Abstract
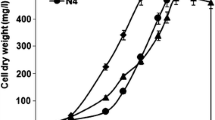
We investigated the proteomic and physiological responses of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa, to nitrogen (N) starvation, phosphorus (P) starvation, and the simultaneous starvation of N and P. Our results suggested that M. aeruginosa could maintain nearly normal growth under P starvation for at least 7 days, whereas N deficiency significantly decreased M. aeruginosa growth. Orange carotenoid-binding proteins, metallothionein, and several conserved exported hypothetical proteins were found differentially regulated with a similar manner responding to N starvation and P starvation, indicating general stress response roles for these proteins. Upon N starvation, the expression of several proteins involved in cellular carbon metabolism and carbon fixation was enhanced, which may enable their effective reuse of cellular substrates and accumulate glycogen for long-term survival. Upon P starvation, several proteins relating to protein synthesis and the assimilation of carbon and N were downregulated, suggesting a general reduction in the cell’s metabolic rate, which could save energy and reducing power to maintain the basal growth. Though M. aeruginosa growth was significantly reduced when both N and P were unavailable, very limited significant changes in the proteomic composition were identified.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MM (1984) Cyanobacterial cell inclusions. Annu Rev Microbiol 38:1–25
Behrenfeld MJ, Worthington K, Sherrell RM, Chavez FP, Strutton P, McPhaden M, Shea DM (2006) Controls on tropical Pacific Ocean productivity revealed through nutrient stress diagnostics. Nature 442:1025–1028
Blindauer CA, Leszczyszyn OI (2010) Metallothioneins: unparalleled diversity in structures and functions for metal ion homeostasis and more. Nat Prod Rep 27:720–741
Chaffin JD, Bridgeman TB (2014) Organic and inorganic nitrogen utilization by nitrogen-stressed cyanobacteria during bloom conditions. J Appl Phycol 26:299–309
Dai RH, Liu HJ, Qu JH et al (2008) The effects of nitrogen limitation and phosphorus limitation on the growth and microcystin production of Microcystis aeruginosa. Acta Sci Circumst 28:1739–1744
Dyhrman S, Chappell P, Haley S, Moffett J, Orchard E, Waterbury J, Webb E (2006) Phosphonate utilization by the globally important marine diazotroph Trichodesmium. Nature 439:68–71
Gan CS (2006) Response of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 to photoperiod and phosphate alterations using functional proteomics approaches. Dissertation, University of Sheffield
Gomez-Garcia MR, Losada M, Serrano A (2003) Concurrent transcriptional activation of ppa and ppx genes by phosphate deprivation in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp strain PCC 6803. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 302:601–609
Grasses T, Grimm B, Koroleva O, Jahns P (2001) Loss of alpha-tocopherol in tobacco plants with decreased geranylgeranyl reductase activity does not modify photosynthesis in optimal growth conditions but increases sensitivity to high-light stress. Planta 213:620–628
Harke MJ, Gobler CJ (2013) Global Transcriptional responses of the toxic cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa, to nitrogen stress, phosphorus stress, and growth on organic matter. PLoS One 8:e69834
Huang S, Chen L, Te R, Qiao J, Wang J, Zhang W (2013) Complementary iTRAQ proteomics and RNA-seq transcriptomics reveal multiple levels of regulation in response to nitrogen starvation in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Mol BioSyst 9:2565–2574
Huisman J, Matthijs HC, Visser PPM (2005) Harmful cyanobacteria. Springer, Dordrecht
Ishii A, Hihara Y (2008) An AbrB-like transcriptional regulator, Sll0822, is essential for the activation of nitrogen-regulated genes in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Physiol 148:660–670
Kaniya Y, Kizawa A, Miyagi A, Kawai-Yamada M, Uchimiya H, Kaneko Y, Nishiyama Y, Hihara Y (2013) Deletion of the transcriptional regulator cyAbrB2 deregulates primary carbon metabolism in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Physiol 162:1153–1163
Kulaev IS, Vagabov VM (1983) Polyphosphate metabolism in micro-organisms. Adv Microb Physiol 24:83–171
Kurian D, Phadwal K, Mäenpää P (2006) Proteomic characterization of acid stress response in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Proteomics 6:3614–3624
Liu XD, Zeng BF, Xu JG, Zhu HB, Xia QC (2006) Proteomic analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with lumbar disk herniation. Proteomics 6:1019–1028
Moisander PH, Ochiai M, Lincoff A (2009) Nutrient limitation of Microcystis aeruginosa in northern California Klamath River reservoirs. Harmful Algae 8:889–897
Moore CM, Mills MM, Langlois R, Milne A, Achterberg EP, La Roche J, Geider RJ (2008) Relative influence of nitrogen and phosphorus availability on phytoplankton physiology and productivity in the oligotrophic sub-tropical North Atlantic Ocean. Limnol Oceanogr 53:291–305
O’Neil JM, Davis TW, Burford MA, Gobler CJ (2012) The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: the potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 14:313–334
Rao NN, Kornberg A (1999) Inorganic polyphosphate regulates responses of Escherichia coli to nutritional stringencies, environmental stresses and survival in the stationary phase. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 23:183–195
Salomon E, Bar-Eyal L, Sharon S, Keren N (2013) Balancing photosynthetic electron flow is critical for cyanobacterial acclimation to nitrogen limitation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1827:340–347
Sauer J, Schreiber U, Schmid R, Völker U, Forchhammer K (2001) Nitrogen starvation-induced chlorosis in Synechococcus PCC 7942. Low-level photosynthesis as a mechanism of long-term survival. Plant Physiol 126:233–243
Schwarz R, Forchhammer K (2005) Acclimation of unicellular cyanobacteria to macronutrient deficiency: emergence of a complex network of cellular responses. Microbiology 151:2503–2514
Shpilyov AV, Zinchenko VV, Shestakov SV, Grimm B, Lokstein H (2005) Inactivation of the geranylgeranyl reductase (ChlP) gene in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Biochim Biophys Acta 1706:195–203
Smith VH, Joye SB, Howarth RW (2006) Eutrophication of freshwater and marine ecosystems. Limnol Oceanogr 51:351–355
Solorzano L, Sharp JH (1980) Determination of total dissolved phosphorus and particulate phosphorus in natural waters. Limnol Oceanogr 25:754–758
Sun MM, Sun J, Qiu JW, Jing H, Liu H (2012) Characterization of the proteomic profiles of the brown tide alga Aureoumbra lagunensis under phosphate- and nitrogen-limiting conditions and of its phosphate limitation-specific protein with alkaline phosphatase activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:2025–2033
Wegener KM, Singh AK, Jacobs JM, Elvitigala T, Welsh EA, Keren N, Gritsenko MA, Ghosh BK, Camp DG II, Smith RD, Pakrasi HB (2010) Global proteomics reveal an atypical strategy for carbon/nitrogen assimilation by a cyanobacterium under diverse environmental perturbations. Mol Cell Proteomics 9:2678–2689
Wilson A, Ajlani G, Verbavatz J-M, Vass I, Kerfeld CA, Kirilovsky D (2006) A soluble carotenoid protein involved in phycobilisome-related energy dissipation in cyanobacteria. Plant Cell 18:992–1007
Wilson A, Punginelli C, Gall A, Bonetti C, Alexandre M, Routaboul J-M, Kerfeld CA, van Grondelle R, Robert B, Kennis JT (2008) A photoactive carotenoid protein acting as light intensity sensor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:12075–12080
Xu H, Paerl HW, Qin B, Zhu G, Gao G (2010) Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol Oceanogr 55:420–432
Yue D, Peng Y, Qian X, Xiao L (2014) Spatial and seasonal patterns of size-fractionated phytoplankton growth in Lake Taihu. J Plankton Res 36:709–721
Acknowledgments
We thank Chen-rui Hou from Shanghai Applied Protein Technology Co., Ltd. for technical assistance. We thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive and helpful comments on this work. This research was supported by the National Basic Research Program (973) of China (No. 2008CB418003), the National Special Program of Water Environment (2012ZX07101006), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41071313).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, D., Peng, Y., Yin, Q. et al. Proteomic analysis of Microcystis aeruginosa in response to nitrogen and phosphorus starvation. J Appl Phycol 27, 1195–1204 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0405-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0405-4