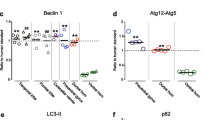
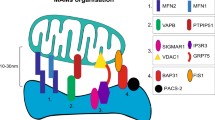
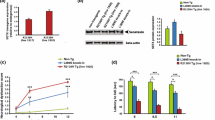
Abstract
Mitochondria contribute to neuronal function not only via their ability to generate ATP, but also via their ability to buffer large Ca2+ loads. This review summarizes evidence that mitochondrial Ca2+ sequestration is especially important for sustaining the function of vertebrate motor nerve terminals during repetitive stimulation. Motor terminal mitochondria can sequester large amounts of Ca2+ because they have mechanisms for limiting both the mitochondrial depolarization and the increase in matrix free [Ca2+] associated with Ca2+ influx. In mice expressing mutations of human superoxide dismutase −1 (SOD1) that cause some cases of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (fALS), motor terminals degenerate well before the death of motor neuron cell bodies. This review presents evidence for early and progressive mitochondrial dysfunction in motor terminals of mutant SOD1 mice (G93A, G85R). This dysfunction would impair mitochondrial ability to sequester stimulation-associated Ca2+ loads, and thus likely contributes to the early degeneration of motor terminals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruijn LI, Becher MW, Lee MK, Anderson KL, Jemkins NA, Copeland NG et al (1997) Neuron 18:327–338
Burke RE (2004) In: Engel AG, Franzini-Armstrong D (eds) Myology, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Chiu AY, Zhai P, Dalcanto MC, Peters TM, Kwon YW, Prattis SM et al (1995) Mol Cell Neurosci 6:349–362
Damiano M, Starkov AA, Petri S, Kipiani K, Kiaei M, Mattiazzi M et al (2006) J Neurochem 96:1349–1361
David G (1999) J Neurosci 19:7495–7506
David G, Barrett EF (2000) J Neurosci 20:7290–7296
David G, Barrett EF (2003) J Physiol 548:425–438
David G, Barrett JN, Barrett EF (1998) J Physiol 509:59–65
David G, Talbot J, Barrett EF (2003) Cell Calcium 33:197–206
Fischer LR, Culver DG, Tennant P, Davis AA, Wang M, Castellano-Sanchez A et al (2004) Exp Neurol 185:232–240
Frey D, Schneider C, Xu L, Borg J, Spooren W, Caroni P (2000) J Neurosci 20:2534–2542
García-Chacón L, Nguyen K, David G, Barrett EF (2006) J Physiol 574:663–675
Gordon R, Hegedus J, Tam SL (2004) Neurol Res 26:174–185
Grosskreutz J, Van Den Bosch L, Keller BU (2010) Cell Calcium 47:165–174
Gunter TE, Pfeiffer DR (1990) Am J Physiol 258:C755–C786
Gurney ME, Pu H, Chiu AY, Dal Canto MC, Polchow CY, Alexander DD et al (1994) Science 264:1772–1775
Johnson-Cadwell LI, Jekabsons MB, Wang A, Polster BM, Nicholls DG (2007) J Neurochem 101:1619–1631
Kirichok Y, Krapivinsky G, Clapham DE (2004) Nature 427:360–364
Laube G, Bernstein HG, Wolf G, Veh RW (2002) J Comp Neurol 444:369–386
Li Q, Van de Velde C, Israelson A, Xie J, Bailey AO, Dong M-Q, Chun S-J, Roy T, Winer L, Yates JR, Capaldi RA, Cleveland DW, Miller TM (2010) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:21146–21151
Murray LM, Talbot K, Gillingwater TH (2010) Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 36:133–156
Naga KK, Sullivan PG, Geddes JW (2007) J Neurosci 27:7469–7475
Nguyen KT, García-Chacón LE, Barrett JN, Barrett EF, David G (2009) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:2007–2011
Nguyen KT, Barrett JN, García-Chacón LE, David G, Barrett EF (2011) Neurobiol Dis 42:381–390
Nicholls DG, Chalmers S (2004) J Bioenerg Biomembr 36:277–281
Nicholls DG, Ferguson SJ (2002) Bioenergetics 3. Academic, London
Salvi M, Toninello A (2004) Biochim Biophys Acta 1661:113–124
Shi P, Gal J, Kwinter DM, Liu X, Zhu H (2010) Biochim Biophys Acta 1802:45–51
Talbot JD, David G, Barrett EF (2003) J Neurophysiol 90:491–502
Talbot JD, Barrett JN, Barrett EF, David G (2007) J Physiol 579:783–798
Tang Y, Zucker RS (1997) Neuron 18:483–491
Valentine JS, Doucette PA, Zittinpotter S (2005) Annu Rev Biochem 74:563–593
Vila L, Barrett EF, Barrett JN (2003) J Physiol 549:719–728
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barrett, E.F., Barrett, J.N. & David, G. Mitochondria in motor nerve terminals: function in health and in mutant superoxide dismutase 1 mouse models of familial ALS. J Bioenerg Biomembr 43, 581–586 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-011-9392-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-011-9392-1