Abstract
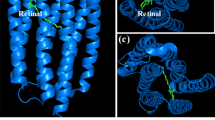
The proteorhodopsin family consists of hundreds of homologous retinal containing membrane proteins found in bacteria in the photic zone of the oceans. They are colour tuned to their environment and act as light-driven proton pumps with a potential energetic and regulatory function. Precise structural details are still unknown. Here, the green proteorhodopsin variant has been selected for a chemical shift analysis of retinal and Schiff base by solid-state NMR. Our data show that the chromophore exists in mainly all-trans configuration in the proteorhodopsin ground state. The optical absorption maximum together with retinal and Schiff base chemical shifts indicate a strong interaction network between chromophore and opsin.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- bR:
-
Bacteriorhodopsin
- PR:
-
Proteorhodopsin
- wt:
-
Wild type
- PSB:
-
Protonated Schiff base
- DA:
-
Dark adapted
- LA:
-
Light adapted
- MAS:
-
Magic angle sample spinning
References
Albeck A, Livnah N, Gottlieb H, Sheves M (1992) C-13 Nmr-studies of model compounds for bacteriorhodopsin––factors affecting the retinal chromophore chemical-shifts and absorption maximum. J Am Chem Soc 114:2400–2411
Beja O, Aravind L, Koonin EV, Suzuki MT, Hadd A, Nguyen LP, Jovanovich SB, Gates CM, Feldman RA, Spudich JL, Spudich EN, DeLong EF (2000) Bacterial rhodopsin: evidence for a new type of phototrophy in the sea. Science 289:1902–1906
Bergo V, Amsden JJ, Spudich EN, Spudich JL, Rothschild KJ (2004) Structural changes in the photoactive site of proteorhodopsin during the primary photoreaction. Biochemistry 43:9075–9083
Bremser W, Paust J (1974) C-13 Nmr-spectrum of beta-carotene and charge-distribution in poly chain of apocarotinals. Org Magn Resonance 6:433–435
Creemers AFL, Klaassen CHW, Bovee-Geurts PHM, Kelle R, Kragl U, Raap J, de Grip WJ, Lugtenburg J, de Groot HJM (1999) Solid state 15N NMR evidence for a complex Schiff base counterion in the visual G-protein-coupled receptor rhodopsin. Biochemistry 38:7195–7199
de Groot HJM, Harbison GS, Herzfeld J, Griffin RG (1989) Nuclear magnetic-resonance study of the Schiff-base in bacteriorhodopsin––counterion effects on the N-15 shift anisotropy. Biochemistry 28:3346–3353
Dioumaev AK, Brown LS, Shih J, Spudich EN, Spudich JL, Lanyi JK (2002) Proton transfers in the photochemical reaction cycle of proteorhodopsin. Biochemistry 41:5348–5358
Dreuw A (2006) Quantum chemical methods for the investigation of photoinitiated processes in biological systems: theory and applications. Chemphyschem 7:2259–2274
Engelhard M, Hess B, Metz G, Kreutz W, Siebert F, Soppa J, Oesterhelt D (1990) High-resolution C-13-solid state Nmr of bacteriorhodopsin––assignment of specific aspartic acids and structural implications of single site mutations. Eur Biophys J 18:17–24
Feng X, Verdegem PJE, Eden M, Sandstrom D, Lee YK, Bovee-Geurts PHM, de Grip WJ, Lugtenburg J, de Groot HJM, Levitt MH (2000) Determination of a molecular torsional angle in the metarhodopsin-I photointermediate of rhodopsin by double-quantum solid-state NMR. J Biomol Nmr 16:1–8
Friedrich T, Geibel S, Kalmbach R, Chizhov I, Ataka K, Heberle J, Engelhard M, Bamberg E (2002) Proteorhodopsin is a light-driven proton pump with variable vectoriality. J Mol Biol 321:821–838
Fung BM, Khitrin AK, Ermolaev K (2000) An improved broadband decoupling sequence for liquid crystals and solids. J Magn Reson 142:97–101
Han M, Dedecker BS, Smith SO (1993) Localization of the retinal protonated Schiff-base counterion in rhodopsin. Biophys J 65:899–906
Harbison GS, Herzfeld J, Griffin RG (1983) Solid-state N-15 nuclear magnetic-resonance study of the Schiff-base in bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry 22:1–5
Harbison GS, Smith SO, Pardoen JA, Courtin JML, Lugtenburg J, Herzfeld J, Mathies RA, Griffin RG (1985) Solid-state C-13 Nmr detection of a perturbed 6-S-trans chromophore in bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry 24:6955–6962
Harbison GS, Smith SO, Pardoen JA, Mulder PPJ, Lugtenburg J, Herzfeld J, Mathies R, Griffin RG (1984) Solid-state C-13 Nmr-studies of retinal in bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry 23:2662–2667
Hatcher ME, Hu JGG, Belenky M, Verdegem P, Lugtenburg J, Griffin RG, Herzfeld J (2002) Control of the pump cycle in bacteriorhodopsin: mechanisms elucidated by solid-state NMR of the D85N mutant. Biophys J 82:1017–1029
Hohenfeld IP, Wegener AA, Engelhard M (1999) Purification of histidine tagged bacteriorhodopsin, pharaonis halorhodopsin and pharaonis sensory rhodopsin II functionally expressed in Escherichia coli. Febs Lett 442:198–202
Hu JG, Griffin RG, Herzfeld J (1994) Synergy in the spectral tuning of retinal pigments: complete accounting of the opsin shift in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8880–8884
Hu JGG, Griffin RG, Herzfeld J (1997a) Interactions between the protonated Schiff base and its counterion in the photointermediates of bacteriorhodopsin. J Am Chem Soc 119:9495–9498
Hu JGG, Sun BQQ, Petkova AT, Griffin RG, Herzfeld J (1997b) The predischarge chromophore in bacteriorhodopsin: a N-15 solid-state NMR study of the L photointermediate. Biochemistry 36:9316–9322
Ikeda D, Furutani Y, Kandori H (2007) FTIR study of the retinal Schiff base and internal water molecules of proteorhodopsin. Biochemistry 46:5365–5373
Imasheva ES, Balashov SP, Wang JM, Dioumaev AK, Lanyi JK (2004) Selectivity of retinal photoisomerization in proteorhodopsin is controlled by aspartic acid 227. Biochemistry 43:1648–1655
Imasheva ES, Shimono K, Balashov SP, Wang JM, Zadok U, Sheves M, Kamo N, Lanyi JK (2005) Formation of a long-lived photoproduct with a deprotonated Schiff base in proteorhodopsin, and its enhancement by mutation of Asp227. Biochemistry 44:10828–10838
Kinsey RA, Kintanar A, Oldfield E (1981) Dynamics of amino-acid side-chains in membrane-proteins by high-field solid-state deuterium nuclear magnetic-resonance spectroscopy––phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan. J Biol Chem 256:9028–9036
Kolbe M, Besir H, Essen LO, Oesterhelt D (2000) Structure of the light-driven chloride pump halorhodopsin at 1.8 A resolution. Science 288:1390–1396
Krebs RA, Dunmire D, Partha R, Braiman MS (2003) Resonance Raman characterization of proteorhodopsin’s chromophore environment. J Phys Chem B 107:7877–7883
Lanyi JK, Schobert B (2002) Crystallographic structure of the retinal and the protein after deprotonation of the Schiff base: the switch in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. J Mol Biol 321:727–737
Lee YK, Kurur ND, Helmle M, Johannessen OG, Nielsen NC, Levitt MH (1995) Efficient dipolar recoupling in the Nmr of rotating solids––a sevenfold symmetrical radiofrequency pulse sequence. Chem Phys Lett 242:304–309
Lenz MO, Huber R, Schmidt B, Gilch P, Kalmbach R, Engelhard M, Wachtveitl J (2006) First steps of retinal photoisomerization in proteorhodopsin. Biophys J 91:255–262
Lenz MO, Woerner AC, Glaubitz C, Wachtveitl J (2007) Photoisomerization in proteorhodopsin mutant D97N. Photochem Photobiol 83:226–231
Luecke H, Lanyi JK (2003) Structural clues to the mechanism of ion pumping in bacteriorhodopsin. Adv Protein Chem 63:111–130
Luecke H, Schobert B, Lanyi JK, Spudich EN, Spudich JL (2001) Crystal structure of sensory rhodopsin II at 2.4 angstroms: insights into color tuning and transducer interaction. Science 293:1499–1503
Luecke H, Schobert B, Richter HT, Cartailler JP, Lanyi JK (1999) Structure of bacteriorhodopsin at 1.55 A resolution. J Mol Biol 291:899–911
Mason AJ, Turner GJ, Glaubitz C (2005) Conformational heterogeneity of transmembrane residues after the Schiff base reprotonation of bacteriorhodopsin––N-15 CPMAS NMR of D85N/T170C membranes. Febs J 272:2152–2164
Muchmore DC, Mcintosh LP, Russell CB, Anderson DE, Dahlquist FW (1989) Expression and N-15 labeling of proteins for proton and N-15 nuclear-magnetic-resonance. Method Enzymol 177:44–73
Sabehi G, Loy A, Jung KH, Partha R, Spudich JL, Isaacson T, Hirschberg J, Wagner M, Beja O (2005) New insights into metabolic properties of marine bacteria encoding proteorhodopsins. Plos Biol 3:1409–1417
Varo G, Brown LS, Lakatos M, Lanyi JK (2003) Characterization of the photochemical reaction cycle of proteorhodopsin. Biophys J 84:1202–1207
Walter JM, Greenfield D, Bustamante C, Liphardt J (2007) Light-powering Escherichia coli with proteorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:2408–2412
Wang WW, Sineshchekov OA, Spudich EN, Spudich JL (2003) Spectroscopic and photochemical characterization of a deep ocean proteorhodopsin. J Biol Chem 278:33985–33991
Acknowledgments
This work has been financially supported by SFB 472 (“Molecular Bioenergetics”). Cells and plasmids were kindly provided by E. Bamberg, Frankfurt and M. Engelhard, Dortmund. The 10,11-13C2 retinal was a generous gift of Marina Carravetta and Malcolm Levitt, Southampton. Ute Hellmich and Christoph Kaiser are acknowledged for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mark Lorch and Andreas C. Woerner contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfleger, N., Lorch, M., Woerner, A.C. et al. Characterisation of Schiff base and chromophore in green proteorhodopsin by solid-state NMR. J Biomol NMR 40, 15–21 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-007-9203-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-007-9203-5