Abstract
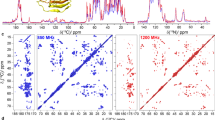
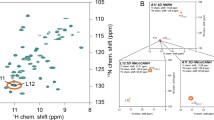
The 1H dipolar network, which is the major obstacle for applying proton detection in the solid-state, can be reduced by deuteration, employing the RAP (Reduced Adjoining Protonation) labeling scheme, which yields random protonation at non-exchangeable sites. We present here a systematic study on the optimal degree of random sidechain protonation in RAP samples as a function of the MAS (magic angle spinning) frequency. In particular, we compare 1H sensitivity and linewidth of a microcrystalline protein, the SH3 domain of chicken α-spectrin, for samples, prepared with 5–25 % H2O in the E. coli growth medium, in the MAS frequency range of 20–60 kHz. At an external field of 19.96 T (850 MHz), we find that using a proton concentration between 15 and 25 % in the M9 medium yields the best compromise in terms of sensitivity and resolution, with an achievable average 1H linewidth on the order of 40–50 Hz. Comparing sensitivities at a MAS frequency of 60 versus 20 kHz, a gain in sensitivity by a factor of 4–4.5 is observed in INEPT-based 1H detected 1D 1H,13C correlation experiments. In total, we find that spectra recorded with a 1.3 mm rotor at 60 kHz have almost the same sensitivity as spectra recorded with a fully packed 3.2 mm rotor at 20 kHz, even though ~20× less material is employed. The improved sensitivity is attributed to 1H line narrowing due to fast MAS and to the increased efficiency of the 1.3 mm coil.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal V, Reif B (2008) Residual methyl protonation in perdeuterated proteins for multi-dimensional correlation experiments in MAS solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 194:16–24
Agarwal V, Xue Y, Reif B, Skrynnikov NR (2008) Protein side-chain dynamics as observed by solution- and solid-state NMR spectroscopy: a similarity revealed. J Am Chem Soc 130:16611–16621
Akbey U, Lange S, Franks WT, Linser R, Rehbein K, Diehl A, van Rossum BJ, Reif B, Oschkinat H (2010) Optimum levels of exchangeable protons in perdeuterated proteins for proton detection in MAS solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 46:67–73
Asami S, Reif B (2012) Assignment strategies for aliphatic protons in the solid-state in randomly protonated proteins. J Biomol NMR 52:31–39
Asami S, Schmieder P, Reif B (2010) High resolution H-1-detected solid-state NMR spectroscopy of protein aliphatic resonances: access to tertiary structure information. J Am Chem Soc 132:15133–15135
Bak M, Rasmussen JT, Nielsen NC (2000) SIMPSON: a general simulation program for solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 147:296–330
Bak M, Schultz R, Vosegaard T, Nielsen NC (2002) Specification and visualization of anisotropic interaction tensors in polypeptides and numerical simulations in biological solid-state NMR. J Magn Reson 154:28–45
Bielecki A, Kolbert AC, Levitt MH (1989) Frequency-switched pulse sequences: homonuclear decoupling and dilute spin NMR in solids. Chem Phys Lett 155:341–346
Bockmann A, Gardiennet C, Verel R, Hunkeler A, Loquet A, Pintacuda G, Emsley L, Meier BH, Lesage A (2009) Characterization of different water pools in solid-state NMR protein samples. J Biomol NMR 45:319–327
Bosman L, Madhu PK, Vega S, Vinogradov E (2004) Improvement of homonuclear dipolar decoupling sequences in solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance utilising radiofrequency imperfections. J Magn Reson 169:39–48
Castellani F, van Rossum B, Diehl A, Schubert M, Rehbein K, Oschkinat H (2002) Structure of a protein determined by solid-state magic-angle-spinning NMR spectroscopy. Nature 420:98–102
Chevelkov V, Chen Z, Bermel W, Reif B (2005) Resolution enhancement in MAS solid-state NMR by application of 13C homonuclear scalar decoupling during acquisition. J Magn Reson 172:56–62
Chevelkov V, Rehbein K, Diehl A, Reif B (2006) Ultrahigh resolution in proton solid-state NMR spectroscopy at high levels of deuteration. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:3878–3881
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) Nmrpipe—a multidimensional spectral processing system based on Unix pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293
Ernst M, Samoson A, Meier BH (2001) Low-power decoupling in fast magic-angle spinning NMR. Chem Phys Lett 348:293–302
Ferguson N, Becker J, Tidow H, Tremmel S, Sharpe TD, Krause G, Flinders J, Petrovich M, Berriman J, Oschkinat H, Fersht AR (2006) General structural motifs of amyloid protofilaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:16248–16253
Franks WT, Wylie BJ, Schmidt HLF, Nieuwkoop AJ, Mayrhofer RM, Shah GJ, Graesser DT, Rienstra CM (2008) Dipole tensor-based atomic-resolution structure determination of a nanocrystalline protein by solid-state NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:4621–4626
Gardner KH, Rosen MK, Kay LE (1997) Global folds of highly deuterated, methyl-protonated proteins by multidimensional NMR. Biochemistry 36:1389–1401
Helmus JJ, Jaroniec CP (2011) NMR glue, http://code.google.com/p/nmrglue, The Ohio State University
Hong M, Jakes K (1999) Selective and extensive C-13 labeling of a membrane protein for solid-state NMR investigations. J Biomol NMR 14:71–74
Hoult DI, Richards RE (1976) Signal-to-noise ratio of nuclear magnetic-resonance experiment. J Magn Reson 24:71–85
Huber M, Hiller S, Schanda P, Ernst M, Bockmann A, Verel R, Meier BH (2011) A proton-detected 4D solid-state NMR experiment for protein structure determination. ChemPhysChem 12:915–918
Huber M, With O, Schanda P, Verel R, Ernst M, Meier BH (2012) A supplementary coil for (2)H decoupling with commercial HCN MAS probes. J Magn Reson 214:76–80
Igumenova TI, McDermott AE (2005) Homo-nuclear 13C J-decoupling in uniformly 13C-enriched solid proteins. J Magn Reson 175:11–20
Kehlet C, Nielsen JT, Tosner Z, Nielsen NC (2011) Resolution-enhanced solid-state NMR (13)C-(13)C correlation spectroscopy by optimal control dipolar-driven spin-state-selective coherence transfer. J Phys Chem Lett 2:543–547
Knight MJ, Webber AL, Pell AJ, Guerry P, Barbet-Massin E, Bertini I, Felli IC, Gonnelli L, Pierattelli R, Emsley L, Lesage A, Herrmann T, Pintacuda G (2011) Fast resonance assignment and fold determination of human superoxide dismutase by high-resolution proton-detected solid-state MAS NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 50:11697–11701
Laage S, Lesage A, Emsley L, Bertini I, Felli IC, Pierattelli R, Pintacuda G (2009) Transverse-dephasing optimized homonuclear j-decoupling in solid-state NMR spectroscopy of uniformly 13C-labeled proteins. J Am Chem Soc 131:10816–10817
LeMaster DM, Kushlan DM (1996) Dynamical mapping of E-coli thioredoxin via C-13 NMR relaxation analysis. J Am Chem Soc 118:9255–9264
Levitt MH, Kolbert AC, Bielecki A, Ruben DJ (1993) High-resolution H-1-NMR in solids with frequency-switched multiple-pulse sequences. Solid State Nucl Mag 2:151–163
Lewandowski JR, Dumez JN, Akbey U, Lange S, Emsley L, Oschkinat H (2011) Enhanced resolution and coherence lifetimes in the solid-state NMR spectroscopy of perdeuterated proteins under ultrafast magic-angle spinning. J Phys Chem Lett 2:2205–2211
Linser R, Fink U, Reif B (2008) Proton-detected scalar coupling based assignment strategies in MAS solid-state NMR spectroscopy applied to perdeuterated proteins. J Magn Reson 193:89–93
Linser R, Bardiaux B, Higman V, Fink U, Reif B (2011a) Structure calculation from unambiguous long-range amide and methyl (1)h-(1)h distance restraints for a microcrystalline protein with MAS solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 133:5905–5912
Linser R, Dasari M, Hiller M, Higman V, Fink U, Lopez Del Amo JM, Markovic S, Handel L, Kessler B, Schmieder P, Oesterhelt D, Oschkinat H, Reif B (2011b) Proton-detected solid-state NMR spectroscopy of fibrillar and membrane proteins. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 50:4508–4512
Reif B, Griffin RG (2003) H-1 detected H-1, N-15 correlation spectroscopy in rotating solids. J Magn Reson 160:78–83
Sakellariou D, Lesage A, Hodgkinson P, Emsley L (2000) Homonuclear dipolar decoupling in solid-state NMR using continuous phase modulation. Chem Phys Lett 319:253–260
Schanda P, Huber M, Verel R, Ernst M, Meier BH (2009) Direct detection of (3 h)J(NC′) hydrogen-bond scalar couplings in proteins by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:9322–9325
Shaka AJ, Keeler J, Frenkiel T, Freeman R (1983) An improved sequence for broad-band decoupling: Waltz-16. J Magn Reson 52:335–338
Shi L, Peng X, Ahmed MA, Edwards D, Brown LS, Ladizhansky V (2008) Resolution enhancement by homonuclear J-decoupling: application to three-dimensional solid-state magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 41:9–15
Straus SK, Bremi T, Ernst RR (1996) Resolution enhancement by homonuclear J decoupling in solid-state MAS NMR. Chem Phys Lett 262:709–715
Tang M, Comellas G, Mueller LJ, Rienstra CM (2010) High resolution 13C-detected solid-state NMR spectroscopy of a deuterated protein. J Biomol NMR 48:103–111
Tian Y, Chen L, Niks D, Kaiser JM, Lai J, Rienstra CM, Dunn MF, Mueller LJ (2009) J-Based 3D sidechain correlation in solid-state proteins. Phys Chem Chem Phys 11:7078–7086
Vinogradov E, Madhu PK, Vega S (1999) High-resolution proton solid-state NMR spectroscopy by phase-modulated Lee-Goldburg experiment. Chem Phys Lett 314:443–450
Vranken WF, Boucher W, Stevens TJ, Fogh RH, Pajon A, Llinas M, Ulrich EL, Markley JL, Ionides J, Laue ED (2005) The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: development of a software pipeline. Proteins 59:687–696
Vuister GW, Bax A (1992) Resolution enhancement and spectral editing of uniformly C-13-enriched proteins by homonuclear broad-band C-13 decoupling. J Magn Reson 98:428–435
Wasmer C, Lange A, Van Melckebeke H, Siemer AB, Riek R, Meier BH (2008) Amyloid fibrils of the HET-s(218–289) prion form a beta solenoid with a triangular hydrophobic core. Science 319:1523–1526
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Leibniz- and the Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft, the DFG (Re1435, SFB449, SFB740) and the Bio-NMR project (European Commission’s Framework Program 7, project number: 261863). We are grateful to the Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich (CIPS-M) for financial support and to Bruker BioSpin for providing measurement time, especially to S. Wegner and G. Althoff for technical support. P.S. acknowledges funding from the French Research Agency (Contract ANR-10-PDOC-011-01 ProtDynByNMR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asami, S., Szekely, K., Schanda, P. et al. Optimal degree of protonation for 1H detection of aliphatic sites in randomly deuterated proteins as a function of the MAS frequency. J Biomol NMR 54, 155–168 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-012-9659-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-012-9659-9