Abstract
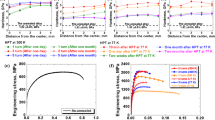
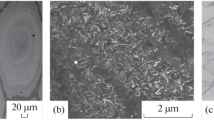
The process of high-pressure torsion (HPT) was applied to control the size and distribution of ferromagnetic Co particles in a Cu–Co alloy. Electron probe microanalysis, X-ray diffraction analysis, and transmission electron microscopy confirmed that the Co particles were significantly refined through fragmentation and dissolved with intense straining by HPT. Magnetoresistance appeared by ~2.5% at 77 K with an isotropic feature corresponding to giant magnetoresistance (GMR). It is demonstrated that HPT is a potential process for creating GMR in the Cu–Co alloy prepared by conventional ingot metallurgy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkowitz AE, Mitchell JR, Carey MJ, Young AP, Zhang S, Spada FE et al (1992) Phys Rev Lett 68:3745. doi:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.68.3745
Xiao JQ, Jiang JS, Chien CL (1992) Phys Rev Lett 68:3749. doi:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.68.3749
Takanashi K, Park J, Sugawara T, Hono K, Goto A, Yasuda H et al (1996) Thin Solid Films 275:106. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-6090(95)07064-8
Wang W, Zhu F, Weng J, Xiao J, Lai W (1998) Appl Phys Lett 72:1118. doi:https://doi.org/10.1063/1.120942
Kim IJ, Takeda H, Echigoya J, Kataoka N, Fukamichi K, Shimada Y (1996) Mater Sci Eng A 217–218:363. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(96)10347-6
Aizawa T, Zhou C (2000) Mater Sci Eng A 285:1. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(00)00709-7
Larde R, Le Breton JM (2005) J Magn Magn Mater 290:1120. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2004.11.471
Rattanasakulthong W, Sirisathitkul C (2005) Physica B 369:160. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2005.08.010
Massalski TB, Murray JL, Bennett LH, Baker H, Kacprzak L (1987) Binary phase diagrams, vol 1. American Society of Metals, Metals Park, OH, p 758
Rentenberger C, Karnthaler HP (2005) Acta Mater 53:3031. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2005.03.016
Waitz T, Kazykhanov V, Karnthaler HP (2004) Acta Mater 52:137. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2003.08.036
Sabirov I, Pippan R (2005) Scr Mater 52:1293. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.02.017
Kai M, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2008) Mater Sci Eng A 488:117
Senkov ON, Froes FH, Stolyarov VV, Valiev RZ, Liu J (1998) Nanostruct Mater 10:691. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0965-9773(98)00107-X
Sauvage X, Wetscher F, Pareige P (2005) Acta Mater 53:2127
Sakai G, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2005) Mater Sci Eng A 393:344. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.11.007
Valiev RZ, Estrin Y, Horita Z, Langdon TG, Zehetbauer MJ, Zhu YT (2006) JOM 58(4):33. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-006-0213-7
Segal VM, Reznikov VI, Drobyshevskiy AE, Kopylov VI (1981) Russ Metall 1:99
Saito Y, Utsunomiya H, Tsuji N, Sakai T (1999) Acta Mater 47:579. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(98)00365-6
Dutkiewicz J, Kuśnierz J, Maziarz W, Lejkowska M, Garbacz H, Lewandowska M et al (2005) Phys Status Solidi 202:2309. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.200521235
Stolyarov VV, Gunderov DV, Popov AG, Puzanova TZ, Raab GI, Yavari AR et al (2002) J Magn Magn Mater 242–245:1399. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(01)01244-6
Vorhauer A, Rumpf K, Granitzer P, Kleber S, Krenn H, Pippan R (2006) Mater Sci Forum 503–504:299
Suehiro K, Nishimura S, Horita Z (2008) Mater Trans 49:102. doi:https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.ME200725
Servi IS, Turnbull D (1966) Acta Metall 14:161. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(66)90297-5
Fujii T, Tamura T, Kato M, Onaka S (2002) Microsc Microanal 8(Suppl. 2):1434CD
Suryanarayana C (2001) Prog Mater Sci 46:1. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6425(99)00010-9
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan, in Priority Areas “Giant Straining Process for Advanced Materials Containing Ultra-High Density Lattice Defects” and in part by Kyushu University Interdisciplinary Programs in Education and Projects in Research Development (P&P).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suehiro, K., Nishimura, S., Horita, Z. et al. High-pressure torsion for production of magnetoresistance in Cu–Co alloy. J Mater Sci 43, 7349–7353 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2813-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2813-9