Abstract
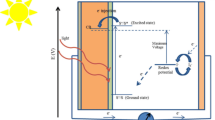
In our present study, firstly, Cd1−xZnxS (x = 0.25, 0.5, 1, 3 and 5%) quantum dots were synthesized at room temperature by the chemical precipitation technique. 1-thioglycerol was used as a capping agent to avoid any agglomeration. The incident photons to current efficiency measurements were carried out to determine Zn concentration in the Cd1−xZnxS quantum dots. Cd1−xZnxS (x = 3%) quantum dots showed the highest efficiency of quantum dot sensitized solar cells compare to other Zn concentrations. Secondly, after the determination of the optimum Zn content in the Cd1−xZnxS quantum dots, Mn (0.25, 0.5, 1, 3 and 5%): Cd1−xZnxS (x = 3%) quantum dots were synthesized at room temperature by same technique, then the incident photons to current efficiency measurements were performed to determine the optimum Mn concentration in the Mn (0.25, 0.5, 1, 3 and 5%): Cd1−xZnxS (x = 3%) quantum dots. It was found that Mn (3%): Cd1−xZnxS (x = 3%) quantum dots have the highest incident photons to current efficiency value compare to other Mn concentrations. Finally, structural, elemental and optical properties of Cd1−xZnxS (x = 3%) and Mn (3%): Cd1−xZnxS (x = 3%) quantum dots-have the highest incident photons to current efficiency value in their category-have been investigated. The effect of Mn on the photovoltaic properties of Mn (0.25, 0.5, 1, 3 and 5%): Cd1−xZnxS (x = 3%) quantum dots have been reported for the first time in this study and our study suggests that Mn (3%): Cd1−xZnxS (x = 3%) quantum dots can be used unique materials to enhance performance of quantum dot sensitized solar cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Abraham, A. Rufus, C. Unni, D. Philip, Nanostructured ZnO with bio-capping for nano fluid and natural due based solar cell applications. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 16527 (2017)
R. Kisslinger, W. Hua, K. Shankar, Bulk heterojunction solar cells based on blends of conjugated polymers with II–VI and IV–VI inorganic semiconductor quantum dots. Polymers 9, 35 (2017)
J. Owen, L. Brus, Chemical synthesis and applications of colloidal semiconductor quantum dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 10939 (2017)
V. Kumar, S. Junega, S.K. Sharma, V. Singh, T.P. Sharma, Optimization of sintering temperature in CdZnS films using reflection spectroscopy. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 7, 399 (2010)
D. Ompong, Investigating the optical properties of Cd1–xZnxS thin films deposited by the dip technique, M.Sc Thesis Kwamme Nkrumah University Science of Technology (2010)
G. Hodes, Chemical Solution Deposition of Semiconductor Films. (New York, Marcel Dekker Inc., 2002) p. 3
N. Gaewdang, T. Gaewdang, Investigations on chemically deposited Cd1–xZnxS thin films with low Zn content. Mater. Lett. 59, 3577 (2005)
S. Herodotou, R.E. Treharne, K. Durose, G.J. Tatlock, R.J. Potter, The effects of Zr doping on the optical, electrical and microstructural properties of thin ZnO films deposited by atomic layer deposition. Materials (Basel) 8, 7230 (2015)
S. Horoz, O. Sahin, Investigations of structural, optical and photovoltaic properties of Fe-alloyed ZnS quantum dots. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 9559 (2017)
R.N. Bhargava, D. Gallagher, X. Hong, A. Nurmikko, Optical properties of manganese-alloyed nanocrystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 416 (1994)
S. A.Nag, S.S. Sapra, A. Gupta, A. Prakash, N. Ghangrekar, D.D. Periasamy, Sarma, Luminescence in Mn-alloyed CdS nanocrystals. Bull. Mater. Sci. 31, 561 (2008)
S.M. Liu, F.Q. Liu, H.Q. Guo, Z.H. Zhang, Z.G. Wang, Surface states induced photoluminescence from Mn2+ alloyed CdS nanoparticles. Solid State Commun. 115, 615 (2002)
P.K. Santra, P.V. Kamat, Mn-alloyed quantum dot sensitized solar cells: a strategy to boost efficiency over 5%. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 2508 (2012)
S. Horoz, Q. Dai, F.S. Maloney, B. Yakami, J. Pikal, X. Zhang, W. Wang, J. Tang, Absorption induced by Mn doping of ZnS for improved sensitized quantum-dot solar cells. Phys. Rev. Appl. 3, 024011 (2016)
H. A.Pan, R. Yang, R. Liu, B. Yu, Z. Zhou, Wang, Color-tunable photoluminescence of alloyed CdSxSe1–x nanobelts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 15692 (2005)
L.M. Yu, C.C. Zhu, X.H. Fan, L.J. Qi, W. Yang, CdS/SiO2 nanowire arrays and CdS nanobelt synthesized by thermal evaporation. J. Zhejing Univ. Sci. A 7, 1956 (2006)
R. Kripal, A.K. Gupta, S.K. Mishra, R.K. Srivastava, A.C. Pandey, S.G. Prakash, Photoluminescence and photoconductivity of ZnS:Mn (2+) nanoparticles synthesized via- co-precipitation method. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 76, 523 (2010)
H.P. Klong, L.F. Alexander, X-ray Diffraction Procedures for Crystallinne and Amorphous Structure. (New York, Wiley, 1954)
S. Horoz, M.S. Izgi, O. Sahin, Chracterization and photovoltaic studies of capped ZnS, CdS and CdxZn1–xS (x = 0.025) nanoparticles. 2017. Bitlis Eren Univ. J. Sci. 6, 61 (2017)
P. Yang, M.K. Lu, C.F. Song, S.W. Liu, D. Chu, D.R. Yuan, X.F. Cheng, Preparation and tunable photoluminescence characteristic of Ni2+: SrAl2O4. Opt. Mater. 24, 575 (2003)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Research Fund of the Siirt University. Project Number: 2017-SIUFED-29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horoz, S., Ekinci, A. & Sahin, O. Synthesis, characterization and photovoltaic properties of Cd1−xZnxS and Mn: Cd1−xZnxS quantum dots. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 5830–5836 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8555-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8555-9