Abstract
Objective
The fabrication of bioactive coatings on metallic implants to enhance osseointegration has become a topic of general interest in orthopedics and dentistry. Hydroxyapatite (HA) coating has been shown to induce bone formation and promote bone-implant integration. Unfortunately, poor mechanical performance has hindered this from becoming a favorable coating material. The majority of present studies have focused in incorporating different elements into HA coatings to improve mechanical properties. In recent years, tantalum (Ta) has received increasing attention due to its excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. The aim of on the present study was to investigate the fabrication and biological performance of Ta-incorporated HA coatings.
Methods
Ta-incorporated HA coatings were fabricated using the plasma spray technique on a titanium substrate, and the surface characteristics and mechanical properties were examined. In addition, the effects of Ta-incorporated HA coatings on the biological behavior of mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) were investigated.
Results
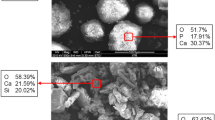
Ta-incorporated HA coatings with microporous structure had higher roughness and wettability. In addition, the bonding strength of Ta/HA coatings with the substrate was substantially superior to HA coatings. Furthermore, Ta-incorporated HA coatings not only facilitated initial cell adhesion and faster proliferation, but also promoted the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs.
Conclusion
These results indicate that the incorporation of Ta could improve mechanical performance and increase the osteogenic activity of HA coatings. The Ta-incorporated HA coating fabricated by plasma spraying is expected to be a promising bio-coating material for metallic implants.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kulkarni M, Patil-Sen Y, Junkar I, Kulkarni CV, Lorenzetti M, Iglič A. Wettability studies of topologically distinct titanium surfaces. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;129:47–53.
Salou L, Hoornaert A, Stanovici J, Briand S, Louarn G, Layrolle P. Comparative bone tissue integration of nanostructured and microroughened dental implants. Nanomedicine. 2015;10:741–51.
Park JW, Kwon TG, Suh JY. The relative effect of surface strontium chemistry and super-hydrophilicity on the early osseointegration of moderately rough titanium surface in the rabbit femur. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013;24:706–9.
Liu P, Hao Y, Zhao Y, Yuan Z, Ding Y, Cai K. Surface modification of titanium substrates for enhanced osteogenetic and antibacterial properties. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;160:110–6.
Guillot R, Pignot-Paintrand I, Lavaud J, Decambron A, Bourgeois E, Josserand V, et al. Assessment of a polyelectrolyte multilayer film coating loaded with BMP-2 on titanium and PEEK implants in the rabbit femoral condyle. Acta Biomater. 2016;36:310–22.
Mas-Moruno C, Fraioli R, Rechenmacher F, Neubauer S, Kapp TG, Kessler H. αvβ3-or α5β1-integrin-selective peptidomimetics for surface coating. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2016;55:7048–67.
Thorfve A, Lindahl C, Xia W, Igawa K, Lindahl A, Thomsen P, et al. Hydroxyapatite coating affects the Wnt signaling pathway during peri-implant healing in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2014;10:1451–62.
Rau JV, Cacciotti I, Laureti S, Fosca M, Varvaro G, Latini A. Bioactive, nanostructured Si-substituted hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium prepared by pulsed laser deposition. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103:1621–31.
Tao ZS, Zhou WS, He XW, Liu W, Bai BL, Zhou Q, et al. Acomparative study of zinc, magnesium, strontium-incorporated hydroxyapatite-coated titanium implants for osseointegration of osteopenic rats. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;62:226–32.
Shi LY, Wang A, Zang FZ, Wang JX, Pan XW, Chen HJ. Tantalum-coated pedicle screws enhance implant integration. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2017;160:22–32.
Frandsen CJ, Brammer KS, Noh K, Johnston G, Jin S. Tantalum coating on TiO2 nanotubes induces superior rate of matrix mineralization and osteofunctionality in human osteoblasts. Mater Sci Eng C. 2014;37:332–41.
Roy M, Balla VK, Bandyopadhyay A, Bose S. MgO doped tantalum coating on Ti: microstructural study and biocompatibility evaluation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4:4577–80.
Wang L, Hu X, Ma X, Ma Z, Zhang Y, Lu Y, et al. Promotion of osteointegration under diabetic conditions by tantalum coating-based surface modification on 3-dimensional printed porous titanium implants. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;148:440–52.
Costa DO, Prowse PD, Chrones T, Sims SM, Hamilton DW, Rizkalla AS, et al. The differential regulation of osteoblast and osteoclast activity by surface topography of hydroxyapatite coatings. Biomaterials. 2013;34:7215–26.
Ben-Nissan B, Choi AH, Roest R, Latella BA, Bendavid A. Adhesion of hydroxyapatite on titanium medical implants. In: Mucalo M, editor. Hydroxyapatite(HAp) for biomedical applications. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials; 2015. p. 21–52.
Tao ZS, Bai BL, He XW, Liu W, Li H, Zhou Q, et al. A comparative study of strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite coating on implant’s osseointegration for osteopenic rats. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2016;54:1959–68.
Vahabzadeh S, Roy M, Bandyopadhyay A, Bose S. Phase stability and biological property evaluation of plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings for orthopedic and dental applications. Acta Biomater. 2015;17:47–55.
Li X, Li Y, Liao Y, Li J, Zhang L, Hu J. The effect of magnesium-incorporated hydroxyapatite coating on titanium implant fixation in ovariectomized rats. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014;29:196–202.
Yang H, Yan X, Ling M, Xiong Z, Ou C, Lu W. In vitro corrosion and cytocompatibility properties of nano-whisker hydroxyapatite coating on magnesium alloy for bone tissue engineering applications. Int J Mol Sci 2015;16:6113–23.
Zhong Z, Ma J. Fabrication, characterization, and in vitro study of zinc substituted hydroxyapatite/silk fibroin composite coatings on titanium for biomedical applications. Biomater Appl 2017;32:399–409.
El-Wassefy NA, Reicha FM, Aref NS. Electro-chemical deposition of nano hydroxyapatite-zinc coating on titanium metal substrate. Int J Implant Dent 2017;3:39.
Lou W, Dong Y, Zhang H, Jin Y, Hu X, Ma J, et al. Preparation and characterization of lanthanum-incorporated hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium substrates. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16:21070–86.
Swain S, Rautray TR. Silver doped hydroxyapatite coatings by sacrificial anode deposition under magnetic field. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017;28:160.
Kang JI, Son MK, Choe HC. Hydroxyapatite coatings containing Mn and Si on the oxidized Ti-6Al-4V alloy for dental applications. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2018;18:833–6.
Ma J, Sun W, Gao F, Guo W, Wang Y, Li Z. Porous tantalum implant in treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head: still a viable option? Sci Rep. 2016;21:28227.
Olsen M, Lewis PM, Morrison Z, McKee MD, Waddell JP, Schemitsch EH. Total hip arthroplasty following failure of core decompression and tantalum rod implantation. Bone Jt J. 2016;98-B:1175–9.
Balla VK, Bodhak S, Bose S, Bandyopadhyay A. Porous tantalum structures for bone implants: fabrication, mechanical and in vitro biological properties. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:3349–59.
Davies JE, Mendes VC, Ko JC, Ajami E. Topographic scale-range synergy at the functional bone/implant interface. Biomaterials. 2014;35:25–35.
Davies JE, Ajami E, Moineddin R, Mendes VC. he roles of different scale ranges of surface implant topography on the stability of the bone/implant interface. Biomaterials. 2013;34:3535–46.
Razavi S, Karbasi S, Morshed M, Zarkesh Esfahani H, Golozar M, Vaezifar S. Cell Attachment and proliferation of human adipose-derived stem cells on PLGA/chitosan electrospun nano-biocomposite. Cell J. 2015;17:429–37.
Li G, Cao H, Zhang W, Ding X, Yang G, Qiao Y, et al. Enhanced osseointegration of hierarchical micro/nanotopographic titanium fabricated by microarc oxidation and electrochemical treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2016;8:3840–52.
Buijnsters JG, Zhong R, Tsyntsaru N, Celis JP. Surface wettability of macroporous anodized aluminum oxide. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5:3224–33.
Rakngarm Nimkerdphol A, Otsuka Y, Mutoh Y. Effect of dissolution/precipitation on the residual stress redistribution of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coating on titanium substrate in simulated body fluid (SBF). J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2014;36:98–108.
Baiula M, Galletti P, Martelli G, Soldati R, Belvisi L, Civera M, et al. New β-lactam derivatives modulate cell adhesion and signaling mediated by RGD-binding and leukocyte integrins. J Med Chem. 2016;59:9721–42.
Zhao L, Liu L, Wu Z, Zhang Y, Chu PK. Effects of micropitted/nanotubular titania topographies on bone mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation. Biomaterials. 2012;33:2629–41.
Ren D, Wei F, Hu L, Yang S, Wang C, Yuan X. Phosphorylation of Runx2, induced by cyclic mechanical tension via ERK1/2 pathway, contributes to osteodifferentiation of human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230:2426–36.
Wu M, Chen G, Li YP. TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast, skeletal development, and bone formation, homeostasis and disease. Bone Res. 2016;26:16009.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2015AA033502), Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (No. 7182125), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81271180) and Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (No. 2017000062586G232).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, RJ., Wang, X., He, HX. et al. Tantalum-incorporated hydroxyapatite coating on titanium implants: its mechanical and in vitro osteogenic properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 30, 111 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-019-6308-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-019-6308-9