Abstract
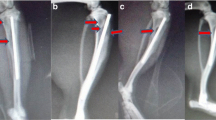
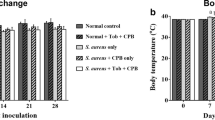
Pure magnesium (Mg) granules were implanted into the tibial medullary cavity of osteomyelitis modeled animals after debridement, and the animals without implant were taken as the control group. The antibacterial and osteogenic effects on bone tissue during Mg degradation were evaluated through detecting Mg ions, counting bacteria culture in peripheral blood, histology and iconography. The results showed that there was no significant difference for the concentration of serum Mg between the preoperative and postoperative animals within 5 weeks, maintaining in the normal range, and the number of bacteria in bone tissue of the Mg implant group was significantly lower than that of the control group. Mg implantation showed good biocompatibility no harmful to the liver, spleen, kidney and other organs in the modeled animals. In addition, the formation rate of new bone tissues around the implanted Mg was faster, indicating that the degradation of Mg could also promote the osteogenic process with good biocompatibility.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmidt-Rohlfing B, Lemmen SW, Pfeifer R, et al. Osteomyelitis in adults: diagnostic principles and therapeutic strategies. Unfallchirurg. 2012;115:55–66.
Geng F, Tan LL, Zhang BC, et al. Study on β-TCP coated porous Mg as a bone tissue engineering scaffold material. J Mater Sci Technol. 2009;25:123–9.
Ren YB, Huang JJ, Yang K, et al. Study of bio-corrosion of pure magnesium. Acta Metall Sin. 2005;41:1228–32.
Saris NE, Mervaala E, Karppanen H, et al. Magnesium: an update on physiological, clinical and analytical aspects. Clin Chim Acta. 2000;294:1–26.
Witte F, Kaese V, Haferkamp H, et al. In vivo corrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response. Biomaterials. 2005;26:3557–63.
Witte F, Ulrich H, Rudert M, et al. Biodegradable magnesium scaffolds part I: appropriate inflammatory response. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007;81:748–56.
Witte F, Ulrich H, Palm C, et al. Biodegradable magnesium scaffolds part II: peri-implant bone remodeling. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007;81:757–65.
Janning C, Willbold E, Vogt C, et al. Magnesium hydroxide temporarily enhancing osteoblast activity and decreasing the osteoclast number in peri-implant bone remodelling. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:l861–8.
Abed E, Moreau R. Importance of melastatin-like transient receptor potential 7 and magnesium in the stimulation of osteoblast proliferation and migration by platelet-derived growth factor. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009;297:C360–8.
Wolf FI, Cittadini A. Chemistry and biochemistry of magnesium. Mol Aspects Med. 2003;24:3–9.
Sacks FM, Willett WC, Smith A, et al. Effect on blood pressure of potassium, calcium and magnesium in women with low habitual intake. Hypertension. 1998;31:131–8.
Vormann J. Magnesium: nutrition and metabolism. Mol Aspects Med. 2003;24:27–37.
Gao JC, Wu S, Qiao LY, et al. Corrosion behavior of Mg and Mg-Zn alloys in simulated body fluid. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China. 2008;18:588–92.
Xin YC, Jiang J, Huo KF, et al. Corrosion resistance and cytocompatibility of biodegradable surgical magnesium alloy coated with hydrogenated amorphous silicon. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2009;89:717–26.
Slottow TL, Pakala R, Okabe T, et al. Optical coherence tomography and intravascular ultrasound imaging of bioabsorbable magnesium stent degradation in porcine coronary arteries. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2008;9:248–54.
Robinson DA, Griffith RW, Shechtman D, et al. In vitro antibacterial properties of magnesium metal against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:1869–77.
Ren Ling, Lin Xiao, Tan Lili, et al. Effect of surface coating on antibacterial behavior of magnesium based metals. Mater Lett. 2011;65:3509–11.
White D. Membrane bioenergetics: the proton potential. In: The physiology and biochemistry of prokaryotes, 3rd ed. New York: Oxford University Press; 2007.p.83–119.
Padan E, Bibi E, Ito M, et al. Alkaline pH homeostasis in bacteria: new insights. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1717:67–88.
Hallab NJ, Vermes C, Messina C, et al. Concentration- and composition-dependent effects of metal ions on human MG-63 osteoblasts. J Biomed Res. 2002;A60:420–33.
Kuwahara H, Al-Abdullat Y, Mazald N, Tsutsumi S, et al. Precipitation of magnesium apatite on pure magnesium surface during immersing in Hank’s solution. Materials Transactions. 2001;42:1317–21.
Witte F, Feyerabend F, Maier P, et al. Biodegradable magnesium-hydroxyapatite metal matrix composites. Biomaterials. 2007;28:2163–74.
Chen ZH, Yan HG, Chen JH, et al. Magnesium Alloys[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press; 2004. p. 386.
Mader JT, Stevens CM, Stevens JH, et al. Treatment of experimental osteomyelitis with a fibrin sealant antibiotic implant. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;403:58–72.
Minpeng Lu, Jiang Dianming, Quan Zhengxue, et al. The establishment of the rabbit tibia chronic osteomyelitis animal model. Chin J Exp Surg. 2010;27:664–6.
Liu Feng, Wang Baogen, Zhu Shutao, et al. Experimental animals and trace elements I: Determination of the six elements in the New Zealand white rabbit serum. Shanghai Lab Anim Sci. 1987;7:234.
Zhang Guangdao, Huang Jingjing, Yang Ke, et al. Experimental study of in vivo implantation of a magnesium alloy at early stage. Acta Metall Sin. 2007;43:1186–90.
Chen HW, Huang HB, Zhao GS, et al. Treatment of chronic osteomyelitis with antibiotic-loaded calcium phosphate cement. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2008;21:79–81.
Tang H, Xu Y, Li G, et al. Treatment of chronic osteomyelitis of rabbit with liposomal gentamicin-impregnated allogeneic cortical bone. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010;24:482–6.
Shi P, Zuo Y, Li X, et al. Gentamicin-impregnated chitosan/nanohydroxyapatite/ethyl cellulose microspheres granules for chronic osteomyelitis therapy. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;93:1020–31.
Jiang JL, Li YF, Fang TL, et al. Vancomycin-loaded nano-hydroxyapatite pellets to treat MRSA-induced chronic osteomyelitis with bone defect in rabbits. Inflamm Res. 2012;61:207–15.
Chen D, Harris MA, Rossini G, et al. Bone morphogentic protein 2 enhances BMP-3, BMP-4, and bone cell differentiation maker gene expression during the induction of mineralized bone matrix formation in cultures of fetal rat calvarial osteoblasts. Calcif Tissue Int. 1997;60:283–90.
Urist MR, Strates BS. The classic: bone morphogenetic protein. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:3051–62.
Chen S, Guttridge DC, Tang E, et al. Suppression of Tumor Necrosis Factor-mediated Apoptosis by Nuclear Factor kB-independent Bone Morphogenetic Protein/Smad Signaling. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:39259–63.
Liu Z, Shi W, Ji X, et al. Molecules mimicking Smad1 interacting with Hox stimulate bone formation. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:11313–9.
Tachi K, Takami M, Sato H, et al. Enhancement of bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced ectopic bone formation by transforming growth factor-β1. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17:597–606.
Zhang E, Xu L, Yu G, et al. In vivo evaluation of biodegradable magnesium alloy bone implant in the first 6 months implantation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;90:882–93.
Chen D, He Y, Tao H, et al. Biocompatibility of magnesium-zinc alloy in biodegradable orthopedic implants. Int J Mol Med. 2011;28:343–8.
Kraus T, Fischerauer SF, Hänzi AC, et al. Magnesium alloys for temporary implants in osteosynthesis: in vivo studies of their degradation and interaction with bone. Acta Biomater. 2012;8:1230–8.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by funds from Higher Excellent Talents Support Program of Liaoning Province (NO. LJQ2011089) and a National Basic Research Program (No.2012CB619101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, J., Ren, L., Yuan, Y. et al. Short-term effect of magnesium implantation on the osteomyelitis modeled animals induced by Staphylococcus aureus . J Mater Sci: Mater Med 24, 2405–2416 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-013-4982-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-013-4982-6