Abstract
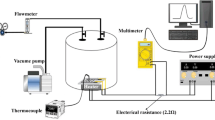
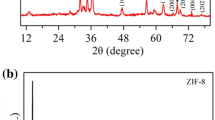
This paper demonstrated a SO2 sensor based on metal organic frameworks (MOFs)-derived titanium dioxide (TiO2)/reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanocomposite. The MOFs-derived TiO2/rGO film was deposited on an epoxy substrate with interdigital electrodes and served as sensing material. The properties of MOFs TiO2/rGO nanocomposite in terms of microstructure, elementary composition and morphology were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The SO2-sensing properties of the MOFs TiO2/rGO film sensor were measured at room temperature. The results illustrate that the MOFs-derived TiO2/rGO sensor exhibits a great sensing performance toward SO2 gas, including high response value, quick response/recovery time, and outstanding stability. These results render the MOFs TiO2/rGO nanocomposite an efficient sensing material for constructing high-performance SO2 sensor. Finally, the mechanism of the enhanced SO2 sensing properties was attributed to the unique nanostructure and the large specific surface area of MOFs TiO2/rGO nanocomposite.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.X. Zhong, Y.B. Shen, S.K. Zhao, X.X. Chen, C. Han, D.Z. Wei, P. Fang, D. Meng, SO2 sensing properties of SnO2 nanowires grown on a novel diatomite-based porous substrate. Ceram. Int. 45, 2556–2565 (2019)
M.A.H. Khan, M.V. Rao, Q.L. Li, Recent advances in electrochemical sensors for detecting toxic gases: NO2, SO2 and H2S. Sensors 19, 905 (2019)
D. Zhang, J. Wu, P. Li, Y. Cao, Room-temperature SO2 gas sensing properties based on metal-doped MoS2 nanoflower: an experimental and density functional theory investigation. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 20666–20677 (2017)
A. Queralto, D. Graf, R. Frohnhoven, T. Fischer, H. Vanrompay, S. Bals, A. Bartasyte, S. Mathur, LaFeO3 Nanofibers for high detection of sulfur-containing gases. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 6023–6032 (2019)
L.B. An, X.T. Jia, Y. Liu, Adsorption of SO2 molecules on Fe-doped carbon nanotubes: the first principles study. Adsorption 25, 217–224 (2019)
M.R. Tchalala, P.M. Bhatt, K.N. Chappanda, S.R. Tavares, K. Adil, Y. Belmabkhout, A. Shkurenko, A. Cadiau, N. Heymans, G.D. Weireld, G. Maurin, K.N. Salama, M. Eddaoudi, Fluorinated MOF platform for selective removal and sensing of SO2 from flue gas and air. Nat. Commun. 10, 1328 (2019)
Q. Zhang, H. Liu, X.J. Zhang, H.X. Xing, H.Y. Hu, H. Yao, Novel utilization of conditioner CaO for gas pollutants control during co-combustion of sludge and coal. Fuel 206, 541–545 (2017)
J.N. Yun, C. Zhu, Q. Wang, Q.L. Hu, G. Yang, Catalytic conversions of atmospheric sulfur dioxide and formation of acid rain over mineral dusts: molecular oxygen as the oxygen source. Chemosphere 217, 18–25 (2019)
J.N. Yun, C. Zhu, Q. Wang, Q.L. Hu, G. Yang, Strong affinity of mineral dusts for sulfur dioxide and catalytic mechanisms towards acid rain formation. Catal. Commun. 114, 79–83 (2018)
K.K. Liu, C.X. Shan, H.Z. Liu, Q. Lou, D.Z. Shen, Fluorescence of ZnO/carbon mixture and application in acid rain detection. RSC Adv. 7, 1841–1846 (2017)
X. Liang, T. Zhong, B. Quan, B. Wang, H. Guan, Solid-state potentiometric SO2 sensor combining NASICON with V2O5-doped TiO2 electrode. Sens. Actuators, B 134, 25–30 (2008)
S. Gersen, M.V. Essen, P. Visser, M. Ahmad, A. Mokhov, A. Sepman, R. Alberts, A. Douma, H. Levinsky, Detection of H2S, SO2 and NO2 in CO2 at pressures ranging from 1 to 40 bar by using broadband absorption spectroscopy in the UV/VIS range. Energy Procedia 63, 2570–2582 (2014)
Y. Uneme, S. Tamura, N. Imanaka, Sulfur dioxide gas sensor based on Zr4+ and O2− ion conducting solid electrolytes with lanthanum oxysulfate as an auxiliary sensing electrode. Sens. Actuators, B 177, 529–534 (2013)
W. Yang, P. Wan, X.D. Zhou, J.M. Hu, Y.F. Guan, L. Feng, Self-assembled In2O3 truncated octahedron string and its sensing properties for formaldehyde. Sens. Actuators, B 201, 228–233 (2014)
S. Zhang, P. Song, J. Li, J. Zhang, Z.X. Yang, Q. Wang, Facile approach to prepare hierarchical Au-loaded In2O3 porous nanocubes and their enhanced sensing performance towards formaldehyde. Sens. Actuators, B 241, 1130–1138 (2017)
C. Zhao, H.M. Gong, W.Z. Lan, R. Ramachandran, H. Xu, S. Liu, F. Wang, Facile synthesis of SnO2 hierarchical porous nanosheets from graphene oxide sacrificial scaffolds for high-performance gas sensors. Sens. Actuators, B 258, 492–500 (2018)
P. Tyagi, A. Sharma, M. Tomar, V. Gupta, SnO2 thin film sensor having NiO catalyst for detection of SO2 gas with improved response characteristics. Sens. Actuators, B 248, 998–1005 (2017)
R. Godbole, V.P. Godbole, S. Bhagwat, Surface morphology dependent tungsten oxide thin films as toxic gas sensor. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 63, 212–219 (2017)
Y.Y. Liu, X.Y. Xu, Y. Chen, Y. Zhang, X.H. Gao, P.C. Xu, X.X. Li, J.H. Fang, W.J. Wen, An integrated micro-chip with Ru/Al2O3/ZnO as sensing material for SO2 detection. Sens. Actuators, B 262, 26–34 (2018)
D. Zhang, M. Pang, J. Wu, Y. Cao, Experimental and density functional theory investigation of Pt-loaded titanium dioxide/molybdenum disulfide nanohybrid for SO2 gas sensing application. New J. Chem. 43, 4900–4907 (2019)
Z.Y. Qin, C. Ouyang, J. Zhang, L. Wan, S.M. Wang, C.S. Xie, D.W. Zeng, 2D WS2 nanosheets with TiO2 quantum dots decoration for high-performance ammonia gas sensing at room temperature. Sens. Actuators, B 253, 1034–1042 (2017)
F. Yakuphanoglu, Semiconducting and quartz microbalance (QCM) humidity sensor properties of TiO2 by sol gel calcination method. Solid State Sci. 14, 673–676 (2012)
F. Fedorov, M. Vasilkov, A. Lashkov, A. Varezhnikov, D. Fuchs, C. Kubel, M. Bruns, M. Sommer, V. Sysoev, Toward new gas-analytical multisensor chips based on titanium oxide nanotube array. Sci. Rep. 7, 9732 (2017)
N. Huang, Y.N. Xie, B. Sebo, Y.M. Liu, X.H. Sun, T. Peng, W.W. Sun, C.H. Bu, S.S. Guo, X.Z. Zhao, Morphology transformations in tetrabutyl titanate–acetic acid system and sub-micron/micron hierarchical TiO2 for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Power Sources 242, 848–854 (2013)
D.Z. Zhang, J.J. Liu, C.X. Jiang, P. Li, Y. Sun, High-performance sulfur dioxide sensing properties of layer-by-layer self-assembled titania-modified graphene hybrid nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators, B 245, 560–567 (2017)
J. Nisar, Z. Topalian, A.D. Sarkar, L. Osterlund, R. Ahuja, TiO2-based gas sensor: a possible application to SO2. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 5, 8516–8522 (2013)
X. Zhang, J. Zhang, Y. Jia, P. Xiao, J. Tang, TiO2 nanotube array sensor for detecting the SF6 decomposition product SO2. Sensors 12, 3302–3313 (2012)
D. Morris, R.G. Egdell, Application of V-doped TiO2 as a sensor for detection of SO2. J. Mater. Chem. 11, 3207–3210 (2001)
Z. Xiu, M.H. Alfaruqi, J. Gim, J. Song, S. Kim, T.V. Thi, P.T. Duong, J.P. Baboo, V. Mathew, J. Kim, Hierarchical porous anatase TiO2 derived from a titanium metal–organic framework as a superior anode material for lithium ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 61, 12274–12277 (2015)
C.X. Li, Z.Q. Li, Q. Li, Z.W. Zhang, S.H. Dong, L.W. Yin, MOFs derived hierarchically porous TiO2 as effective chemical and physical immobilizer for sulfur species as cathodes for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries. Electrochim. Acta 215, 689–698 (2016)
X.J. Zhang, M. Wang, G. Zhu, D.S. Lia, D. Yana, T. Lu, L.K. Pan, Porous cake-like TiO2 derived from metal-organic frameworks as superior anode material for sodium ion batteries. Ceram. Int. 43, 2398–2402 (2017)
D.Z. Zhang, H.Y. Chang, L. Peng, Fabrication and characterization of an ultrasensitive ultrasensitive humidity sensor based on metal oxide/graphene hybrid nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators, B 225, 233–240 (2016)
D.Z. Zhang, C.X. Jiang, X.Y. Zhou, Fabrication of Pd-decorated TiO2/MoS2 ternary nanocomposite for enhanced benzene gas sensing performance at room temperature. Talanta 182, 324–332 (2018)
P.Y. Wang, J.W. Lang, D.X. Liu, X.B. Yan, TiO2 embedded in carbon submicron-tablets: synthesis from a metal–organic framework precursor and application as a superior anode in lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 51, 11370–11373 (2015)
H.N. Ma, L.M. Yu, X. Yuan, Y. Li, C. Li, M.L. Yin, X.H. Fan, Room temperature photoelectric NO2 gas sensor based on direct growth of walnut-like In2O3 nanostructures. J. Alloys Compd. 782, 1121–1126 (2019)
K.S. Huang, C.X. Yan, K. Wang, Y.P. Zhang, Z.C. Ju, Phases hybriding and graphene-like TiO2 for high-performance Na-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 687, 683–688 (2016)
J.H. Kirn, W.I. Cho, H.G. Jung, S.H. Oh, K.Y. Chung, W. Cho, I.H. Oh, I.W. Nah, Anatase TiO2-reduced graphene oxide nanostructures with high-rate sodium storage performance. J. Alloys Compd. 690, 390–396 (2017)
D.Z. Zhang, T. Jun, X.B. Kai, Humidity-sensing properties of chemically reduced graphene oxide/polymer nanocomposite film sensor based on layer-by-layer nano self-assembly. Sens. Actuators, B 197, 66–72 (2014)
Z.L. Xiu, M.H. Alfaruqi, J. Gim, J.J. Song, S.J. Kim, T.V. Thi, P.T. Duong, J.P. Baboo, V. Mathew, J. Kim, Hierarchical porous anatase TiO2 derived from a titanium metal–organic framework as a superior anode material for lithium ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 51, 12274–12277 (2015)
Z. Xiu, M.H. Alfaruqi, J. Gim, J. Song, S. Kim, P.T. Duong, J.P. Baboo, V. Mathew, J. Kim, MOF-derived mesoporous anatase TiO2 as anode material for lithium-ion batteries with high rate capability and long cycle stability. J. Alloys Compd. 674, 174–178 (2016)
P. Hidalgo, R.H. Castro, D. Gouvea, A.C. Coelho, Surface segregation and consequent SO2 sensor response in SnO2-NiO. Chem. Mater. 17, 4149–4153 (2005)
S. Das, S. Rana, S.M. Mursalin, P. Rana, A. Sen, Sonochemically prepared nanosized BiFeO3 as novel SO2 sensor. Sens. Actuators, B 218, 122–127 (2015)
A. Marikutsa, M. Rumyantseva, A. Baranchikov, A. Gaskov, Nanocrystalline BaSnO3 as an alternative gas sensor material: surface reactivity and high sensitivity to SO2. Materials 8, 6437–6454 (2015)
N. Izu, G. Hagen, D. Schonauer, U. Roder-Roith, R. Moos, Application of V2O5/WO3/TiO2 for resistive-type SO2 sensors. Sensors 11, 2982–2991 (2011)
A. Stankova, X. Vilanova, J. Calderer, E. Llobet, P. Ivanov, I. Gracia, C. Cane, X. Correig, Detection of SO2 and H2S in CO2 stream by means of WO3-based micro-hotplate sensors. Sens. Actuators, B 102, 219–225 (2004)
B. Bhowmik, K. Dutta, A. Hazra, P. Bhattacharyya, Low temperature acetone detection by p-type nano-titania thin film: equivalent circuit model and sensing mechanism. Solid State Electron. 99, 84–92 (2014)
S.L. Bai, L. Du, J.H. Sun, R.X. Luo, D.Q. Li, A. Chen, C.C. Liu, Preparation of reduced graphene oxide/Co3O4 composites and sensing performance to toluene at low temperature. RSC Adv. 6, 60109–60116 (2016)
D. Zhang, J. Liu, B. Xia, Quantitative detection of formaldehyde and ammonia gas via metal oxide-modified graphene-based sensor array combining with neural network model. Sens. Actuators, B 240, 55–65 (2017)
D.Z. Zhang, C.X. Jiang, J.J. Liu, Y.H. Cao, Carbon monoxide gas sensing at room temperature using copper oxide-decorated graphene hybrid nanocomposite prepared by layer-by-layer self-assembly. Sens. Actuators, B 247, 875–882 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51777215), the Key Research & Development Plan Project of Shandong Province (Grant No. 2018GSF117002), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (Grant No. 18CX07010A), the Open Funds of National Engineering Laboratory for Mobile Source Emission Control Technology (Grant No. NELMS2017B03), and the Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Marine Spill Oil Identification and Damage Assessment Technology, State Oceanic Administration of China (Grant No. 201801).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Wu, D., Zong, X. et al. Enhanced SO2 gas sensing properties of metal organic frameworks-derived titanium dioxide/reduced graphene oxide nanostructure. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 11070–11078 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01449-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01449-z