Abstract
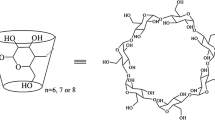
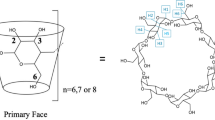
Cyclodextrins (CyD) have proven effects on the stability of proteins and can be used in the formulation of aggregation prone therapeutic proteins. This effect stems from specific interactions between the CyD (preferably β-CyD) and solvent exposed amino acid residues. Here the interaction with hydrophobic aromatic amino acid residues stands out and the interaction between CyDs and these amino acid residues holds the key to understanding the observed effects, which CyDs exerts on proteins and peptides. Here we present a comparative study of the interactions between free and peptide bound aromatic amino acids and their derivatives with α, β and γ-CyDs using NMR spectroscopy. We propose a novel, quantitative means of assessing the penetration depth of guest molecules in CyD cavities, the penetration gauge Π, and apply it to the observed interaction patterns from ROESY NMR spectra. We demonstrate that the penetration depths of the aromatic rings within the CyDs rely highly on the nature of the remainder of the guest molecule. Thus the presence of charges, neighboring amino acids and the specific positioning on the surface of a protein highly influences the penetration depth and geometry of guest–CyD interactions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Branchu, S., Forbes, R.T., York, P., Nyqvist, H.: The Effect of Cyclodextrins in Monomere Protein Unfolding. Biocalorimetry Applications of Calorimetry in the Biological Sciences, vol. 1. Wiley, West Sussex (1998)
Cooper, A.: Effect of cyclodextrins on the thermal stability of globular protein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114(23), 9208–9209 (1992)
Cooper, A., McAuley-Hecht, K.E.: Microcalorimetry and the molecular recognition of peptides and proteins. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 345, 23–35 (1993)
Brewster, M.E., Hora, M.S., Simpkins, J.W., Boder, N.: Use of 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin as a solubilizing and stabilizing excipient for protein drugs. Pharm. Res. 8, 792–795 (1991)
Charman, S.A., Mason, K.L., Charman, W.N.: Techniques for assessing the effects of pharmaceutical excipients in the aggregation of porcine growth hormone. Pharm. Res. 10, 954–961 (1993)
Izutsu, K.-L., Yoshioka, S., Terao, T.: Stabilization of beta-galactosidase by amphiphilic additives during freeze-drying. Int. J. Pharm. 90, 187–194 (1993)
Karuppiah, N., Sharma, A.: Cyclodextrin as protein folding aids. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 211(1), 60–66 (1995)
Katakam, M., Banga, A.K.: Aggregation of proteins and its prevention by carbohydrate excipients: albumins and gamma-globulin. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 47, 103–107 (1995)
Lee, M.-J., Fennema, O.R.: Ability of cyclodextrins to inhibit aggregation of beta-casein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 39, 17–21 (1991)
Sigurjónsdóttir, J.F., Loftsson, T., Másson, M.: Influence of cyclodextrins on the stability of the peptide salmon calcitonin in aqueous solution. Int. J. Pharm. 186, 205–213 (1998)
Linde, G.A., Laverde, A., de Faria, E.V., Colauto, N.B., de Moraes, F.F., Zanin, G.M.: Taste modification of amino acids and protein hydrolysate by alpha-cyclodextrin. Food Res. Int. 42(7), 814–818 (2009)
Linde, G.A., Laverde, A., De Faria, E.V., Colauto, N.B., De Moraes, F.F., Zanin, G.M.: The use of 2D NMR to study beta-cyclodextrin complexation and debittering of amino acids and peptides. Food Res. Int. 43(1), 187–192 (2010)
Yamamoto, T., Fukui, N., Hori, A., Matsui, Y.: Circular dichroism and fluorescence spectroscopy studies of the effect of cyclodextrins on the thermal stability of chicken egg white lysozyme in aqueous solution. J. Mol. Struct. 782(1), 60–66 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2005.01.024
Yoshikiyo, K., Takeshita, R., Yamamoto, T., Takahashi, T., Matsui, Y.: The effects of cyclodextrins on the thermal denaturation and renaturation processes of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A in an aqueous solution studied by circular dichroism and fluorescence spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 832(1–3), 96–100 (2007)
Otzen, D.E., Knudsen, B.R., Aachmann, F., Larsen, K.L., Wimmer, R.: Structural basis for cyclodextrins’ suppression of human growth hormone aggregation. Prot. Sci. 11(7), 1779–1787 (2002)
Aachmann, F.L., Otzen, D.E., Larsen, K.L., Wimmer, R.: Structural background of cyclodextrin–protein interactions. Prot. Eng. 16(12), 905–912 (2003)
Matilainen, L., Larsen, K.L., Wimmer, R., Keski-Rahkonen, P., Auriola, S., Jarvinen, T., Jarho, P.: The effect of cyclodextrins on chemical and physical stability of glucagon and characterization of glucagon/gamma-CD inclusion complexes. J. Pharm. Sci. 97(7), 2720–2729 (2008)
Creighton, T.E.: Proteins: structures and molecular properties, 2nd edn. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York (1993)
Bartels, C., Xia, T.-H., Billeter, M., Günter, P., Wüthrich, K.: The program XEASY for computer supported NMR spectral of biological macromolecules. J. Biomol. NMR 5, 1–10 (1995)
Szejtli, J.: In: Szejtli, J., Osa, T. (eds.) Comprehensive Supramolecular Chemistry, vol. 3. Pergamon, Exeter, UK (1996)
Inoue, Y., Hoshi, H., Sakurai, M., Chujo, R.: Geometry of cyclohexaamylase inclusion complexes with some substituted benzenes in aqueous solution based on carbon-13 NMR chemical shifts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 107, 2319–2323 (1985)
Inoue, Y., Okuda, T., Miyata, Y., Chujo, R.: N.M.R. Studies of cycloamylose inclusion-complexes with p-substituted phenols. Carbohydr. Res. 125, 65–76 (1984)
Komiyama, M., Harai, H.: Carbon-13 NMR study on the cyclodextrin inclusion complexes in solution. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 54(3), 828–831 (1981)
Hamilton, J.A., Sabesan, M.N., Steirauf, L.K., Geddes, A.: The crystal structure of a complex of cycloheptaamylose with 2,5-diiodobenzoic acid. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 73, 659–664 (1976)
Lipkowitz, K.N., Raghothama, S., Yang, J.: Enantioselective binding of tryptophan by alfa-cyclodextrin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114, 1554–1562 (1992)
Kahle, C., Holzgrabe, U.: Determination of binding constants of cyclodextrin inclusion complexes with amino acids and dipeptides by potentiometric titration. Chirality 16(8), 509–515 (2004)
Hembury, G., Rekharsky, M., Nakamura, A., Inoue, Y.: Direct correlation between complex conformation and chiral discrimination upon inclusion of amino acid derivatives by beta- and gamma-cyclodextrins. Org. Lett. 2(21), 3257–3260 (2000)
Horský, J., Pitha, J.: Inclusion complexes of proteins: interaction of cyclodextrins with peptides containing aromatic amino acids studied by competitive spectrophotometry. J. Incl. Phenom. Mol. 18, 291–300 (1994)
Mrozek, J., Banecki, B., Karolczak, J., Wiczk, W.: Influence of the separation of the charged groups and aromatic ring on interaction of tyrosine and phenylalanine analogues and derivatives with beta-cyclodextrin. Biophys. Chem. 116(3), 237–250 (2005)
Waibel, B., Scheiber, J., Meier, C., Hammitzsch, M., Baumann, K., Scriba, G.K.E., Holzgrabe, U.: Comparison of cyclodextrin-dipeptide inclusion complexes in the absence and presence of urea by means of capillary electrophoresis, nuclear magnetic resonance and molecular modeling. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 18, 2921–2930 (2007)
Bekos, E.J., Gardella, J.A., Bright, F.V.: The binding of free oligopeptides to cyclodextrins: the role of the tyrosine group. J. Incl. Phenom. Mol. 26(4), 185–195 (1996)
Camilleri, C., Haskins, N.J., New, A.P., Saunders, M.R.: Analysing the complexation of amino acids and peptides with beta-cyclodextrin using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spec. 7, 949–952 (1993)
Acknowledgments
FLA thanks KMB project (182695/I40), Norwegian Research Council for financial support. The NMR laboratory at Aalborg University is supported by the Obel Foundation. We would to thank Kate Bowman for proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aachmann, F.L., Larsen, K.L. & Wimmer, R. Interactions of cyclodextrins with aromatic amino acids: a basis for protein interactions. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 73, 349–357 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-011-0071-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-011-0071-y