Abstract
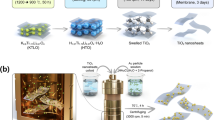
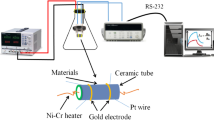
A controlled synthetic strategy is established for the development of TiO2@Au heterojunction nanorods using a facile wet-chemical method for the detection of NO2 gas under atmospheric pressure conditions. Structural studies reveal the existence of metastable anatase phase along with thermodynamically stable rutile phase with high degree of crystallinity. The structural analysis divulges the uniform surface anchoring of Au nanoclusters onto mono-dispersed TiO2 nanorods introducing interfacial metal–semiconductor heterojunctions. TiO2@Au heterojunction nanorods exhibited excellent sensor performance towards trace level exposure of NO2 gas. Owing to the interfacial electron transfer process at the heterojunction the optimum operating temperature of TiO2@Au heterojunction nanorods determined to be 250 °C, which is much less as compared to pristine TiO2 gas sensors (400 °C). Sensor response was found to be linear for the trace level concentration range of 0.5–5 ppm with lowest detection limit as 500 ppb. The TiO2@Au heterojunction nanorods exhibited higher sensitivity at atmospheric pressure conditions compared to vacuum conditions because of the changes in surface O2 adsorption properties of the heterojunction material at different oxygen partial pressure and existence of mixed phases in TiO2 nanorods. The superior gas sensor performance of the material under atmospheric pressure conditions point towards their potential for real-time applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Alessandri, E. Comini, E. Bontempi, G. Faglia, L.E. Depero, G. Sberveglieri, Cr- inserted TiO2 thin films for chemical gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 128, 312–319 (2007)
G. Korotcenkov, B.K. Cho, Engineering approaches to improvement of conductometric gas sensor parameters. Part 2: decrease of dissipated (consumable) power and improvement stability and reliability. Sens. Actuators B 198, 316–341 (2014)
X. Chen, C.K.Y. Wong, C.A. Yuan, G. Zhang, Nanowire-based gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 177, 178–195 (2013)
B. Saruhan, A. Yüce, Y. Gönüllü, K. Kelm, Effect of Al doping on NO2 gas sensing of TiO2 at elevated temperatures. Sens. Actuators B 187, 586–597 (2013)
H. Wang, Z. Guo, S. Wang, W. Liu, One-dimensional titania nanostructures: synthesis and applications in dye-sensitized solar cells. Thin Solid Films 558, 1–19 (2014)
N.S. Ramgir, Y. Yang, M. Zacharias, Nanowire-based sensors. Small 6, 1705–1722 (2010)
E. Şennik, U. Soysal, Z.Z. Öztürk, Pd loaded spider-web TiO2 nanowires: fabrication, characterization and gas sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B 199, 424–432 (2014)
A.M. Ruiz, G. Sakai, A. Cornet, K. Shimanoe, J.R. Morante, N. Yamazoe, Cr-doped TiO2 gas sensor for exhaust NO2 monitoring. Sens. Actuators B 93, 509–518 (2003)
Y.J. Choi, Z. Seeley, A. Bandyopadhyay, S. Bose, S.A. Akbar, Aluminum-doped TiO2 nano-powders for gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 124, 111–117 (2007)
G.B. Song, J.K. Liang, F.S. Liu, T.J. Peng, G.H. Rao, Preparation and phase transformation of anatase–rutile crystals in metal doped TiO2/muscovite nanocomposites. Thin Solid Films 491, 110–116 (2005)
X. Li, R. Ramasamy, P.K. Dutta, Study of the resistance behaviour of anatase and rutile thick films towards carbon monoxide and oxygen at high temperatures and possibilities for sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B 143, 308–315 (2009)
N. Yamazoe, G. Sakai, K. Shimanoe, Oxide semiconductor gas sensors. Catal. Surv. Asia 7, 63–75 (2003)
H. Liu, W. Yang, M. Wang, L. Xiao, S. Liu, Fabrication of lotus-like Au@TiO2 nanocomposites with enhanced gas-sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B 236, 490–498 (2016)
D.T. Thu, H.T. Hien, D.T.A. Thu, P.Q. Ngan, G.H. Thai, C.V. Tuan, T. Trung, H.T. Giang, Schottky contacts of (Au, Pt)/nanotube-titanates for fast response to NO2 gas at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B 244, 941–948 (2017)
Q. Zhang, L. Gao, Preparation of oxide nanocrystals with tunable morphologies by the moderate hydrothermal method: insights from rutile TiO2. Langmuir 19, 967–971 (2002)
M.M. Khan, S.A. Ansari, J. Lee, M.H. Cho, Enhanced optical, visible light catalytic and electrochemical properties of Au@TiO2 nanocomposites. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 19, 1845–1850 (2013)
S. Abdulla, T.L. Mathew, B. Pullithadathil, Highly sensitive, room temperature gas sensor based on polyaniline-multiwalled carbon nanotubes (PANI/MWCNTs) nanocomposite for trace-level ammonia detection. Sens. Actuators B 221, 1523–1534 (2015)
X. Pan, Y.-J. Xu, Efficient thermal- and photzocatalyst of Pd nanoparticles on TiO2 achieved by an oxygen vacancies promoted synthesis strategy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 1879–1886 (2014)
U. Balachandran, N.G. Eror, Raman spectra of titanium dioxide. J. Solid State Chem. 42, 276–282 (1982)
C.Y. Xu, P.X. Zhang, L. Yan, Blue shift of Raman peak from coated TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Raman Spectrosc. 32, 862–865 (2001)
H.C. Choi, Y.M. Jung, S.B. Kim, Size effects in the Raman spectra of TiO2 nanoparticles. Vib. Spectrosc. 37, 33–38 (2005)
W. Su, J. Zhang, Z. Feng, T. Chen, P. Ying, C. Li, Surface phases of TiO2 nanoparticles studied by UV Raman spectroscopy and FT-IR spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 7710–7716 (2008)
X.Z. Li, F.B. Li, Study of Au/Au3+-TiO2 Photocatalysts toward visible photooxidation for water and wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Technol 35, 2381–2387 (2001)
J. Esmaeilzadeh, E. Marzbanrad, C. Zamani, B. Raissi, Fabrication of undoped-TiO2 nanostructure-based NO2 high temperature gas sensor using low frequency AC electrophoretic deposition method. Sens. Actuators B 161, 401–405 (2012)
A. Kolmakov, D.O. Klenov, Y. Lilach, S. Stemmer, M. Moskovits, Enhanced gas sensing by individual SnO2 nanowires and nanobelts functionalized with Pd catalyst particles. Nano Lett. 5, 667–673 (2005)
N. Barsan, D. Koziej, U. Weimar, Metal oxide-based gas sensor research: how to? Sens. Actuators B 121, 18–35 (2007)
A. Teleki, S.E. Pratsinis, K. Kalyanasundaram, P.I. Gouma, Sensing of organic vapors by flame-made TiO2 nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators, B 119, 683–690 (2006)
P. Knauth, H.L. Tuller, Electrical and defect thermodynamic properties of nanocrystalline titanium dioxide. J. Appl. Phys. 85, 897–902 (1999)
A. Tricoli, M. Righettoni, A. Teleki, Semiconductor gas sensors: dry synthesis and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 7632–7659 (2010)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by IGCAR-PSGCT project (IGCAR-PSG/213) and authors wish to acknowledge the facilities and support provided by PSG Sons and Charities, Coimbatore and Materials Science Group, IGCAR, Kalpakkam.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of intrest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponnuvelu, D.V., Pullithadathil, B., Prasad, A.K. et al. Highly sensitive, atmospheric pressure operatable sensor based on Au nanoclusters decorated TiO2@Au heterojunction nanorods for trace level NO2 gas detection. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 9738–9748 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6725-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6725-9