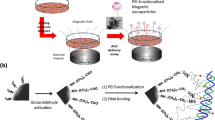
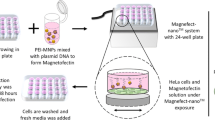
Abstract
Polyethylenimine (PEI) functionalized magnetic nanoparticles were synthesized as a potential non-viral vector for gene delivery. The nanoparticles could provide the magnetic-targeting, and the cationic polymer PEI could condense DNA and avoid in vitro barriers. The magnetic nanoparticles were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray powder diffraction, dynamic light scattering measurements, transmission electron microscopy, vibrating sample magnetometer and atomic force microscopy. Agarose gel electrophoresis was used to asses DNA binding and perform a DNase I protection assay. The Alamar blue assay was used to evaluate negative effects on the metabolic activity of cells incubated with PEI modified magnetic nanoparticles and their complexes with DNA both in the presence or absence of an external magnetic field. Flow cytometry and fluorescent microscopy were also performed to investigate the transfection efficiency of the DNA-loaded magnetic nanoparticles in A549 and B16-F10 tumor cells with (+M) or without (−M) the magnetic field. The in vitro transfection efficiency of magnetic nanoparticles was improved obviously in a permanent magnetic field. Therefore, the magnetic nanoparticles show considerable potential as nanocarriers for gene delivery.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yao Z, Fenoglio S, Gao DC, Camiolo M, Stiles B, Lindsted T, Schlederer M, Johns C, Altorki N, Mittal V. TGF-β IL-6 axis mediates selective and adaptive mechanisms of resistance to molecular targeted therapy in lung cancer. PANS. 2010;107:15535–40.
Day ES, Morton JG, West JL. Nanoparticles for thermal cancer therapy. J Biomech Eng. 2009;131:074001.
Redd WH, Montgomery GH, DuHamel KN. Behavioral intervention for cancer treatment side effects. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:810.
Lungwitz U, Breunig M, Blunk T, Gopferich A. Polyethylenimine-based non-viral gene delivery systems. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2005;60:247–66.
Godbey W, Wu KK, Mikos AG. Poly (ethylenimine) and its role in gene delivery. J Controlled Release. 1999;60:149–60.
Thomas CE, Ehrhardt A, Kay MA. Progress and problems with the use of viral vectors for gene therapy. Nat Rev Genet. 2003;4:346–58.
Jackson DA, Juranek S, Lipps HJ. Designing nonviral vectors for efficient gene transfer and long-term gene expression. Mol Ther. 2006;14:613–26.
Floch V, Loisel S, Guenin E, Hervé AC, Clément JC, Yaouanc JJ, Abbayes H, Férec C. Cation substitution in cationic phosphonolipids: a new concept to improve transfection activity and decrease cellular toxicity. J Med Chem. 2000;43:4617–28.
Floch V, Legros N, Loisel S, Guillaume C, Guilbot J, Benvegnu T, Ferrieres V, Plusquellec D, Ferec C. New biocompatible cationic amphiphiles derivative from glycine betaine: A novel family of efficient nonviral gene transfer agents* 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;251:360–5.
Hobel S, Prinz R, Malek A, Urban-Klein B, Sitterberg J, Bakowsky U, Czubayko F, Aigner A. Polyethylenimine PEI F25-LMW allows the long-term storage of frozen complexes as fully active reagents in siRNA-mediated gene targeting and DNA delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;70:29–41.
Jiang X, Lok MC, Hennink WE. Degradable-brushed pHEMA–pDMAEMA synthesized via ATRP and click chemistry for gene delivery. Bioconjugate Chem. 2007;18:2077–84.
Lin C, Zhong Z, Lok MC, Jiang X, Hennink WE, Feijen J, Engbersen JFJ. Novel bioreducible poly (amido amine)s for highly efficient gene delivery. Bioconjugate Chem. 2007;18:138–45.
Fukushima S, Miyata K, Nishiyama N, Kanayama N, Yamasaki Y, Kataoka K. PEGylated polyplex micelles from triblock catiomers with spatially ordered layering of condensed pDNA and buffering units for enhanced intracellular gene delivery. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:2810–1.
Morris MC, Chaloin L, Méry J, Heitz F, Divita G. A novel potent strategy for gene delivery using a single peptide vector as a carrier. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27:3510–7.
Morishita N, Nakagami H, Morishita R, Takeda S, Mishima F. Magnetic nanoparticles with surface modification enhanced gene delivery of HVJ-E vector. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;334:1121–6.
Liu Z, Winters M, Holodniy M, Dai H. siRNA delivery into human T cells and primary cells with carbon-nanotube transporters. Angew Chem. 2007;119:2069–73.
Srinivasan C, Lee J, Papadimitrakopoulos F, Silbart LK, Zhao M, Burgess DJ. Labeling and intracellular tracking of functionally active plasmid DNA with semiconductor quantum dots. Mol Ther. 2006;14:192–201.
Christou P, McCabe DE, Martinell BJ, Swain WF. Soybean genetic engineering-commercial production of transgenic plants. Trends Biotechnol. 1990;8:145–51.
Olton D, Li J, Wilson ME, Rogers T, Close J, Huang L, Kumta PN, Sfeir C. Nanostructured calcium phosphates (NanoCaPs) for non-viral gene delivery: influence of the synthesis parameters on transfection efficiency. Biomaterials. 2007;28:1267–79.
Yang J, Lee ES, Noh MY, Koh SH, Lim EK, Yoo A. Ambidextrous magnetic nanovectors for synchronous gene transfection and labeling of human MSCs. Biomaterials. 2011;32:6174–82.
Liu Y, Chen Z, Gu N, Wang J. Effects of DMSA-coated Fe (3) O (4) magnetic nanoparticles on global gene expression of mouse macrophage RAW264. 7 cells. Toxicol Lett. 2011;28:6174–82.
Lei Y, Rahim M, Ng Q, Segura T. Hyaluronic acid and fibrin hydrogels with concentrated DNA/PEI polyplexes for local gene delivery. J Controlled Release. 2011;153:255–61.
Sun K, Wang J, Zhang J, Hua M, Liu C, Chen T. Dextran-g-PEI nanoparticles as a carrier for co-delivery of adriamycin and plasmid into osteosarcoma cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2011;49:173–80.
Neu M, Fischer D, Kissel T. Recent advances in rational gene transfer vector design based on poly (ethylene imine) and its derivatives. J Gene Med. 2005;5:992–1009.
Ragusa A, García I, Penadés S. Nanoparticles as nonviral gene delivery vectors. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2007;6:319–30.
Lübbe AS, Alexiou C, Bergemann C. Clinical applications of magnetic drug targeting. J Surg Res. 2001;95:200–6.
Bae KH, Choi SH, Park SY, Lee Y, Park TG. Thermosensitive pluronic micelles stabilized by shell cross-linking with gold nanoparticles. Langmuir. 2006;22:6380–4.
Lu J, Ma S, Sun J, Xia C, Liu C, Wang Z, Zhao X, Gao F, Gong Q, Song B. Manganese ferrite nanoparticle micellar nanocomposites as MRI contrast agent for liver imaging. Biomaterials. 2009;30:2919–28.
Lee PW, Hsu SH, Wang JJ, Tsai JS, Lin KJ, Wey SP, Chen FR, Lai CH, Yen TC. Sung H W: The characteristics, biodistribution, magnetic resonance imaging and biodegradability of superparamagnetic core-shell nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2010;31:1316–24.
Chen D, Jiang M, Li N, Gu H, Xu Q, Ge J, Xia X, Lu J. Modification of magnetic silica/iron oxide nanocomposites with fluorescent polymethacrylic acid for cancer targeting and drug delivery. J Mater Chem. 2010;20:6422–9.
Hong R, Fischer NO, Emrick T, Rotello VM. Surface PEGylation and ligand exchange chemistry of FePt nanoparticles for biological applications. Chem Mater. 2005;17:4617–21.
Huang C, Zhou YB, Jin Y, Zhou X, Tang ZM, Guo X, Zhou SB. Preparation and characterization of temperature-responsive and magnetic nanomicelles. J Mater Chem. 2011;21:5660–7.
Sun J, Zhou SB, Hou P, Yang Y, Weng J, Li XH, Li MY. Synthesis and characterization of biocompatible Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007;80:333–41.
Kobayashi M, Ryosuke M, Hideyuki O, Atsushi T. Precise surface structure control of inorganic solid and metal oxide nanoparticles through surface-initiated radical polymerization. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2006;7:617–28.
Wang L, Neoh KN, Kang ET, Shuter B, Wang SC. Biodegradable magnetic-fluorescent magnetite/poly(DL-lactic acid-co-a, b-malic acid) composite nanoparticles for stem cell labeling. Biomaterials. 2010;31:3502–11.
Kim MS, Chen YF, Liu YC, Peng XG. Super-stable, high-quality Fe3O4 dendron-nanocrystals dispersible in both organic and aqueous solutions. Adv Mater. 2005;17:1429–32.
Lee JH, Lee KR, Moon SH, Lee YH, Park TG, Cheon JW. All-in-one target-cell-specific magnetic nanoparticles for simultaneous molecular imaging and siRNA delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2009;121:4238–43.
Shi S, Guo QF, Kan B, Fu SZ, Wang XH, Gong CY, Deng HX, Luo F, Zhao X, Wei YQ. A novel poly (ε-caprolactone)-pluronic-poly (ε-caprolactone) grafted polyethyleneimine (PCFC-g-PEI), Part 1, synthesis, cytotoxicity, and in vitro transfection study. BMC Biotechnol. 2009;9:65.
Lu X, Wang QQ, Xu FJ, Tang GP, Yang WT. A cationic prodrug/therapeutic gene nanocomplex for the synergistic treatment of tumors. Biomaterials. 2011;32:4849–56.
Mikhaylova M, Kim DK, Bobrysheva N, Osmolowsky M, Semenov V. Superparamagnetism of magnetite nanoparticles: dependence on surface modification. Langmuir. 2004;20:2472–7.
Huang FW, Wang HY, Li C, Wang HF, Sun YX, Feng J, Zhang XZ, Zhuo RX. PEGylated PEI-based biodegradable polymers as non-viral gene vectors. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:4285–95.
Xenariou S, Griesenbach U, Ferrari S, Dean P, Scheule R, Cheng S, Geddes D, Plank C, Alton E. Using magnetic forces to enhance non-viral gene transfer to airway epithelium in vivo. Gene Ther. 2006;13:1545–52.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2012CB933602), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30970723 and No. 51173150), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (SWJTU11ZT10) and the Open Research Fund of the Key Laboratory of Biotherapy, West China Hospital, West China Medicine School, Sichuan University under Grant No. SKLB200907.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Tang, Z., Shi, C. et al. Polyethylenimine functionalized magnetic nanoparticles as a potential non-viral vector for gene delivery. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 23, 2697–2708 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-012-4720-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-012-4720-5