupting spatial learning, whereas neocortical function remains unaffected.
Highlights
A two-hit protocol using HFD + L-NAME induces metabolic dysfunction in rats.
Spatial memory is impacted in HFD + L-NAME rats.
Hippocampal but not neocortex bioenergetics is affected in HFD + L-NAME rats.
OPA-1 expression is upregulated in the hippocampus of HFD + L-NAME rats.
Cortical calcium dynamics was not affected by HFD + L-NAME.
AbstractSection Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the first author, W.R.V and the corresponding author, A.F.B., upon reasonable request.
References
Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA et al (2009) Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 120(16):1640–1645. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192644
Aoun M, Feillet-Coudray C, Fouret G, Chabi B, Crouzier D, Ferreri C et al (2012) Rat liver mitochondrial membrane characteristics and mitochondrial functions are more profoundly altered by dietary lipid quantity than by dietary lipid quality: effect of different nutritional lipid patterns. Br J Nutr 107(5):647–659. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711451100331X
Belosludtseva NV, Kireeva TA, Belosludtsev KN, Khunderyakova NV, Mironova GD (2021) Comparative study of functional changes in Heart Mitochondria in two modes of Epinephrine exposure modeling myocardial Injury in rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 171(6):727–731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-021-05304-2
Bliss TV, Cooke SF (2011) Long-term potentiation and long-term depression: a clinical perspective. Clin (Sao Paulo) 66(Suppl 1):3–17. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1807-59322011001300002
Cavaliere G, Trinchese G, Penna E, Cimmino F, Pirozzi C, Lama A et al (2019) High-Fat Diet induces Neuroinflammation and mitochondrial impairment in mice cerebral cortex and synaptic fraction. Front Cell Neurosci 13:509. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00509
Cordero-Herrera I, Guimaraes DD, Moretti C, Zhuge Z, Han H, McCann Haworth S et al (2020) Head-to-head comparison of inorganic nitrate and metformin in a mouse model of cardiometabolic disease. Nitric Oxide 97:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2020.01.013
de Bem AF, Krolow R, Farias HR, de Rezende VL, Gelain DP, Moreira JCF et al (2020) Animal models of metabolic disorders in the study of neurodegenerative diseases: an overview. Front Neurosci 14:604150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.604150
de Mello AH, Schraiber RB, Goldim MPS, Garcez ML, Gomes ML, de Bem Silveira G et al (2019) Omega-3 fatty acids attenuate brain alterations in High-Fat Diet-Induced obesity model. Mol Neurobiol 56(1):513–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1097-6
de Paula GC, Brunetta HS, Engel DF, Gaspar JM, Velloso LA, Engblom D et al (2021) Hippocampal function is impaired by a short-term High-Fat Diet in mice: increased blood-brain barrier permeability and neuroinflammation as triggering events. Front Neurosci 15:734158. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.734158
Diaz A, Munoz-Arenas G, Venegas B, Vazquez-Roque R, Flores G, Guevara J et al (2021) Metforminium Decavanadate (MetfDeca) Treatment ameliorates hippocampal neurodegeneration and Recognition Memory in a metabolic syndrome model. Neurochem Res 46(5):1151–1165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03250-z
Dutheil S, Ota KT, Wohleb ES, Rasmussen K, Duman RS (2016) High-Fat Diet Induced anxiety and Anhedonia: impact on brain homeostasis and inflammation. Neuropsychopharmacology 41(7):1874–1887. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.357
Flamment M, Gueguen N, Wetterwald C, Simard G, Malthiery Y, Ducluzeau PH (2009) Effects of the cannabinoid CB1 antagonist rimonabant on hepatic mitochondrial function in rats fed a high-fat diet. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297(5):E1162–1170. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00169.2009
Gao W, Wang W, Zhang J, Deng P, Hu J, Yang J et al (2019) Allicin ameliorates obesity comorbid depressive-like behaviors: involvement of the oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, autophagy, insulin resistance and NOX/Nrf2 imbalance in mice. Metab Brain Dis 34(5):1267–1280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00443-y
Gavini K, Parameshwaran K (2023) Western blot. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL) ineligible companies. Kodeeswaran Parameshwaran declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies, Disclosure
Hakala JO, Pahkala K, Juonala M, Salo P, Kahonen M, Hutri-Kahonen N et al (2021) Cardiovascular Risk factor trajectories since childhood and cognitive performance in midlife: the Cardiovascular Risk in Young finns Study. Circulation 143(20):1949–1961. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.052358
Hao S, Dey A, Yu X, Stranahan AM (2016) Dietary obesity reversibly induces synaptic stripping by microglia and impairs hippocampal plasticity. Brain Behav Immun 51:230–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2015.08.023
Hirode G, Wong RJ (2020) Trends in the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in the United States, 2011–2016. JAMA 323(24):2526–2528. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.4501
Hutter E, Unterluggauer H, Garedew A, Jansen-Durr P, Gnaiger E (2006) High-resolution respirometry–a modern tool in aging research. Exp Gerontol 41(1):103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2005.09.011
Johns C, Gavras I, Handy DE, Salomao A, Gavras H (1996) Models of experimental hypertension in mice. Hypertension 28(6):1064–1069. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.hyp.28.6.1064
Kitakata H, Endo J, Hashimoto S, Mizuno E, Moriyama H, Shirakawa K et al (2021) Imeglimin prevents heart failure with preserved ejection fraction by recovering the impaired unfolded protein response in mice subjected to cardiometabolic stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 572:185–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.07.090
Knopman DS, Mosley TH, Catellier DJ, Coker LH (2009) & Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study Brain, M. R. I. S. Fourteen-year longitudinal study of vascular risk factors, APOE genotype, and cognition: the ARIC MRI Study. Alzheimers Dement, 5(3), 207–214, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2009.01.027
Kowaltowski AJ, Menezes-Filho SL, Assali EA, Goncalves IG, Cabral-Costa JV, Abreu P et al (2019) Mitochondrial morphology regulates organellar ca(2+) uptake and changes cellular ca(2+) homeostasis. FASEB J 33(12):13176–13188. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201901136R
Livingston JM, McDonald MW, Gagnon T, Jeffers MS, Gomez-Smith M, Antonescu S et al (2020) Influence of metabolic syndrome on cerebral perfusion and cognition. Neurobiol Dis 137:104756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104756
Mancini G, Dias C, Lourenco CF, Laranjinha J, de Bem A, Ledo A (2021) A High Fat/Cholesterol Diet recapitulates some Alzheimer’s Disease-Like features in mice: focus on hippocampal mitochondrial dysfunction. J Alzheimers Dis 82(4):1619–1633. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-210122
Mellendijk L, Wiesmann M, Kiliaan AJ (2015) Impact of Nutrition on cerebral circulation and cognition in the metabolic syndrome. Nutrients 7(11):9416–9439. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7115477
Moreira PI, Santos MS, Seica R, Oliveira CR (2007) Brain mitochondrial dysfunction as a link between Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes. J Neurol Sci 257(1–2):206–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2007.01.017
Moreno-Fernandez S, Garces-Rimon M, Vera G, Astier J, Landrier JF, Miguel M (2018) High Fat/High glucose Diet induces metabolic syndrome in an experimental rat model. Nutrients 10(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101502
Mottillo S, Filion KB, Genest J, Joseph L, Pilote L, Poirier P et al (2010) The metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 56(14):1113–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2010.05.034
Nath S, Ghosh SK, Choudhury Y (2017) A murine model of type 2 diabetes mellitus developed using a combination of high fat diet and multiple low doses of streptozotocin treatment mimics the metabolic characteristics of type 2 diabetes mellitus in humans. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 84:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vascn.2016.10.007
National Research Council (2011) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals, 8th edn. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Park HS, Cho HS, Kim TW (2018) Physical exercise promotes memory capability by enhancing hippocampal mitochondrial functions and inhibiting apoptosis in obesity-induced insulin resistance by high fat diet. Metab Brain Dis 33(1):283–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0160-8
Park G, Lee JY, Han HM, An HS, Jin Z, Jeong EA et al (2021) Ablation of dynamin-related protein 1 promotes diabetes-induced synaptic injury in the hippocampus. Cell Death Dis 12(5):445. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03723-7
Pintana H, Apaijai N, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC (2013) DPP-4 inhibitors improve cognition and brain mitochondrial function of insulin-resistant rats. J Endocrinol 218(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-12-0521
Pinti MV, Fink GK, Hathaway QA, Durr AJ, Kunovac A, Hollander JM (2019) Mitochondrial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus: an organ-based analysis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 316(2):E268–E285. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00314.2018
Pratchayasakul W, Sa-Nguanmoo P, Sivasinprasasn S, Pintana H, Tawinvisan R, Sripetchwandee J et al (2015) Obesity accelerates cognitive decline by aggravating mitochondrial dysfunction, insulin resistance and synaptic dysfunction under estrogen-deprived conditions. Horm Behav 72:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.04.023
Putti R, Migliaccio V, Sica R, Lionetti L (2015) Skeletal Muscle Mitochondrial Bioenergetics and morphology in high Fat Diet Induced obesity and insulin resistance: focus on Dietary Fat source. Front Physiol 6:426. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2015.00426
Quillfeldt JA (2016) Behavioral methods to study learning and memory in rats. In: Andersen, M, Tufik, S. (eds) Rodent model as tools in ethical Biomedical Research. Springer, Cham
Ruegsegger GN, Vanderboom PM, Dasari S, Klaus KA, Kabiraj P, McCarthy CB et al (2019) Exercise and metformin counteract altered mitochondrial function in the insulin-resistant brain. JCI Insight 4(18). https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.130681
Saklayen MG (2018) The global epidemic of the metabolic syndrome. Curr Hypertens Rep 20(2):12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-018-0812-z
Santos TO, Mazucanti CH, Xavier GF, Torrao AS (2012) Early and late neurodegeneration and memory disruption after intracerebroventricular streptozotocin. Physiol Behav 107(3):401–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2012.06.019
Serna JDC, Caldeira da Silva CC, Kowaltowski AJ (2020) Functional changes induced by caloric restriction in cardiac and skeletal muscle mitochondria. J Bioenerg Biomembr 52(4):269–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-020-09838-4
Siervo M, Harrison SL, Jagger C, Robinson L, Stephan BC (2014) Metabolic syndrome and longitudinal changes in cognitive function: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis 41(1):151–161. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-132279
Tarantini S, Tucsek Z, Valcarcel-Ares MN, Toth P, Gautam T, Giles CB et al (2016) Circulating IGF-1 deficiency exacerbates hypertension-induced microvascular rarefaction in the mouse hippocampus and retrosplenial cortex: implications for cerebromicrovascular and brain aging. Age (Dordr) 38(4):273–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-016-9931-0
Trevino S, Aguilar-Alonso P, Flores Hernandez JA, Brambila E, Guevara J, Flores G et al (2015) A high calorie diet causes memory loss, metabolic syndrome and oxidative stress into hippocampus and temporal cortex of rats. Synapse 69(9):421–433. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.21832
Trevino S, Vazquez-Roque RA, Lopez-Lopez G, Perez-Cruz C, Moran C, Handal-Silva A et al (2017) Metabolic syndrome causes recognition impairments and reduced hippocampal neuronal plasticity in rats. J Chem Neuroanat 82:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2017.02.007
Vercesi AE, Castilho RF, Kowaltowski AJ, de Oliveira HCF, de Souza-Pinto NC, Figueira TR et al (2018) Mitochondrial calcium transport and the redox nature of the calcium-induced membrane permeability transition. Free Radic Biol Med 129:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.08.034
Vilas-Boas EA, Cabral-Costa JV, Ramos VM, Caldeira da Silva CC, Kowaltowski AJ (2023) Goldilocks calcium concentrations and the regulation of oxidative phosphorylation: too much, too little, or just right. J Biol Chem 299(3):102904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.102904
Vilela WR, Bellozi PMQ, Picolo VL, Cavadas BN, Marques KVS, Pereira LTG et al (2023) Early-life metabolic dysfunction impairs cognition and mitochondrial function in mice. J Nutr Biochem 117:109352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109352
Wang D, Yan J, Chen J, Wu W, Zhu X, Wang Y (2015) Naringin improves neuronal insulin signaling, brain mitochondrial function, and cognitive function in High-Fat Diet-Induced obese mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35(7):1061–1071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-015-0201-y
Yang C, Sui G, Li D, Wang L, Zhang S, Lei P et al (2021) Exogenous IGF-1 alleviates depression-like behavior and hippocampal mitochondrial dysfunction in high-fat diet mice. Physiol Behav 229:113236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2020.113236
Zamorano-Leon JJ, Modrego J, Mateos-Caceres PJ, Macaya C, Martin-Fernandez B, Miana M et al (2010) A proteomic approach to determine changes in proteins involved in the myocardial metabolism in left ventricles of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Cell Physiol Biochem 25(2–3):347–358. https://doi.org/10.1159/000276567
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Dra. Paula Maria Quaglio Bellozi for the support in graphic design.
Funding
This study was supported by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (13/07937-8, 20/06970-5); Fundação de Apoio à Pesquisa do Distrito Federal (FAPDF grants: 00193–00000884/2021-89, 00193–0000002348/2022-07); Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq grant 424809-2018-4); Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES/STINT grant 88881.465507/2019-01); and Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia e Neuro-ImunoModulação (INCT-NIM grant 485489/2014-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.R.V.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation, Writing - original draft preparation, Visualization. L.S.R.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization. L.R.G.B.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization. J.V.C-C.: Investigation, Methodology, Visualization. J.D.C.S.: Investigation, Methodology, Visualization. A.J.K.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Writing - review & editing, Visualization. G.F.X.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Data curation, Writing - review & editing, Visualization. J.C.B.F.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Resources, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Visualization. A.F.B.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Resources, Data curation, Writing - review & editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The procedures fulfilled the guidelines for animal care from the NIH (National Research Council, 2011) and were approved by the Ethics Committee on the Use of Animals at the University of São Paulo (CEUA/USP No 9236210120).
Competing interests
Alicia J. Kowaltowski declare that she is editor of the Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vilela, W.R., Ramalho, L.S., Bechara, L.R.G. et al. Metabolic dysfunction induced by HFD + L-NAME preferentially affects hippocampal mitochondria, impacting spatial memory in rats. J Bioenerg Biomembr 56, 87–99 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-024-10005-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-024-10005-2