Abstract
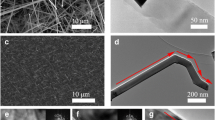
A new process has been developed to grow silicon (Si) nanowires (NWs), and their growth mechanisms were explored and discussed. In this process, SiNWs were synthesized by simply oxidizing and then reducing Si wafers in a high temperature furnace. The process involves H2, in an inert atmosphere, reacts with thermally grown SiO2 on Si at 1100 °C enhancing the growth of SiNWs directly on Si wafers. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy studies show that the NWs consists of a crystalline core of ~25 nm in diameter and an amorphous oxide shell of ~2 nm in thickness, which was also supported by selected area electron diffraction patterns. The NWs synthesized exhibit a high aspect ratio of ~167 and room temperature phonon confinement effect. This simple and economical process to synthesize crystalline SiNWs opens up a new way for large scale applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cui Y, Zhong Z, Wang D, Wang WU, Lieber CM (2003) Nano Lett 3:149
He R, Yang P (2006) Nature Nanotechnol 1:42
Chan CK, Peng H, Liu G, Mcllwrath K, Zhang XF, Huggins RA, Cui Y (2008) Nature Nanotechnol 3:31035
Granett E, Yang P (2010) Nano Lett 10:1082
Pignalosa P, Lee H, Qiao L, Tseng M, Yi AY (2011) AIP Advances 1:032124
Kalita G, Adhikari S, Aryal HR, Afre R, Soga T, Sharon M, Koichi W, Umeno M (2009) J Phys D 42:115104
Schmidt V, Wittemann JV, Senz S, Gosele U (2009) Adv Mater 21:2681
Wu Y, Cui Y, Huynh L, Barrelet CJ, Bell DC, Lieber CM (2004) Nano Lett 4:433
Ferry DK (2008) Science 319:579
Colli A, Hofmann S, Fasoli A, Ferrari AC, Ducati C, Dunin-Borokowski RE, Robertson J (2006) Appl Phys A 85:247
Kim BS, Koo TW, Lee JH, Kim DS, Jung YC, Hwang SW, Choi BL, Lee EK, Kim JM, Whang D (2009) Nano Lett 9:864
Wang N, Tang YH, Zhang YF, Lee CS, Lee ST (1998) Phys Rev B 58:R16024
Pan ZW, Dai ZR, Xu L, Lee ST, Wang ZL (2001) J Phys Chem B 105:2507
Garnett EC, Liang W, Yang P (2007) Adv Mater 19:2946
Schmidt V, Wittemann JV, Gosele U (2010) Chem Rev 110:361
Holmes JD, Johnston KP, Doty RC, Korgel BA (2000) Science 287:1471
Schubert L, Werner P, Zakharov ND, Gerth G, Kolb FM, Long L, Gosel U, Tan TY (2004) Appl Phys Lett 84:4968
Morales AM, Lieber CM (1998) Science 279:208
Niu J, Sha J, Yang D (2004) Physica E 23:131
Yang HJ, Yuan FW, Tuan HY (2010) Chem Commun 46:6105
Zhang RQ, Lifshitz Y, Lee ST (2003) Adv Mater 15:635
Wang N, Tang YH, Zhang YF, Yu DP, Lee CS, Bello I, Lee ST (1998) Chem Phys Lett 283:368
Wang N, Tang YH, Zhang YF, Lee CS, Bello I, Lee ST (1999) Chem Phys Lett 299:237
Menga F, Li J, Hong Z, Zhia M, Sakla A, Xianga C, Wua N (2013) Catal Today 199:48
Lu J, Zeng X, Liu H, Zhang W, Zhang Y (2012) J Phys Chem C 116:23013
Dhar S, Giri PK (2011) Int J Nanosci 10:13
Piscanec S, Ferrari AC, Cantoro M, Hofmann S, Zapien JA, Lifshitz Y, Lee ST, Robertson J (2003) J Mater Sci Eng C 23:931
Compaan A, Lee MC, Trott G (1985) Phys Rev B 32:6731
Jellison GE, Modine FA (1983) Phys Rev B 27:7446
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Foreign Affairs and International Trade Canada (DFAIT) under Commonwealth Graduate Student Exchange Program Scholarship (2011–2012). Q.Y. and A.H. acknowledge the support from NSERC and Canada Research Chair Program. S.K.B. and Q.Y. acknowledge the technical assistance from Dave McColl, Plasma Physics Laboratory, Rob Peace, Department of Mechanical Engineering and Jason Maley, SSSC, University of Saskatchewan, Canada. S.K.B. and O.J. acknowledges Prof. T. Harinarayana, Director, GERMI Research, Innovation and Incubation Centre, India. The EM research described in this paper was performed at the Canadian Centre for Electron Microscopy at McMaster University, which is supported by NSERC and other government agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behura, S.K., Yang, Q., Hirose, A. et al. Catalyst-free synthesis of silicon nanowires by oxidation and reduction process. J Mater Sci 49, 3592–3597 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7476-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7476-5