Abstract
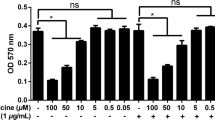
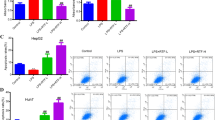
The phlorotannin compounds, dieckol and phlorofucofuroeckol (PFF), extracted from Ecklonia cava, have been suggested to exhibit anti-inflammatory, anti-adipogenic or anti-tumorigenic activity. However, role of dieckol or PFF in LPS/TLR-4 signaling that regulates cancer development still remains to be determined. Here we report that dieckol or PFF blocked lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced migration and invasion of human breast cancer MCF-7 or MDA-MB-231 cells by about 50% (p < 0.0001) or 60% (p = 0.0001), respectively. Also, PFF as well as dieckol markedly attenuated both of LPS-induced Toll-like receptor4 (TLR-4) expression and NF-κB promoter-driven transcriptional activity, which are essential for the migration and invasion. Moreover, LPS induction of NF-κB-dependent gene, matrix metalloproteinase9 (MMP-9) was markedly decreased about 2.6 or 2.5 fold by dieckol and PFF, respectively. In addition, LPS-induced MMP-2 gene expression was reduced about 1.7 or 2.1 fold by dieckol and PFF, respectively. Significantly, each inhibitor of MMP-9 or NF-κB notably reduced invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells in response to LPS by about 70% (p = 0.0115) or 40% (p < 0.0001), respectively. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that both of dieckol and PFF functions as a critical inhibitor of LPS-induced breast cancer cell invasion through downregulation of TLR-4-NF-κB-MMP-9 signaling axis, suggesting a potential role of the phlorotannins in inflammation-mediated breast cancer development.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed A, Redmond HP, Wang JH (2013) Links between toll-like receptor 4 and breast cancer. Oncoimmunology 2:e22945
Ahn MJ, Yoon KD, Min SY, Lee JS, Kim JH, Kim TG, Kim SH, Kim NG, Huh H, Kim J (2004) Inhibition of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and protease by phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia cava. Biol Pharm Bull 27:544–547
Choi HJ, Park JH, Lee BH, Chee HY, Lee KB, Oh SM (2014) Suppression of NF-κB by dieckol extracted from Ecklonia cava negatively regulates LPS induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase gene. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173:957–967
Chuang HC, Huang CC, Chien CY, Chuang JH (2012) Toll-like receptor 3-mediated tumor invasion in head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol 48:226–232
Ehsan N, Murad S, Ashiq T, Mansoor MU, Gul S, Khalid S, Younas M (2013) Significant correlation of TLR-4 expression with the clinicopathological features of invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Tumour Biol 34:1053–1059
Eo HJ, Kwon TH, Park GH, Song HM, Lee SJ, Park NH, Jeong JB (2016) In vitro anticancer activity of phlorofucofuroeckol a via upregulation of activating transcription factor 3 against human colorectal cancer cells. Mar Drugs 14:69
Eom SH, Lee DS, Jung YJ, Park JH, Choi JI, Yim MJ, Jeon JM, Kim HW, Son KT, Je JY, Lee MS, Kim YM (2014) The mechanism of antibacterial activity of phlorofucofuroeckol-A against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:9795–9804
Erridge C (2010) Endogenous ligands of TLR2 and TLR-4: agonists or assistants? J Leukoc Biol 87:989–999
Gialeli C, Theocharis AD, Karamanos NK (2011) Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their pharmacological targeting. FEBS J 278:16–27
Güney Eskiler G, Deveci Özkan A, Kaleli S, Bilir C (2019) Inhibition of TLR4/TRIF/IRF3 signaling pathway by curcumin in breast cancer cells. J Pharm Pharm Sci 22:281–291
Harmey JH, Bucana CD, Lu W, Byrne AM, McDonnell S, Lynch C, Bouchier-Hayes D, Dong Z (2002) Lipopolysaccharide-induced metastatic growth is associated with increased angiogenesis, vascular permeability and tumor cell invasion. Int J Cancer 101:415–422
Hassan F, Islam S, Tumurkhuu G, Naiki Y, Koide N, Mori I, Yoshida T, Yokochi T (2006) Intracellular expression of toll-like receptor 4 in neuroblastoma cells and their unresponsiveness to lipopolysaccharide. BMC Cancer 6:281
Jung HA, Jin SE, Ahn BR, Lee CM, Choi JS (2013) Anti-inflammatory activity of edible brown alga Eisenia bicyclis and its constituents fucosterol and phlorotannins in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Food Chem Toxicol 59:199–206
Jung HA, Jung HJ, Jeong HY, Kwon HJ, Ali MY, Choi JS (2014) Phlorotannins isolated from the edible brown alga Ecklonia stolonifera exert anti-adipogenic activity on 3T3-L1 adipocytes by downregulating C/EBPα and PPARγ. Fitoterapia 92:260–269
Kang HS, Chung HY, Kim JY, Son BW, Jung HA, Choi JS (2004) Inhibitory phlorotannins from the edible brown alga Ecklonia stolonifera on total reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Arch Pharm Res 27:194–198
Kim IH, Nam TJ (2017) Enzyme-treated Ecklonia cava extract inhibits adipogenesis through the downregulation of C/EBPα in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Int J Mol Med 39:636–644
Kim AR, Lee MS, Shin TS, Hua H, Jang BC, Choi JS, Byun DS, Utsuki T, Ingram D, Kim HR (2011) Phlorofucofuroeckol A inhibits the LPS-stimulated iNOS and COX-2 expressions in macrophages via inhibition of NF-κB, Akt, and p38 MAPK. Toxicol in Vitro 25:1789–1795
Kim AR, Lee MS, Choi JW, Utsuki T, Kim JI, Jang BC, Kim HR (2013) Phlorofucofuroeckol a suppresses expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2, and pro-inflammatory cytokines via inhibition of nuclear factor-κB, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases, and Akt in microglial cells. Inflammation 36:259–271
Kim EK, Tang Y, Kim YS, Hwang JW, Choi EJ, Lee JH, Lee SH, Jeon YJ, Park PJ (2015) First evidence that Ecklonia cava-derived dieckol attenuates MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cell migration. Mar Drugs 13:1785–1797
Kim JJ, Kang YJ, Shin SA, Bak DH, Lee JW, Lee KB, Yoo YC, Kim DK, Lee BH, Kim DW, Lee J, Jo EK, Yuk JM (2016) Phlorofucofuroeckol improves glutamate-induced neurotoxicity through modulation of oxidative stress-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction in PC12 cells. PLoS One 11:e0163433
Kwon TH, Wu YX, Kim JS, Woo JH, Park KT, Kwon OJ, Seo HJ, Kim T, Park NH (2015) 6,6'-Bieckol inhibits adipocyte differentiation through downregulation of adipogenesis and lipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. J Sci Food Agric 95:1830–1837
Lee MS, Lee B, Park KE, Utsuki T, Shin T, Oh CW, Kim HR (2015) Dieckol enhances the expression of antioxidant and detoxifying enzymes by the activation of Nrf2-MAPK signalling pathway in HepG2 cells. Food Chem 174:538–546
Li D, Gu R, Yang X, Hu C, Li Y, Gao M, Yu Y (2014) TLR3 correlated with cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med 7:5111–5117
Liao SJ, Zhou YH, Yuan Y, Li D, Wu FH, Wang Q, Zhu JH, Yan B, Wei JJ, Zhang GM, Feng ZH (2012) Triggering of toll-like receptor 4 on metastatic breast cancer cells promotes αvβ3-mediated adhesion and invasive migration. Breast Cancer Res Treat 133:853–863
Lim B, Woodward WA, Wang X, Reuben JM, Ueno NT (2018) Inflammatory breast cancer biology: the tumour microenvironment is key. Nat Rev Cancer 18:485–499
Lu YC, Yeh WC, Ohashi PS (2008) LPS/TLR-4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 42:145–151
Myung CS, Shin HC, Bao HY, Yeo SJ, Lee BH, Kang JS (2005) Improvement of memory by dieckol and phlorofucofuroeckol in ethanol-treated mice: possible involvement of the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase. Arch Pharm Res 28:691–698
Park GS, Kim JH (2015) LPS up-regulates ICAM-1 expression in breast cancer cells by stimulating a MyD88-BLT2-ERK-linked cascade, which promotes adhesion to monocytes. Mol Cell 38:821–828
Park GB, Kim D (2017) TLR5/7-mediated PI3K activation triggers epithelial-mesenchymal transition of ovarian cancer cells through WAVE3-dependent mesothelin or OCT4/SOX2 expression. Oncol Rep 38:3167–3176
Prasad S, Ravindran J, Aggarwal BB (2010) NF-κB and cancer: how intimate is this relationship. Mol Cell Biochem 336:25–37
Radisky ES, Radisky DC (2015) Matrix metalloproteinases as breast cancer drivers and therapeutic targets. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 20:1144–1163
Seol MA, Park JH, Jeong JH, Lyu J, Han SY, Oh SM (2017) Role of TOPK in lipopolysaccharide-induced breast cancer cell migration and invasion. Oncotarget 8:40190–40203
Slattery ML, John E, Torres-Mejia G, Stern M, Lundgreen A, Hines L, Giuliano A, Baumgartner K, Herrick J, Wolff RK (2013) Matrix metalloproteinase genes are associated with breast cancer risk and survival: the breast cancer health disparities study. PLoS One 8:e63165
Szajnik M, Szczepanski MJ, Czystowska M, Elishaev E, Mandapathil M, Nowak-Markwitz E, Spaczynski M, Whiteside TL (2009) TLR-4 signaling induced by lipopolysaccharide or paclitaxel regulates tumor survival and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 28:4353–4363
Wang W, Wang J (2018) Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4)/cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) regulates prostate cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by NF-κB activation. Med Sci Monit 24:5588–5597
Wang X, Yu X, Wang Q, Lu Y, Chen H (2017) Expression and clinical significance of SATB1 and TLR-4 in breast cancer. Oncol Lett 14:3611–3615
Wijesekara I, Yoon NY, Kim SK (2010) Phlorotannins from Ecklonia cava (Phaeophyceae): biological activities and potential health benefits. Biofactors 36:408–414
Yang H, Wang B, Wang T, Xu L, He C, Wen H, Yan J, Su H, Zhu X (2014) Toll-like receptor 4 prompts human breast cancer cells invasiveness via lipopolysaccharide stimulation and is overexpressed in patients with lymph node metastasis. PLoS One 9:e109980
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grants funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (NRF-2016R1A2B1013313). This work was also supported in part by the Priority Research Centers Program through the NRF funded by the MEST (NRF-2017R1A6A1A03015713).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YJ., Park, JH., Park, SA. et al. Dieckol or phlorofucofuroeckol extracted from Ecklonia cava suppresses lipopolysaccharide-mediated human breast cancer cell migration and invasion. J Appl Phycol 32, 631–640 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01899-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01899-2