Abstract
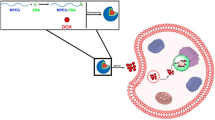
A two-phase route was developed to form a new theranostics-based system. The comb polymer poly (glycidyl methacrylate)-graft-ethane diamine-graft-polyethylene glycol (PGMA-g-EDA-g-PEG) was used to modify the quantum dots (QDs) by the method of ligand exchange. Subsequently, due to a large amount of amino groups on the surface of QDs, the doxorubicin (DOX) was conjugated by amine bonds to form pH-sensitive drug release system. UV–vis transmission spectra and PL spectra showed that the nanoparticles maintained the optical properties of QDs and DOX. The transmission electron microscopy analysis indicated that QDs were well dispersed in water and still had small sizes (7 nm) after ligand exchange and conjugated with DOX. Then the thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) revealed that about 80 wt% comb-shaped polymers coated on the surface of QDs, and about 10 wt% QDs was in nanoparticles PGMA-g-EDA-g-PEG-QDs-DOX. In vitro release studies showed that PGMA-g-EDA-g-PEG -DOX and PGMA-g-EDA-g-PEG-QDs-DOX were pH sensitive. Findings from this study suggested that nanoparticles PGMA-g-EDA-g-PEG-QDs-DOX can be used in a new field combined both imaging and targeted therapy.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao XH, Cui YY, Levenson RM, Chung LWK, Nie SM (2004) In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 22:969–976
Ma ML, Zhang QY, Xin TJ, Zhang HP, Geng WC, Zhou J (2013) Preparation and characterization of structure-tailored magnetic fluorescent Fe3O4/P(GMA–EGDMA–NVCz) core–shell microspheres. J Mater Sci 48:5302–5308
Christoforou TK, Georgiou KT (2013) Polymeric theranostics: using polymer-based systems for simultaneous imaging and therapy. J Mater Chem B 1:3002–3025
Zhao Q, g Rong XL, Ma HB, Tao GH (2013) Aqueous synthesis of CdSe and CdSe/CdS quantum dots with controllable introduction of Se and S sources. J Mater Sci 48:2135–2141
Derfus AM, Chan WCW, Bhatia S (2004) Probing the cytotoxicity of semiconductor quantum dots. N Adv Mater 16:961–966
Gao XH, Yang LL, Petros JA, Marshall FF, Simons JW, Nie SM (2005) In vivo molecular and cellular imaging with quantum dots. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:63–72
Ma YS, Zhang BB, Gu M, Huang SM, Liu XL, Liu B, Ni C (2013) Bulk synthesis of homogeneous and transparent bulk core/multishell quantum dots/PMMA nanocomposites with bright luminescence. J Appl Polym. doi:10.1002/APP.39338
Macotela LGV, Torchynska TV, Douda J, Sierra RP, Shcherbyna (2011) Radiative interface state study in CdSe/ZnS quantum dots covered by polymer. L. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 176:1349–1352
Zhang T, Yuan HP, Suo HL (2009) Water-soluble CdSe/ZnS quantum dots passivated by poly (glycino amino acid) phosphazenes. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc 19:645–650
Sun T, Li K, Li CJ, Zhao WO, Chen L, Chang YL (2012) Optimizing conditions for encapsulation of QDs by varying PEG chain density of amphiphilic centipede-like copolymer coating and exploration of QDs probes for tumor cell targeting and tracking. New J Chem 36:2383–2391
Zrazheyskiy P, Sena M, Gao XHChem (2010) Designing multifunctional quantum dots for bioimaging, detection, and drugdelivery. Soc Rev 39:4326–4354
Cui Y, Gong XQ, Zhu SJ, Li YH, Su WY, Yang QH, Chang J (2012) A facile method to prepare high-performance magnetic and fluorescent bifunctional nanocomposites and their preliminary application in biomolecule detection. J Mater Chem 22:462–469
Barat B, Sirk SJ, McCabe KE, Li J, Lepin EJ, Remenyi R, Koh AL, Olafsen T, Gambhir SS, Weiss S, Wu AM (2009) Cys-diabody quantum dot conjugates (immunoqdots) for cancer marker detection. Bioconjugate Chem 20:1474–1481
Medintz IL, Clapp AR, Brunel FM, Tiefenbrunn T, Uyeda HT, Chang EL, Deschamps JR, Dawson PE, Mattoussi H (2006) Proteolytic activity monitored by fluorescence resonance energy transfer through quantum-dot-peptide conjugates. Nat Mater 5:581–589
Wang QQ, Kong M, An Y, Liu Y, Li JJ, Zhou X, Feng C, Li J, Jiang SY, Cheng XJ, Chen XG (2013) Hydroxybutyl chitosan thermo-sensitive hydrogel: a potential drug delivery system. J Mater Sci 48:5614–5623
Arap W, Pasqualini R, Ruoslahti E (1998) Cancer treatment by targeted drug delivery to tumor vasculature in a mouse model. Science 279:377–380
Gao QH, Han XL, Zhu J, Chen RJ, Sun BW (2012) A polymer–drug conjugate for doxorubicin: synthesis and biological evaluation of pluronic F127-doxorubicin amide conjugates. J Appl Ploym Sci 124:4960–5953
Kamimura M, Furukawa T, Akiyamac S, Nagasaki Y (2013) Enhanced intracellular drug delivery of pH-sensitive doxorubicin/poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(4-vinylbenzylphosphonate) nanoparticles in multi-drug resistant human epidermoid KB carcinoma cells. Biomater Sci 1:361–367
Bae Y, Fukushima S, Harada A, Kataoka K (2003) Design of environment-sensitive supramolecular assemblies for intracellular drug delivery: polymeric micelles that are responsive to intracellular pH change. Angew Chem 42:4640–4643
Zhao JH, Huang DT, Yin ZY, Chi XQ, Wang XM, Gao JH (2012) Magnetite nanoparticles as smart carriers to manipulate the cytotoxicity of anticancer drugs: magnetic control and pH-responsive release. J Mater Chem 22:15717–15725
Liu YS, Chen WB, Kim H (2012) pH-responsive release behavior of genipin-crosslinked chitosan/poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogels. J Appl Polym Sci 125:290–298
Wang YZ, Zhu M, Huang HL, Li YX, Li YP, Wang JY (2013) SYNTHESIS of comb polymer PGMA-g-EDA and studies of the modified quantum dots. Acta Polym Sin 8:1046–1309
Koktysh D, Bright V, Pham W (2011) Fluorescent magnetic hybrid nanoprobe for multimodal bioimaging. Nanotechnology 22:275606
Barrera C, Herrera AP, Rinaldi C (2009) Colloidal dispersions of monodisperse magnetite nanoparticles modified with poly (ethylene glycol). J Colloid Interf Sci 329:107–113
Zhao YL, Liu S, Li YP, Jiang W, Chang YL, Pan S, Fang XX, Wang YA, Wang JY (2010) Synthesis and grafting of folate–PEG–PAMAM conjugates onto quantum dots for selective targeting of folate-receptor-positive tumor cells. J Colloid Interf Sci 350:44–50
Tian Y, Glogowska A, Zhong W, Klonisch T, Xing M (2013) Polymeric mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a pH-responsive switch to controldoxorubicin intracellular delivery. J Mater Chem B 1:5264–5272
Palma RD, Peeters S, Bael MJV, Rul HVD, Bonroy K, Laureyn W, Mullens J, Borghs G, Maes G (2007) Silane ligand exchange to make hydrophobic superparamagnetic nanoparticles water-dispersible. Chem Mater 19:1821–1831
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20904014) and the Ph.D. Programs Foundation (20120061110076). We are grateful to Dr Y. Andrew Wang (Ocean Nanotech) for providing the quantum dot samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Xu, Z. et al. A pH-sensitive theranostics system based on doxorubicin conjugated with the comb-shaped polymer coating of quantum dots. J Mater Sci 49, 7539–7546 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8461-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8461-3