Abstract
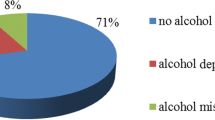
Parenting styles influence youth’s overall well-being and behaviors. Few studies have examined the effects of parenting styles on alcohol use among Hispanic youth. Although the field of alcohol prevention has made progress in recent years, most prevention initiatives lack the capability to directly address the special needs of this high-risk population. The primary aim of our study was to examine the relationship of recent alcohol use, binge drinking (past 30 days) and authoritative parenting among Hispanic youth. We conducted a secondary data analysis of the 2012 National Survey on Drug Use and Health data in the present study. All Hispanic participants from 12 to 17 years of age (N = 3,457) completed the valid and reliable survey in the privacy of their own homes. The university-based Institutional Review Board granted approval to conduct this study. A total of 13.8 % of Hispanic youth reported recent alcohol use, and 8.0 % of these participants reported binge drinking. Hispanic youth who reported having low authoritative parenting was at significantly increased odds for reporting both recent alcohol use and binge drinking. Specifically, Hispanic youth with low authoritative parenting that were at increased risk for reporting alcohol use included males, females, the age group 14–15 years, and the age group 16–17 years compared to their counterparts with high authoritative parenting. Results from our study can be used to assist prevention specialists in more thoroughly understanding the protective influence authoritative parenting has on Hispanic youth involvement in alcohol use.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahr, S. J., & Hoffman, J. P. (2010). Parenting style, religiosity, peers, and adolescent heavy drinking. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 4, 539–543.
Baumrind, D. (1971). Current patterns of parental authority. Developmental Psychology, 4(1, pt 2), 1–103.
Baumrind, D. (1978). Parental disciplinary patterns and social competence in children. Youth and Society, 9, 239–276.
Belendiuk, K., Molina, B. S. G., & Donovan, J. E. (2010). Concordance of adolescent reports of friend alcohol use, smoking, and deviant behavior as predicted by quality of relationship and demographic variables. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 71(2), 253–257.
Bossarte, R. M., & Swahn, M. (2008). Interactions between race/ethnicity and psychosocial correlates of preteen alcohol use initiation among seventh grade students in an urban setting. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 69, 660–665.
Bourdeau, B., Miller, B. A., Duke, M. R., & Ames, G. M. (2011). Parental strategies for knowledge of adolescents’ friends: Distinct from monitoring? Journal of Child and Family Studies, 20(6), 814–821.
Castro, F. G., Stein, J. A., & Bentler, P. M. (2009). Ethnic pride, traditional family values, and acculturation in early cigarette and alcohol use among Latino adolescents. Journal of Primary Prevention, 30, 265–292.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (CDC). (2011). Youth risk behavior surveillance system: Selected 2011 national health risk behaviors and health outcomes by race/ethnicity. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Chen, M. J., Grube, J. W., Nygaard, P., & Miller, B. A. (2008). Identifying social mechanisms for the prevention of adolescent drinking and driving. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 40(2), 576–585.
Chromy, J. R., Feder, M., Gfoerer, J., Hirsch, E., Kennet, J., Morton, K. B., et al. (2010). Reliability of key measures in the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (HHS publication no. SMA 09-4425, Methodology series M-8). Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Office of Applied Studies.
Coatsworth, J. D., Pantin, H., & Szapocznik, J. (2002). Familias Unidas: A family-centered ecodevelopmental intervention to reduce risk for problem behavior among Hispanic adolescents. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 5, 113–132.
Coleman, L. M., & Cater, S. (2005). Underage “binge” drinking: A qualitative study into motivations and outcomes. Drugs, Education, Prevention, and Policy, 12, 125–136.
D’Amico, E. J., & McCarthy, D. M. (2006). Escalation and initiation of younger adolescent’s substance use: The impact of perceived peer use. Journal of Adolescent Health, 39, 481–487.
Demuth, S., & Brown, S. L. (2004). Family structure, family processes, and adolescent delinquency: The significance of parental absence versus parental gender. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 41(1), 58–81.
Driscoll, A. K., Russell, S. T., & Crockett, L. J. (2008). Parenting styles and youth well-being across immigrant generations. Journal of Family Issues, 29(2), 185–209.
Fendrich, M., Johnson, T. P., Sudman, S., Wislar, J. S., & Spiehler, V. (1999). Validity of drug use reporting in a high-risk community sample: A comparison of cocaine and heroin survey reports with hair tests. American Journal of Epidemiology, 149, 955–962.
Gfroerer, J., Eyerman, J., & Chromy, J. (2002). Redesigning an ongoing National Household Survey: Methodological issues (HHS publication no. SMA 03-3768). Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Office of Applied Studies.
Gil, A. G., Wagner, E. F., & Vega, W. A. (2000). Acculturation, familism, and alcohol use among Latino adolescent males: Longitudinal relations. Journal of Community Psychology, 28, 443–458.
Grant, B. F., Stinson, F. S., & Harford, T. C. (2001). Age at onset of alcohol use and DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence: A 12-year follow-up. Journal of Substance Use, 13(4), 493–504.
Guilamo-Ramos, V., Jaccard, J., Johansson, M., & Turrisi, R. (2004). Binge drinking among Latino youth: Role of acculturation-related variables. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 18(2), 135–142.
Hingson, R. W., Heeren, T., & Winter, M. R. (2006). Age at drinking onset and alcohol dependence: Age at onset, duration, and severity. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine, 160, 739–746.
Hussong, A. M., Huang, W., Serrano, D., Curran, P. J., & Chassin, L. (2012). Testing whether and when parent alcoholism uniquely affects various forms of adolescent substance use. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 40(8), 1265–1276.
Institute, Search. (2004). Tapping the power of community: Building assets to strengthen substance abuse prevention. Insights and Evidence, 2, 1–14.
Johnston, L. D., O’Malley, P. M., Bachman, J. G., & Schulenberg, J. E. (2012). Monitoring the future national results on drug use: 2012 Overview, key findings on adolescent drug use. Ann Arbor: Institute for Social Research, The University of Michigan.
Kam, J. A., Potocki, B., & Hecht, M. L. (2014). Encouraging Mexican-heritage youth to intervene when friends drink: The role of targeted parent–child communication against alcohol. Communication Research, 41(5), 644–664.
King, K. A., & Vidourek, R. A. (2010). Recent alcohol use and episodic heavy drinking among Hispanic youth. American Journal of Health Education, 41(4), 231–243.
King, K. A., Vidourek, R. A., Haag, M., & Merianos, A. (2012). Psychosocial factors associated with recent alcohol use among youth. Journal of Behavioral Health, 1(4), 231–242.
Kulis, S., Marsiglia, F. R., Elek, E., Dustman, P., Wagstaff, D. A., & Hecht, M. L. (2005). Mexican/Mexican American adolescents and keepin’ it REAL: An evidence-based substance use prevention program. Children and Schools, 27(3), 133–145.
Latendresse, S. J., Rose, R. J., Viken, R. J., Pulkkinen, L., Kaprio, J., & Dick, D. M. (2008). Parenting mechanisms in links between parents’ and adolescents’ alcohol use behaviors. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 32(2), 322–330.
Maccoby, E. E., & Martin, J. A. (1983). Socialization in the context of the family: Parent–child interaction. In P. H. Mussen (Ed.), Handbook of child psychology. Vol. 4: Socialization, personality, and social development (pp. 1–101). New York: Wiley.
Maradiegue, A. (2010). Central American mothers report family history of depression and alcohol abuse as a predictor of teenage health risk behaviors. Journal of the American Academy of Nurse Practitioners, 22(10), 540–547.
Marsden, J., Boys, A., Farrell, M., Stillwell, G., Hutchings, K., Hillebrand, J., et al. (2005). Personal and social correlates of alcohol consumption among mid-adolescents. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 23, 427–450.
Marsiglia, F. F., Ayers, S., Gance-Cleveland, B., Mettler, K., & Booth, J. (2012). Beyond primary prevention of alcohol use: A culturally specific secondary prevention program for Mexican heritage adolescents. Prevention Science, 13(3), 241–251.
Mogro-Wilson, C. (2008). The influence of parental warmth and control on Latino adolescent alcohol use. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 30, 89–105.
Myers, R., Chou, C. P., Sussman, S., Beazconde-Garbanati, L., Pachon, H., & Valente, T. W. (2009). Acculturation and substance use: Social influence as a mediator among Hispanic alternative high school youth. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 50(2), 164–179.
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. (2013). Parenting to prevent childhood alcohol use. National Institutes of Health. http://www.niaaa.nih.gov/.
Prado, G., & Pantin, H. (2011). Reducing substance use and HIV health disparities among Hispanic youth in the U.S.A.: The familias unidas program of research. Psychosocial Intervention, 20(1), 63–73.
Raffaelli, M., & Ontai, L. L. (2004). Gender socialization in Latino/a families: Results from two retrospective studies. Sex Roles, 50, 287–299.
Sale, E., Sombrano, S., Springer, J. F., Pena, C., Pan, W., & Kasim, R. (2005). Family protection and prevention of alcohol use among Hispanic youth at high risk. American Journal of Community Psychology, 36(3/4), 195–205.
Shakya, H. B., Christakis, N. A., & Fowler, J. H. (2012). Parental influence on substance use in adolescent social networks. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 166(12), 1132–1139.
Simons-Morton, B., & Chen, R. (2005). Latent growth curve analyses of parent influences on drinking progression among early adolescents. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 66(1), 5–13.
Smit, E., Verdurmen, J., Monshouwer, K., & Smit, F. (2008). Family interventions and their effect on adolescent alcohol use in general populations: A meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 97(3), 195–206.
Spoth, R. L., Randall, G. K., Trudeau, L., Shin, C., & Redmond, C. (2008). Substance use outcomes 5½ years past baseline for partnership-based, family-school preventive interventions. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 96(1–2), 57–68.
Steinberg, L. (2001). We know some things: Parent–adolescent relationships in retrospect and prospect. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 11(1), 1–19.
Stephens, P. C., Sloboda, Z., Stephens, R. C., Teasdale, N., Grey, S. F., Hawthorne, R. D., et al. (2009). Universal school-based substance abuse prevention programs: Modeling targeted mediators and outcomes for adolescent cigarette, alcohol, and marijuana use. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 102(1–3), 19–29.
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). (2012). Results from 2012 national survey on drug use and health: Summary of national findings. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Swahn, M. H., & Bossarte, R. M. (2007). Gender, early alcohol use, and suicide ideation and attempts: Findings from the 2005 Youth Risk Behavior Survey. Journal of Adolescent Health, 41, 175–181.
Torres Stone, R. A., & Meyler, D. (2007). Identifying potential risk and protective factors among non-metropolitan Latino youth: Cultural implications for substance use research. Journal of Immigrant Health, 9, 95–107.
Unger, J. B., Ritt-Olson, A., Wagner, K. D., Soto, D. W., & Baezconde-Garbanati, L. (2009). Parent–child acculturation patterns and substance use among Hispanic adolescents: A longitudinal analysis. Journal of Primary Prevention, 30(3–4), 239–313.
U.S. Census Bureau. (2014). USA people quick facts. U.S. Department of Commerce. http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/states/00000.html.
Vaughan, E. L., Kratz, L., & d’Argent, J. (2011). Academics and substance use among Latino adolescents: Results from a national study. Journal of Ethnicity in Substance Use, 10(2), 147–161.
Wilson, N., Battistich, V., Syme, S. L., & Boyce, W. T. (2002). Does elementary school alcohol, tobacco, and marijuana use increase middle school risk? Journal of Adolescent Health, 30(6), 442–447.
Windle, M., & Zucker, R. A. (2010). Reducing underage and young adult drinking. Alcohol Research and Health, 33(1/2), 29–44.
Wu, P., Hoven, C. W., Liu, X., Cohen, P., Fuller, C. J., & Shaffer, D. (2004). Substance use, suicidal ideation, and attempts in children and adolescents. Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior, 34, 408–420.
Yan, F. A., Beck, K. H., Howard, D., Shattuck, T. D., & Kerr, M. H. (2008). A structural model of alcohol use pathways among Latino youth. American Journal of Health Behavior, 32(2), 209–219.
Yasui, M., & Dishion, T. J. (2007). The ethnic context of child and adolescent problem behavior: Implications for child and family interventions. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 20(2), 137–179.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merianos, A.L., King, K.A., Vidourek, R.A. et al. Recent Alcohol Use and Binge Drinking Based on Authoritative Parenting Among Hispanic Youth Nationwide. J Child Fam Stud 24, 1966–1976 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-014-9996-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-014-9996-2