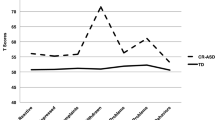
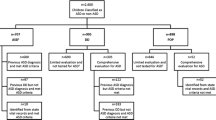
Abstract
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) diagnostic tools are not designed for mental ages (MA) below 12 months. Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) and Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS) were examined in 2-year-olds with ASD-low MA (n = 53), Global Developmental Delay (GDD; n = 175), and ASD-higher MA (n = 425). ADOS and CARS demonstrated similar agreement with clinical diagnosis, but ADOS over-classified ASD in low MA, whereas CARS both over- and under-classified. All ADOS items differentiated GDD from ASD. Elementary social behaviors (e.g., eye contact, social interest) were similar across ASD groups, although advanced skills (e.g., pointing, play) were more impaired in ASD-low MA. ASD-low MA, a severe presentation, may require a modified ADOS algorithm to account for developmental delays.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th edn., text rev.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th edn.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Baranek, G. T. (1999). Autism during infancy: A retrospective video analysis of sensory-motor and social behaviors at 9–12 months of age. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29(3), 213–224.
Baron-Cohen, S., Cox, A., Baird, G., Swettenham, J., Nightingale, N., Morgan, K., … Charman, T. (1996). Psychological markers in the detection of autism in infancy in a large population. British Journal of Psychiatry, 168, 158–163.
Brereton, A. V., Tonge, B. J., MacKinnon, A. J., & Einfeld, S. L. (2002). Screening young people for autism with the Developmental Behavior Checklist. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 41(11), 1369–1375.
Bryson, S. E., Zwaigenbaum, L., McDermott, C., Rombough, V., & Brian, J. (2008). The autism observation scale for infants: Scale development and reliability data. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38, 731–738.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2016). Prevalence and characteristics of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years – Autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2012. April 1st, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report Surveillance Summaries.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2018). Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years – Autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2014. April 27th, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report Surveillance Summaries.
Chlebowski, C., Green, J. A., Barton, M. L., & Fein, D. (2010). Using the Childhood Autism Rating Scale to diagnose autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40(7), 787–799.
Crais, E. R., Watson, L. R., Baranek, G. T., & Reznick, J. S. (2006). Early identification of autism: How early can we go? Seminars in Speech and Language, 27(3), 143–160.
Dahlgren, S. O., & Gillberg, C. (1989). Symptoms in the first two years of life: A preliminary population study of infantile autism. European Archives of Psychiatry and Neurological Sciences, 238, 169–174.
Desombre, H., Malvy, J., Roux, S., de Villard, R., Sauvage, D., Dalery, J., & Lenoir, P. (2006). Autism and developmental delay: A comparative clinical study in very young children using IBSE scale. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 15(6), 343–351.
Einfeld, S. L., & Tonge, B. J. (1996). Population prevalence of psychopathology in children and adolescents with intellectual disability: II. Epidemiological findings. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 40, 99–109.
Frick, R. W. (1995). Accepting the null hypothesis. Memory & Cognition, 23(1), 132–138.
Gardner, L. M., Campbell, J. M., Bush, A. J., & Murphy, L. (2018). Comparing behavioral profiles for autism spectrum disorders and intellectual disabilities using the BASC-2 Parent Rating Scales – Preschool Form. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 36(6), 535–551.
Gotham, K., Risi, S., Pickles, A., & Lord, C. (2007). The Autism Diagnostic observation schedule: Revised algorithms for improved diagnostic validity. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37, 613–627.
Gray, K. M., Tonge, B. J., & Sweeney, D. J. (2008). Using the Autism Diagnostic Interview – Revised and the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule with young children with developmental delay: Evaluating diagnostic validity. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38, 657–667.
Hazlett, H. C., Gu, H., Munsell, B. C., Kim, S. H., Styner, M., Wolff, J. J. … the IBIS Network (2017). Early brain development in infants at high risk for autism spectrum disorder. Nature, 542, 348–351.
Hinnebusch, A. J., Miller, L. E., & Fein, D. A. (2017). Autism spectrum disorders and low mental age: Diagnostic stability and developmental outcomes in early childhood. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 47, 3967–3982.
IBM Corp. (2013). IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 22.0.Armonk NY: IBM Corp.
Inada, N., Kamio, Y., & Koyama, T. (2010). Developmental chronology of preverbal social behaviors in infancy using the M-CHAT: Baseline for early detection of atypical social development. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 4(4), 605–611.
Jeste, S. S., Varcin, K. J., Hellemann, G. S., Gulsrud, A. C., Bhatt, R., Kasari, C., … Nelson, C. A. (2016). Symptom profiles of autism spectrum disorder in tuberous sclerosis complex. Neurology, 87, 766–772.
Jones, W., & Klin, A. (2013). Attention to eyes is present but in decline in 2-6-month-old infants later diagnosed with autism. Nature, 504, 427–431.
Klin, A., Lang, J., Cicchetti, D. V., & Volkmar, F. R. (2000). Brief report: Interrater reliability of clinical diagnosis and DSM-IV criteria for autistic disorder: Results of the DSM-IV field trial. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30(2), 163–167.
Lord, C., Luyster, R. J., Gotham, K., & Guthrie, W. (2012). Autism diagnostic observation schedule, second edition (ADOS-2) (Part II): Toddler module [Manual]. Torrance: Western Psychological Services.
Lord, C., Risi, S., & Lambrecht, L. (2000). The autism diagnostic observation schedule - generic: A standard measure of social and communication deficits associated with the spectrum of autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30(3), 205–223.
Luyster, R., Gotham, K., Guthrie, W., Coffing, M., Petrak, R., Pierce, K., … Risi, S. (2009). The Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule – Toddler Module: A new module of standardized diagnostic measure for autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39(9), 1305–1320.
Maestro, S., Muratori, F., Cesari, A., Cavallaro, M. C., Paziente, A., Pecini, C., … Sommario, C. (2005). Course of autism signs in the first year of life. Psychopathology, 38, 26–31.
Martinez-Pedraza, F. L., & Carter, A. S. (2009). Autism spectrum disorders in young children. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 18(3), 645–663.
Menard, S. (1995). Applied logistic regression analysis. Sage University paper series on quantitative applications in the social sciences (series no. 07). 106. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Morgan, S. (1988). Diagnostic assessment of autism: A review of objective scales. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 6, 139–151.
Mullen, E. M. (1995). Mullen Scales of Early Learning. Circle Pines: American Guidance Services.
Osterling, J. A., Dawson, G., & Munson, J. A. (2002). Early recognition of 1-year-old infants with autism spectrum disorder versus mental retardation. Development and Psychopathology, 14, 239–251.
Ozonoff, S., Iosif, A.-M., Baguio, F., Cook, I. C., Hill, M. M., Hutman, T., … Young, G. S. (2010). A prospective study of the emergence of early behavioral signs of autism. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 49(3), 256–266.
Riou, E. M., Ghosh, S., Francoeur, E., & Shevell, M. I. (2009). Global developmental delay and its relationship to cognitive skills. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, 51(8), 600–606.
Risi, S., Lord, C., Gotham, K., Corsello, C., Chrysler, C., Szatmari, P., … Pickles, A. (2006). Combining information from multiple sources in the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 45(9), 1094–1103.
Rivard, M., Terroux, A., Mercier, C., & Parent-Boursier, C. (2015). Indicators of intellectual disabilities in young children with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45, 127–137.
Robins, D. L., Casagrande, K., Barton, M., Chen, C.-M. A., Dumont-Mathieu, T., & Fein, D. (2014). Validation of the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers, Revised with Follow-up (M-CHAT-R/F). Pediatrics, 133, 37–45.
Robins, D. L., Fein, D., Barton, M. L., & Green, J. A. (2001). The Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers: An initial study investigating the early detection of autism and pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 31(2), 131–144.
Rowberry, J., Macari, S., Chen, G., Campbell, D., Leventhal, J. M., Weitzman, C., & Chawarska, K. (2015). Screening for autism spectrum disorders in 12-month-old high-risk siblings by parental report. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(1), 221–229.
Rutter, M., LeCouteur, A., & Lord, C. (2003). Autism diagnostic interview – revised. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services.
Schopler, E., Reichler, R. J., & Renner, B. R. (1988). Childhood autism rating scale. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services.
Schopler, E., Reichler, R. J., & Renner, B. R. (1995). Childhood autism rating scale: Manual. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services.
Schopler, E., Van Bourgondien, M. E., Wellman, G. J., & Love, S. R. (2010). Childhood autism rating scale, second edition (CARS2) [Manual]. Torrance: Western Psychological Services.
Sparrow, S. S., Balla, D. A., & Cicchetti, D. V. (1984). Vineland adaptive behavior scales. Circle Pines: American Guidance Services.
Sparrow, S. S., Cicchetti, D. V., & Balla, D. A. (2005). Vineland adaptive behavior scales (2nd edn.). Circle Pines: American Guidance Services.
Teal, M. B., & Wiebe, M. J. (1986). A validity analysis of selected instruments used to assess autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 16(4), 485–494.
Ventola, P. E., Kleinman, J., Pandey, J., Barton, M., Allen, S., Green, J., … Fein, D. (2006). Agreement among four diagnostic instruments for autism spectrum disorders in toddlers. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 36, 839–847.
Vig, S., & Jedrysek, E. (1999). Autistic features in young children with significant cognitive impairment: Autism or mental retardation? Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29(3), 235–248.
Watson, L. R., Baranek, G. T., & DiLavore, P. C. (2003). Toddlers with autism: Developmental perspectives. Infants and Young Children, 16(3), 201–214.
Zwaigenbaum, L., Bauman, M. L., Choueiri, R., Kasari, C., Carter, A., Granpeesheh, D., … Natowicz, M. R. (2015). Early intervention for children with autism spectrum disorder under 3 years of age: recommendations for practice and research. Pediatrics, 136(Supplement 1), S60–S81.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors thank the families who participated in the current study, the physicians who assisted by offering the M-CHAT(-R) screening study to their patients, and the research teams at the University of Connecticut and Georgia State University. This manuscript was prepared from LM’s doctoral dissertation; accordingly, she thanks Marianne Barton, Ph.D., Rhiannon Smith, Ph.D., and Juliane Fenster, Ph.D. for their helpful feedback on earlier versions of the text. The authors also acknowledge the following sources of funding: Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Grant R01HD039961, Maternal and Child Health Bureau Grant R40MC00270, U.S. Department of Education Student-Initiated Research Grant, the University of Connecticut’s Research Foundation Faculty Grant, the National Alliance of Autism Research, and a National Institute of Mental Health Predoctoral Fellowship F31MH12550.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Diana Robins and Deborah Fein are part owners of M-CHAT, LLC, which receives royalties from companies that incorporate the M-CHAT(-R) into commercial products and charge for its use. Data reported in this manuscript are from the freely available paper version of the M-CHAT(-R). Lauren Miller and Jeffrey Burke declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from caregivers of all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, L.E., Burke, J.D., Robins, D.L. et al. Diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children with Low Mental Age. J Autism Dev Disord 49, 1080–1095 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-018-3810-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-018-3810-8