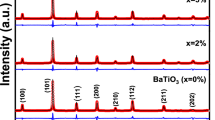
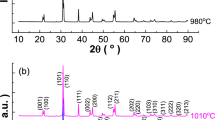
Abstract
We have systematically studied the effects of Sr substitution on the microstructure, crystal structure, Curie temperature, dielectric, ferroelectric, and piezoelectric properties of (Ba1−x Sr x )(Zr0.05Ti0.95)O3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.40) ceramics prepared by the conventional solid-state reaction method. Both X-ray diffraction and dielectric measurements reveal that with increasing Sr content, the room-temperature crystal structure of the samples evolves from tetragonal to orthorhombic around x = 0.2 where the two phases coexist. Dielectric measurements show that Sr doping significantly reduces the Curie temperature (T C ) linearly from 114 °C for x = 0 to 10 °C for x = 0.4 with dT C /dx ≈ −265 °C/mol. Moreover, Sr doping causes linear shrinkage of the lattice constants and unit cell volume as well as considerable changes in the ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties. At room temperature, the sample with x = 0.11 exhibits enhanced piezoelectric properties with d 33 ~ 380 pC/N and the planar mode electromechanical coupling coefficient k p = 0.38. Our results provide useful reference for the optimization of Ba(Zr,Ti)O3-based lead-free piezoelectric materials.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Toda, J. Appl. Phys. 43, 261 (1972)
X.S. Wang, H. Yamada, C.N. Xu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 022905 (2005)
S. Sen, R.N.P. Choudhary, Mater. Chem. Phys. 87, 256–263 (2004)
T. Maiti, R. Guo, A.S. Bhala, Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 122909 (2006)
W. Zhong, D. Vanerbilt, K.M. Rabe, Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 1861 (1994)
S. Saha, T.P. Sinha, A. Mookerjee, Phys. Rev. B 62, 8828 (2000)
R.E. Cohen, Nature 358, 136–138 (1992)
M.H. Frey, D.A. Payne, Phys. Rev. B 54, 3158 (1996)
W. Liu, X.B. Ren, Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 257602 (2009)
P. Wang, Y.X. Li, Y.Q. Lu, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 31, 2005–2012 (2011)
J.G. Wu, D.Q. Xiao, W.J. Wu, J.G. Zhu, J. Wang, J. Alloy Compd. 509, L359–L361 (2011)
S. Su, R.Z. Zuo, S.B. Lu, Z.K. Xu, X.H. Wang, L.T. Li, Curr. Appl. Phys. 11, S120–S123 (2011)
T. Chen, T. Zhang, G.C. Wang, J.F. Zhou, J.W. Zhang, Y.H. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. 47, 4612–4619 (2012)
Y.R. Cui, C.L. Yuan, X.Y. Liu, X.Y. Zhao, X. Shan, J. Mater. Sci. 24, 654–657 (2013)
Y.R. Cui, X.Y. Liu, M.H. Jiang, Y.B. Hu, Q.S. Su, H. Wang, J. Mater. Sci. 23, 1342–1345 (2012)
D.Z. Xue, Y.M. Zhou, H.X. Bao, J.H. Gao, X.B. Ren, Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 122901 (2011)
L.F. Zhu, B.P. Zhang, X.K. Zhao, L. Zhao, F.Z. Yao, X. Han, P.F. Zhou, J.F. Li, Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 072905 (2013)
C. Zhou, W.F. Liu, D.Z. Xue, X.B. Ren, H.X. Bao, J.H. Gao, L.X. Zhang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 222910 (2012)
X.P. Jiang, L. Li, C. Chen, J. Tang, K.P. Zheng, X.H. Li, J. Inorg. Mater. 29, 33–37 (2014)
Y.G. Yao, C. Zhou, D.C. Lv, D. Wang, H.J. Wu, Y.D. Yang, X.B. Ren, Europhys. Lett. 98, 27008 (2012)
S.T.F. Lee, K.H. Lam, X.M. Zhang, H.L.W. Chan, Ultrasonics 51, 811–814 (2011)
N.Y. Chan, S.H. Choy, D.Y. Wang, Y. Wang, J.Y. Dai, H.L.W. Chan, J. Mater. Sci. 25, 2589–2594 (2014)
T.K.Y. Wong, B.J. Kennedy, C.J. Howard, B.A. Hunter, T. Vogt, J. Solid State Chem. 156, 255–263 (2001)
Y. Tian, L.L. Wei, X.L. Chao, Z.H. Liu, Z.P. Yang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 496–502 (2013)
P.F. Zhou, B.P. Zhang, L. Zhao, X.K. Zhao, L.F. Zhu, L.Q. Cheng, J.F. Li, Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 172904 (2013)
L. Jin, F. Li, S.J. Zhang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97, 1–27 (2014)
B.S. Li, Z.G. Zhu, G.R. Li, Q.R. Yin, A.L. Ding, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 43, 1458–1463 (2004)
T.R. Thomas, S.J. Zhang, J. Electroceram. 19, 111–124 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, HR., Chen, CX. & Zheng, RK. Effects of Sr substitution on the structural, dielectric, ferroelectric, and piezoelectric properties of Ba(Zr,Ti)O3 lead-free ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26, 3057–3063 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-2797-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-2797-6