Abstract
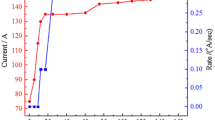
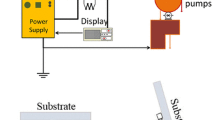
A new electrochromic (EC) arrangement is deposited on fluorine doped tin oxide (FTO) coated glass substrate by physical vapor deposition method. In this method, in the beginning, the WO3 nanoparticles powder are deposited with average rate of 0.4 Ås−1 in vacuum on FTO substrate for 80 min, then the Ag nanoparticles powder is deposited on prior layer for 1 min, again, the WO3 electrochromic layer is deposited on prior layers for 5 min. In the end, the layer of Ag nanoparticles is deposited for 1 min with the rate of 0.1 Å s−1. The nanoparticles of WO3 and Ag, as an n-type semiconductor acts as the cathode electrochromic material, while the nano-sized silver as a noble metal, plays the role of the electron trap centers to facilitate charge separation. That respectively have been used in fabricated electrochromic devices (ECDs), for this purpose, the temperatures of 100, 200 and 500 °C are selected and ECDs annelid for 2 min in vacuum. The thin film that annealed in 200 °C, exhibits good conductivity in cyclic voltammetry (CV) analysis and has a better EC performance. We obtain the maximum of current about 3.5 mA in oxidation state for this sample. Furthermore, the change of transmittance for this sample was upgraded to 40.30% at continuous switching steps. This arrangement (WO3/Ag/WO3/Ag) can be used in ECDs with its excellent properties.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Gholipur, ZKhorshidi, ABahari, Enhanced absorption performance of carbon nanostructure based metamaterials and tuning impedance matching behavior by an external AC electric field. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(14), 12528–12539 (2017)
M. Roeder, A.B. Beleke, U. Guntow, J. Buensow, A. Guerfi, U. Posset, H. Lorrmann, K. Zaghib, G. Sextl, Li4Ti5O12 and LiMn2O4 thin-film electrodes on transparent conducting oxides for all-solid-state and electrochromic applications. J. Power Sources 301, 35–40 (2016)
H. Najafi-Ashtiani, A. Bahari, S. Ghasemi, A dual electrochromic film based on nanocomposite of copolymer and WO3 nanoparticles: enhanced electrochromic coloration efficiency and switching response. J. Electroanal. Chem. 774, 14–21 (2016)
D. Dastan, S.L. Panahi, N.B. Chaure, Characterization of titania thin films grown by dip-coating technique. J. Mater. Sci. 27(12), 12291–12296 (2016)
Y. Ren, Y. Gao, G. Zhao, Facile single-step fabrications of electrochromic WO3 micro-patterned films using the novel photosensitive sol–gel method. Ceram. Int. 41(1), 403–408 (2015)
M. Nakhaei, A. Bahari, Synthesis and investigation of temperature effects on barium titanate (BaTiO3) nanostructural and electrical properties. J. Mater. Sci. 27(6), 5899–5908 (2016)
D. Dastan, A. Banpurkar, Solution processable sol–gel derived titania gate dielectric for organic field effect transistors. J. Mater. Sci. 28(4), 3851–3859 (2016)
M. Roodbari-Shahmiri, A. Bahari, H. Karimi-Maleh, R. Hosseinzadeh, N. Mirnia, Ethynylferrocene–NiO/MWCNT nanocomposite modified carbon paste electrode as a novel voltammetric sensor for simultaneous determination of glutathione and acetaminophen. Sens. Actuators B 177, 70–77 (2013)
A. Bahari, R. Gholipur, Electrical and optical properties of ZrxLa1–xOy nanocrystallites as an advanced dielectric for the next FET devices. J. Mater. Sci. 24(2), 674–686 (2013)
C.-G. Granqvist, G. A. Niklasson, A. Azens. Electrochromics: fundamentals and energy-related applications of oxide-based devices. Appl. Phys. A 89(1), 29–35 (2007)
H. Li, Y. Lv, X. Zhang, X. Wang, X. Liu, High-performance ITO-free electrochromic films based on bi-functional stacked WO3/Ag/WO3 structures. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 136, 86–91 (2015)
H. Najafi-Ashtiani, A. Bahari, S. Ghasemi, A dual electrochromic film based on nanocomposite of aniline and o-toluidine copolymer with tungsten oxide nanoparticles. Org. Electron. 37, 213–221 (2016)
V.R. Buch, A.K. Chawla, S.K. Rawal. Review on electrochromic property for WO3 thin films using different deposition techniques. Mater. Today 3(6), 1429–1437, (2016)
K. Sauvet, L. Sauques, A. Rougier, IR electrochromicWO3 thin films: from optimization to devices. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 93, 2045–2049 (2009)
S. Park, S. Kim, J. Choi, J. Song, M. Taya, S. Ahn, Low-cost fabrication of WO3 films using a room temperature and low-vacuum air-spray based deposition system for inorganic electrochromic device applications. Thin Solid Films 589, 412–418 (2015)
C.-P. Cheng, Y. Kuo, C.-P. Chou, C.-H. Cheng, T.P. Teng, Performance improvement of electrochromic display devices employing micro-size precipitates of tungsten oxide. Appl. Phys. A 116(4), 1553–1559 (2014)
M. Da Rocha, A. Rougier, Electrochromism of non-stoichiometric NiO thin film: as single layer and in full device. Appl. Phys. A 122(4), 1–7 (2016)
K.W. Park, Electrochromic properties of Au–WO3 nanocomposite thin-film electrode. Electrochim. Acta 50, 4690–4693 (2005)
R.R. Kharade, S.S. Mali, S.P. Patil, K.R. Patil, M.G. Gang, P.S. Patil, J.H. Kim, P.N. Bhosale, Enhanced electrochromic coloration in Ag nanoparticle decorated WO3 thin films. Electrochim. Acta 102, 358–368 (2013)
M.A. Gondal, M.A. Suliman, M.A. Dastageer, G.-K. Chuah, C. Basheer, Dan Yang, A. Suwaiyan, Visible light photocatalytic degradation of herbicide (Atrazine) using surface plasmon resonance induced in mesoporous Ag–WO3/SBA-15 composite. J. Mol. Catal. A 425, 208–216 (2016)
P.M. Kadam, N.L. Tarwal, P.S. Shinde, R.S. Patil, H.P. Deshmukh, P.S. Patil, From beads-to-wires-to-fibers of tungsten oxide: electrochromic response. Appl. Phys. A 97(2), 323–330 (2009)
G.F. Cai, J.P. Tu, D. Zhou, J.H. Zhang, X.L. Wang, C.D. Gu. Dual electrochromic film based on WO3/polyaniline core/shell nanowire array. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 122, 51–58 (2014)
S. Hoseinzadeh, R. Ghasemiasl, A. Bahari, A.H. Ramezani, The injection of Ag nanoparticles on surface of WO3 thin film: enhanced electrochromic coloration efficiency and switching response. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. doi:10.1007/s10854-017-7357-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoseinzadeh, S., Ghasemiasl, R., Bahari, A. et al. n-type WO3 semiconductor as a cathode electrochromic material for ECD devices. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 14446–14452 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7306-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7306-7