Abstract
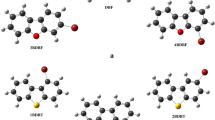
Novel derivatives of OD1 with D–A2–π–A1 configuration have been designed. The calculated geometrical parameters and optoelectronic properties are compared with those of the parent triphenylamine-based dye molecule (OD1) comprising a triphenylamine terminal electron-rich group (D), 3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene π-spacer, fluorophenyl electron-withdrawing group (A1), and cyanoacrylic acid anchor group. The designed derivatives differ from OD1 with D–π–A1 configuration in the incorporation of an electron-acceptor group (A2) between the donor group and π-spacer unit, namely benzotriazole (BTZ), benzothiadiazole (BTDZ), or phthalimide (PHI), denoted as ND2-BTZ, ND3-BTDZ, and ND4-PHI, respectively. The effects of the incorporation of each electron-deficient unit on the geometry, absorption spectra, and electrochemical properties are investigated by using density functional theory (DFT) and time-dependent (TD)DFT methods. Additionally, the preferred dye adsorption process on model Ti(OH)4 is investigated. The results for the binding energy, selected bond distances, highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) energy levels and their distribution, energy gaps, and total density of states (TDOS) plots are discussed and analyzed. The intermolecular interaction between two monomers of each dye and iodine is also investigated, and the complexation energy [corrected for the basis set superposition error (BSSE)] is calculated and analyzed. The results reveal that the introduction of the BTDZ and PHI functional groups is more promising for formation of organic dyes with D–A2–π–A1 configuration.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
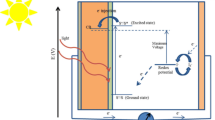
O’Regan, B., Gratzel, M.: A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature 353(6346), 737–740 (1991)
Obotowo, I.N., Obot, I.B., Ekpe, U.J.: Organic sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC): properties from computation, progress and future perspectives. J. Mol. Struct. 1122, 80–87 (2016)
Mishra, A., Fischer, M.K.R., Bäuerle, P.: Metal-free organic dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells: from structure: property relationships to design rules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48(14), 2474–2499 (2009)
Ooyama, Y., Harima, Y.: Photophysical and electrochemical properties, and molecular structures of organic dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells. ChemPhysChem 13(18), 4032–4080 (2012)
Gong, J., Liang, J., Sumathy, K.: Review on dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs): fundamental concepts and novel materials. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 16(8), 5848–5860 (2012)
Xia, H.-Q., et al.: Theoretical studies of electronic and optical properties of the triphenylamine-based organic dyes with diketopyrrolopyrrole chromophore. Dyes Pigm. 113, 87–95 (2015)
Yum, J.-H., et al.: Recent developments in solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells. ChemSusChem 1(8–9), 699–707 (2008)
Yang, Z., et al.: TDDFT screening auxiliary withdrawing group and design the novel D–A–π–A organic dyes based on indoline dye for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 167, 127–133 (2016)
Zhu, W., et al.: Organic D–A–π–A solar cell sensitizers with improved stability and spectral response. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21(4), 756–763 (2011)
Ding, W.-L., et al.: Density functional theory characterization and verification of high-performance indoline dyes with D-A–π–A architecture for dye-sensitized solar cells. Dyes Pigm. 98(1), 125–135 (2013)
Agarwala, P., Kabra, D.: A review on triphenylamine (TPA) based organic hole transport materials (HTMs) for dye sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) and perovskite solar cells (PSCs): evolution and molecular engineering. J. Mater. Chem. A 5(4), 1348–1373 (2017)
Eom, Y.K., et al.: Triphenylamine-based organic sensitizers with π-spacer structural engineering for dye-sensitized solar cells: synthesis, theoretical calculations, molecular spectroscopy and structure–property–performance relationships. Dyes Pigm. 136, 496–504 (2017)
Fahim, Z.M.E., et al.: Ground state geometries, UV/Vis absorption spectra and charge transfer properties of triphenylamine–thiophenes based dyes for DSSCs: a TD–DFT benchmark study. Comput. Theor. Chem. 1125, 39–48 (2018)
Liang, M., Chen, J.: Arylamine organic dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42(8), 3453–3488 (2013)
Chaitanya, K., Ju, X.-H., Heron, B.M.: Can elongation of the π-system in triarylamine derived sensitizers with either benzothiadiazole and/or ortho-fluorophenyl moieties enrich their light harvesting efficiency? A theoretical study. RSC Adv. 5(6), 3978–3998 (2015)
Chen, B.-S., et al.: Donor–acceptor dyes with fluorine substituted phenylene spacer for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 21(6), 1937–1945 (2011)
Wu, Y., Zhu, W.: Organic sensitizers from D–π–A to D-A–π–A: effect of the internal electron-withdrawing units on molecular absorption, energy levels and photovoltaic performances. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42(5), 2039–2058 (2013)
Becke, A.D.: Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 98(7), 5648–5652 (1993)
Yanai, T., Tew, D.P., Handy, N.C.: A new hybrid exchange-correlation functional using the Coulomb-attenuating method (CAM-B3LYP). Chem. Phys. Lett. 393(1–3), 51–57 (2004)
Zhao, Y., Truhlar, D.G.: The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 120(1), 215–241 (2008)
Ernzerhof, M., Perdew, J.P.: Generalized gradient approximation to the angle- and system-averaged exchange hole. J. Chem. Phys. 109(9), 3313–3320 (1998)
Martsinovich, N., Troisi, A.: Theoretical studies of dye-sensitised solar cells: from electronic structure to elementary processes. Energy Environ. Sci. 4(11), 4473–4495 (2011)
Barone, V., Cossi, M.: Quantum calculation of molecular energies and energy gradients in solution by a conductor solvent model. J. Phys. Chem. A 102(11), 1995–2001 (1998)
Hay, P.J., Wadt, W.R.: Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for the transition metal atoms Sc to Hg. J. Chem. Phys. 82(1), 270–283 (1985)
Boys, S.F., Bernardi, F.: Mol. Phys. 19, 553 (1970)
Chitpakdee, C., et al.: Theoretical studies on electronic structures and photophysical properties of anthracene derivatives as hole-transporting materials for OLEDs. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 125, 36–45 (2014)
Wu, Z., et al.: Organic molecules based on dithienyl-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole as new donor materials for solution-processed organic photovoltaic cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 94(12), 2230–2237 (2010)
Scharber, M.C., et al.: Design rules for donors in bulk-heterojunction solar cells—towards 10% energy-conversion efficiency. Adv. Mater. 18(6), 789–794 (2006)
Li, P., et al.: A systematic study of phenoxazine-based organic sensitizers for solar cells. Dyes Pigm. 137, 12–23 (2017)
Fan, W., Tan, D., Deng, W.Q.: Acene-modified triphenylamine dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells: a computational study. ChemPhysChem 13(8), 2051–2060 (2012)
Zhang, J., et al.: How to design proper π-spacer order of the D–π–A dyes for DSSCs? A density functional response. Dyes Pigm. 95(2), 313–321 (2012)
Zhang, G., et al.: Employ a bisthienothiophene linker to construct an organic chromophore for efficient and stable dye-sensitized solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2(1), 92–95 (2009)
Chen, P., et al.: High open-circuit voltage solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells with organic dye. Nano Lett. 9(6), 2487–2492 (2009)
Chi, W.-J., Li, Z.-S.: The theoretical investigation on the 4-(4-phenyl-4-[small alpha]-naphthylbutadieny)-triphenylamine derivatives as hole transporting materials for perovskite-type solar cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17(8), 5991–5998 (2015)
Reiss, H., Heller, A.: The absolute potential of the standard hydrogen electrode: a new estimate. J. Phys. Chem. 89(20), 4207–4213 (1985)
Li, W., et al.: Theoretical investigation of triphenylamine-based sensitizers with different π-spacers for DSSC. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 118, 1144–1151 (2014)
Hilborn, R.C.: Einstein coefficients, cross sections, f values, dipole moments, and all that. Am. J. Phys. 50(11), 982–986 (1982)
Kumar, P.S., et al.: Quantum chemistry calculations of 3-phenoxyphthalonitrile dye sensitizer for solar cells. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 77(1), 45–50 (2010)
Cai-Rong, Z., et al.: DFT and TDDFT study on organic dye sensitizers D5, DST and DSS for solar cells. J. Mol. Struct. (Thoechem) 899(1–3), 86–93 (2009)
Garza, A.J., et al.: Photochromic and nonlinear optical properties of fulgides: a density functional theory study. Comput. Theor. Chem. 1022, 82–85 (2013)
Dvorak, M., Wei, S.-H., Wu, Z.: Origin of the variation of exciton binding energy in semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(1), 016402 (2013)
Frisch, M.J.: Gaussian 09 Programmer’s Reference. Gaussian (2009)
Gorelsky, S.I.: Program for Molecular Orbital Analysis (2015)
Gorelsky, S.I., Lever, A.B.P.: Electronic structure and spectra of ruthenium diimine complexes by density functional theory and INDO/S. Comparison of the two methods. J. Organomet. Chem. 635, 187–196 (2001)
Dennington, R., Keith, T., Millam, J.: GaussView, S. Mission, Editor. Semichem Inc., KS (2009)
Zhurko, G., Zhurko, D.: Chemcraft Program, Academic version 1.8 (2009)
Hilal, R., et al.: Time dependent—density functional theory characterization of organic dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Mol. Simul. 43, 1523–1531 (2017)
Prajongtat, P., et al.: Density functional theory study of adsorption geometries and electronic structures of azo-dye-based molecules on anatase TiO2 surface for dye-sensitized solar cell applications. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 76, 551–561 (2017)
Lu, X., et al.: Can polypyridyl Cu(I)-based complexes provide promising sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells? A theoretical insight into Cu(I) versus Ru(II) sensitizers. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(9), 3753–3761 (2011)
Mandal, S., Rao, S., Ramanujam, K.: Understanding the photo-electrochemistry of metal-free di and tri substituted thiophene-based organic dyes in dye-sensitized solar cells using DFT/TD–DFT studies. Ionics 23, 3545–3554 (2017)
Soto-Rojo, R., Baldenebro-Lopez, J., Glossman-Mitnik, D.: Study of chemical reactivity in relation to experimental parameters of efficiency in coumarin derivatives for dye sensitized solar cells using DFT. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17(21), 14122–14129 (2015)
Guo, Y., et al.: Theoretical design of push-pull porphyrin dyes with π-bridge modification for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 332, 232–240 (2017)
Wazzan, N., El-Shishtawy, R.M., Irfan, A.: DFT and TD–DFT calculations of the electronic structures and photophysical properties of newly designed pyrene-core arylamine derivatives as hole-transporting materials for perovskite solar cells. Theor. Chem. Acc. 137(1), 9 (2017)
Fitri, A., et al.: Theoretical investigation of new thiazolothiazole-based D–π–A organic dyes for efficient dye-sensitized solar cell. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 124, 646–654 (2014)
Li, H.-B., et al.: Theoretical study and design of triphenylamine-malononitrile-based p-type organic dyes with different π-linkers for dyes-sensitized solar cells. Dyes Pigm. 108, 106–114 (2014)
Fu, J.-J., et al.: Theoretical investigation of novel phenothiazine-based D–π–A conjugated organic dyes as dye-sensitizer in dye-sensitized solar cells. Comput. Theor. Chem. 1045, 145–153 (2014)
Mehmood, U., et al.: Theoretical study of benzene/thiophene based photosensitizers for dye sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). Dyes Pigm. 118, 152–158 (2015)
Hosseinzadeh, E., Hadipour, N.L., Parsafar, G.: A computational investigation on the influence of different π spacer groups in the bithiazole-based organic dye sensitizers on the short-circuit photocurrent densities of dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 333, 70–78 (2017)
Fan, W., Deng, W.Q.: Incorporation of thiadiazole derivatives as π-spacer to construct efficient metal-free organic dye sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells: a theoretical study. Commun. Comput. Chem. 1(2), 152–170 (2013)
Huang, Z.-S., et al.: Dithienopyrrolobenzotriazole-based organic dyes with high molar extinction coefficient for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Dyes Pigm. 125, 229–240 (2016)
Garza, A.J., et al.: Nonlinear optical properties of DPO and DMPO: a theoretical and computational study. Theor. Chem. Acc. 132(9), 1384 (2013)
Hara, K., et al.: Molecular design of coumarin dyes for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. B 107(2), 597–606 (2003)
Nazeeruddin, M.K., et al.: Investigation of sensitizer adsorption and the influence of protons on current and voltage of a dye-sensitized nanocrystalline TiO2 solar cell. J. Phys. Chem. B 107(34), 8981–8987 (2003)
Namuangruk, S., et al.: Coumarin-based donor–π–acceptor organic dyes for a dye-sensitized solar cell: photophysical properties and electron injection mechanism. Theor. Chem. Acc. 135(1), 14 (2015)
Wang, Z., et al.: Photosensitization of ITO and nanocrystalline TiO2 electrode with a hemicyanine derivative. Synth. Met. 114(2), 201–207 (2000)
Xu, W., et al.: New triphenylamine-based dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 112(3), 874–880 (2008)
Zhang, J., et al.: Density functional theory characterization and design of high-performance diarylamine-fluorene dyes with different π spacers for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 22(2), 568–576 (2012)
Yella, A., et al.: Molecular engineering of a fluorene donor for dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Mater. 25(13), 2733–2739 (2013)
Wang, X., et al.: A benzothiazole-cyclopentadithiophene bridged D–A–π–A sensitizer with enhanced light absorption for high efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Commun. 50(30), 3965–3968 (2014)
Srinivas, K., et al.: Novel 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives as efficient sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells: a combined experimental and computational study. Synth. Met. 161(15), 1671–1681 (2011)
He, L.-J., et al.: Fine-tuning π-spacer for high efficiency performance DSSC: a theoretical exploration with D–π–A based organic dye. Dyes Pigm. 141, 251–261 (2017)
Green, A.N.M., et al.: Transient absorption studies and numerical modeling of iodine photoreduction by nanocrystalline TiO2 films. J. Phys. Chem. B 109(1), 142–150 (2005)
Acknowledgements
The author gratefully acknowledges King Abdulaziz University’s High-Performance Computing Center (Aziz Supercomputer) (http://hpc.kau.edu.sa) for assisting with the calculations presented herein.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wazzan, N.A. A DFT/TDDFT investigation on the efficiency of novel dyes with ortho-fluorophenyl units (A1) and incorporating benzotriazole/benzothiadiazole/phthalimide units (A2) as organic photosensitizers with D–A2–π–A1 configuration for solar cell applications. J Comput Electron 18, 375–395 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-019-01308-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-019-01308-4