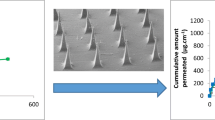
Abstract
Clobetasol propionate (CP) is a high-potency corticosteroid, representing the standard of care for the symptomatic treatment of different skin disorders as well as oral mucosal diseases. Several topical delivery systems are available for treating oral lesions, but the ideal one is still lacking. In this work, we propose a novel class of chitosan (CS) patches, loaded with CP, for the topical treatment of inflammatory chronic oral diseases. Chitosan patches have been fabricated via electrophoretic deposition (EPD), by using a one-pot approach in order to load controlled quantity of CP. Optimized structures showed a water uptake in the range of 200–360% and mechanical properties that allow the design of flexible patches in wet state (E = 0.6 MPa and σbr = 0.55 MPa). Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy was used for the evaluation of both loading and release profile of CP in CS patches. The CP loading has been tuned by adjusting CP concentration in deposition bath—in the range 0.002–0.12 mg cm−2—while releasing curves show an in vitro CP burst of about 80% in the first two hours. Overall, the obtained properties paved the way for the application of this new class of patches for the local oral release of CP.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campisi G, Giandalia G, De Caro V, Di Liberto C, Aricò P, Giannola LI. A new delivery system of clobetasol-17-propionate (lipid-loaded microspheres 0.025%) compared with a conventional formulation (lipophilic ointment in a hydrophilic phase 0.025%) in topical treatment of atrophic/erosive oral lichen planus. A Phase IV, rand. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:984–90. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.05943.x.
Hu FQ, Yuan H, Zhang HH, Fang M. Preparation of solid lipid nanoparticles with clobetasol propionate by a novel solvent diffusion method in aqueous system and physicochemical characterization. Int J Pharm. 2002;239:121–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(02)00081-9.
Cheng S, Kirtschig G, Cooper S, Silcocks P, Thornhill M, Murphy R. Interventions for erosive lichen planus affecting mucosal sites. In: R Murphy, editor. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2009. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD008092.
Agarwal S, Aggarwal S. Mucoadhesive polymeric platform for drug delivery: a comprehensive review. Curr Drug Deliv. 2015;12:139–56.
Gonzalez-Moles MA, Morales P, Rodriguez-Archilla A, Isabel IR-A, Gonzalez-Moles S. Treatment of severe chronic oral erosive lesions with clobetasol propionate in aqueous solution, Oral Surgery. Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontology. 2002;93:264–70. https://doi.org/10.1067/MOE.2002.120522.
Lo Muzio L, della Valle A, Mignogna MD, Pannone G, Bucci P, Bucci E, et al. The treatment of oral aphthous ulceration or erosive lichen planus with topical clobetasol propionate in three preparations: a clinical and pilot study on 54 patients. J Oral Pathol Med. 2001;30:611–7. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0714.2001.301006.x.
Lozada-Nur F, Miranda C, Maliksi R. Double-blind clinical trial of 0.05% clobetasol proprionate ointment in orabase and 0.05% fluocinonide ointment in orabase in the treatment of patients with oral vesiculoerosive diseases. Oral Surg, Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1994;77:598–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/0030-4220(94)90318-2.
Hu FQ, Jiang SP, Du YZ, Yuan H, Ye YQ, Zeng S. Preparation and characteristics of monostearin nanostructured lipid carriers. Int J Pharm. 2006;314:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.01.040.
Şenyiǧit T, Sonvico F, Barbieri S, Özer Ö, Santi P, Colombo P. Lecithin/chitosan nanoparticles of clobetasol-17-propionate capable of accumulation in pig skin. J Control Release. 2010;142:368–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.11.013.
Van Tuyl SAC, Slee PHTJ. Are the effects of local treatment with glucocorticoids only local? Neth J Med. 2002;60:130–2.
Decani S, Federighi V, Baruzzi E, Sardella A, Lodi G. Iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome and topical steroid therapy: case series and review of the literature. J Dermatol Treat. 2014;25:495–500. https://doi.org/10.3109/09546634.2012.755252.
Varoni EM, Molteni A, Sardella A, Carrassi A, Di Candia D, Gigli F. et al. Pharmacokinetics study about topical clobetasol on oral mucosa. J Oral Pathol Med. 2012;41:255–60.
Varoni EM, Altomare L, Cochis A, Ghalayaniesfahani A, Cigada A, Rimondini L, et al. Hierarchic micro-patterned porous scaffolds via electrochemical replica-deposition enhance neo-vascularization. Biomed Mater. 2016;00:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-6041/11/2/025018.
Yang C-C, Lin C-C, Yen S-K. Electrochemical deposition of vancomycin/chitosan composite on Ti alloy. J Electrochem Soc. 2011;158:E152–58. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.105112jes.
Pishbin F, Mouriño V, Flor S, Kreppel S, Salih V, Ryan, MP et al. Electrophoretic deposition of gentamicin-loaded bioactive glass/chitosan composite coatings for orthopaedic implants, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 6 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am5014166.
Simchi A, Pishbin F, Boccaccini AR. Electrophoretic deposition of chitosan. Mater Lett. 2009;63:2253–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.07.046.
Malafaya PB, Silva GA, Reis RL. Natural-origin polymers as carriers and scaffolds for biomolecules and cell delivery in tissue engineering applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59:207–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2007.03.012.
Xu R. Progress in nanoparticles characterization: sizing and zeta potential measurement. Particuology. 2008;6:112–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2007.12.002.
Delgado AV, González-Caballero F, Hunter RJ, Koopal LK, Lyklema J. Measurement and interpretation of electrokinetic phenomena. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2007;309:194–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2006.12.075.
Isfahani AG, Ghorbani M. Electrophoretic deposition of Ni/SiO2 nanocomposite coating: fabrication process and tribological and corrosion properties. J Nano Res. 2013;26:45–51. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/JNanoR.26.45.
Ghalayani Esfahani A, Lazazzera B, Draghi L, Farè S, Chiesa R, De Nardo L, et al. Bactericidal activity of Gallium-doped chitosan coatings against staphylococcal infection. J Appl Microbiol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14133.
Esfahani AG, Soleimanzade M, Campiglio CE, Federici A, Altomare L, Draghi L, et al. Hierarchical Microchannel Architecture in Chitosan/Bioactive Glass Scaffolds via Electrophoretic Deposition Positive-Replica. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36660.
Johnson NR, Wang Y. Drug delivery systems for wound healing. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2015;16:621–9.
Karki S, Kim H, Na S-J, Shin D, Jo K, Lee J. Thin films as an emerging platform for drug delivery. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2016;11:559–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AJPS.2016.05.004.
Needleman IG, Smales FC, Martin GP. An investigation of bioadhesion for periodontal and oral mucosal drug delivery. J Clin Periodontol. 1997;24:394–400. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.1997.tb00203.x.
Senel S, Ikinci G, Kaş S, Yousefi-Rad A, Sargon MF, Hincal AA. Chitosan films and hydrogels of chlorhexidine gluconate for oral mucosal delivery. Int J Pharm. 2000;193:197–203.
Altomare L, Draghi L, Chiesa R, De Nardo L. Morphology tuning of chitosan films via electrochemical deposition. Mater Lett. 2012;78:18–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.03.035.
Besra L, Liu M. A review on fundamentals and applications of electrophoretic deposition (EPD). Prog Mater Sci. 2007;52:1–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2006.07.001.
Runet SEB, Azinet LAB. Electromigration of chitosan D-glucosamine and oligomers in dilute aqueous solutions. J Agric Food Chem. 2006;54:6352–7. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf060165c.
Krueger HG, Knote A, Schindler U, Kern H. Composite ceramic metal coatings by means of combined electrophoretic deposition. Mater Sci. 2004;39:839–44.
Powers RW. The electrophoretic forming of beta‐alumina ceramic. J Electrochem Soc. 1975;122:490–500. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2134246.
Ferrari B, Sánchez-Herencia AJ, Moreno R. Aqueous electrophoretic deposition of AL2O3/ZrO2 layered ceramics. Mater Lett. 1998;35:370–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(97)00280-2.
Mathews T, Rabu N, Sellar J, Muddle B. Fabrication of La1−xSrxGa1−yMgyO3−(x + y)/2 thin films by electrophoretic deposition and its conductivity measurement. Solid State Ion. 2000;128:111–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(99)00308-2.
Shao Z, Vollrath F. The effect of solvents on the contraction and mechanical properties of spider silk. Polym (Guildf). 1999;40:1799–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(98)00266-3.
Bendak A, El-Marsafi SM. Effects of chemical modifications on polyester. Fibres, J Islam Acad Sci. 1991;4:275–84.
Vollrath F, Edmonds DT. Modulation of the mechanical properties of spider silk by coating with water. Nature. 1989;340:305–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/340305a0.
Lin LH, Edmonds DT, Vollrath F. Structural engineering of an orb-spider’s web. Nature. 1995;373:146–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/373146a0.
İkinci G, Şenel S, Akıncıbay H, Kaş S, Erciş S, Wilson C, et al. Effect of chitosan on a periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis. Int J Pharm. 2002;235:121–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(01)00974-7.
Acknowledgements
AGE and LDN would like to thank Dario Picenoni (RIP) for providing the morphology SEM micrographs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghalayani Esfahani, A., Altomare, L., Varoni, E.M. et al. Electrophoretic bottom up design of chitosan patches for topical drug delivery. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 30, 40 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-019-6242-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-019-6242-x