Abstract
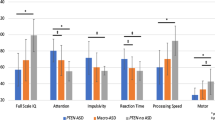
Truncating variants of the MAGEL2 gene, one of the protein-coding genes within the Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) critical region on chromosome 15q11, cause Schaaf-Yang syndrome (SYS)—a neurodevelopmental disorder that shares several clinical features with PWS. The current study sought to characterize the neurobehavioral phenotype of SYS in a sample of 9 patients with molecularly-confirmed SYS. Participants received an assessment of developmental/intellectual functioning, adaptive functioning, autism symptomatology, and behavioral/emotional functioning. Compared to individuals with PWS, patients with SYS manifested more severe cognitive deficits, no obsessions or compulsions, and increased rates of autism spectrum disorder.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Arlington: American Psychiatric Association.
Bennett, J. A., Germani, T., Haqq, A. M., & Zwaigenbaum, L. (2015). Autism spectrum disorder in Prader-Willi syndrome: A systematic review. American Journal of Medical Genetics A, 167(12), 2936–2944.
Cassidy, S. B., Schwartz, S., Miller, J. L., & Driscoll, D. J. (2012). Prader-Willi syndrome. Genetics in Medicine, 14(1), 10–26.
Constantino, J. N., & Gruber, C. P. (2012). Social Responsiveness Scale (2nd ed.). Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services.
Curfs, L. M. G., & Fryns, J.-P. (1992). Prader-Willi syndrome: A review with special attention to the cognitive and behavioral profile. Birth Defects: Original Article Series, 28(1), 99–104.
Dykens, E. M., Cassidy, S. B., & King, B. H. (1999). Maladaptive behavior differences in Prader-Willi syndrome due to paternal deletion versus maternal uniparental disomy. American Journal on Mental Retardation, 104(1), 67–77.
Dykens, E. M., Hodapp, R. M., Walsh, K., & Nash, L. J. (1992). Adaptive and maladaptive behavior in Prader-Willi syndrome. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 31(6), 1131–1136.
Dykens, E. M., & Kasari, C. (1997). Maladaptive behavior in children with Prader-Willi syndrome, Down syndrome, and nonspecific mental retardation. American Journal of Mental Retardation, 102(3), 228–237.
Dykens, E. M., Leckman, J. F., & Cassidy, S. B. (1996). Obsessions and compulsions in Prader-Willi syndrome. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 37, 995–1002.
Dykens, E. M., Lee, E., & Roof, E. (2011). Prader-Willi syndrome and autism spectrum disorders: An evolving story. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 3(3), 225–237.
Dykens, E. M., & Roof, E. (2008). Behavior in Prader-Willi syndrome: Relationship to genetic subtypes and age. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 49(9), 1001–1008.
Dykens, E. M., Roof, E., Hunt-Hawkins, H., Danker, N., Lee, E. B., Shivers, C. M., Daniell, C., & Kim, S.-J. (2017). Diagnoses and characteristics of autism spectrum disorders in children with Prader-Willi syndrome. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 9, 18–30.
Fountain, M. D., Aten, E., Cho, M. T., Juusola, J., Walkiewicz, M. A., Ray, J. W.,… Schaaf, C. P. (2016). The phenotypic spectrum of Schaaf-Yang syndrome: 18 new affected individuals from 14 families. Genetics in Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2016.53.
Fountain, M. D., & Schaaf, C. P. (2016). Prader-Willi syndrome and Schaaf-Yang syndrome: Neurodevelopmental diseases intersecting at the MAGEL2 gene. Diseases, 4(1), 2.
Goodman, W. K., Price, L. H., Rasmussen, S. A., Mazure, C., Fleischmann, R. L., Hill, C. L., Heninger, G. R., & Charney, D. S. (1989). The Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale I: Development, use, and reliability. Archives of General Psychiatry, 46(11), 1006–1011.
Hao, Y. H., Fountain, M. D. Jr., Fon Tacer, K., Xia, F., Bi, W., Kang, S. H., Patel, A., Rosenfeld, J. A., Le Caignec, C., ISidor, B., Krantz, I. D., Noon, S. E., Pfotenhauer, J. P., Morgan, T. M., Moran, R., Pedersen, R. C., Saenz, M. S., Schaaf, C. P., & Potts, P. R. (2015). USP7 acts as a molecular rheostat to promote WASH-dependent endosomal protein recycling and is mutated in a human neurodevelopmental disorder. Molecular Cell, 59(6), 956–969.
Harrison, P. F., & Oakland, T. (2015). Adaptive behavior assessment system (3rd ed.). Torrance: Western Psychological Services.
Holm, V. A., Cassidy, S. B., Butler, M. G., Hanchett, J. M., Greenswag, L. R., Whitman, B. Y., & Greenberg, F. (1993). Prader-Willi syndrome: Consensus diagnostic criteria. Pediatrics, 91(2), 398–402.
Kim, J. W., Yoo, H. J., Cho, S. C., Hong, K. E., & Kim, B. N. (2005). Behavioral characteristics of Prader-Willi syndrome in Korea: Comparison with children with mental retardation and normal controls. Journal of Child Neurology, 20(2), 134–138.
Lord, C., Rutter, M., DiLavore, P. C., Risi, S., Gotham, K., & Bishop, S. (2011). Autism diagnostic observation schedule (2nd ed.). Torrance: Western Psychological Services.
Matarazzo, V., & Muscatelli, F. (2013). Natural breaking of the maternal silence at the mouse and human imprinted Prader-Willi locus: A whisper with functional consequences. Rare Diseases, 1, e27221–e272287.
McCarthy, J. M., McCann-Crosby, B. M., Rech, M. E., Yin, J., Chen, C. A., Ali, M. A., Nguyen, H. N., Miller, J. L., & Schaaf, C. P. (2018). Hormonal, metabolic and skeletal phenotype of Schaaf-Yang syndrome: A comparison to Prader-Willi syndrome. Journal of Medical Genetics, 55(5), 307–315.
Mejlachowicz, D., Nolent, F., Maluenda, J., Ranjatoelina-Randrianaivo, H., Giuliano, F., Gut, I., Sternberg, D., Laquerrière, A., & Melki, J. (2015). Truncating mutations of MAGEL2, a gene within the Prader-Willi locus, are responsible for severe arthrogyposis. American Journal of Human Genetics, 97(4), 616–620.
Mullen, E. M. (1995). Mullen Scales of Early Learning. Circle Pines: American Guidance Service Inc.
Reynolds, C. R., & Kamphaus, R. W. (2015). Behavior Assessment System for Children (3rd ed.). Bloomington: NCS Pearson, Inc.
Rice, L. J., & Einfeld, S. L. (2015). Cognitive and behavioural aspects of Prader-Willi syndrome. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 28(2), 102–106.
Roid, G. H. (2003). Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales, Fifth Edition. Itasca: Riverside Publishing.
Rutter, M., LeCouteur, A., & Lord, C. (2008). Autism diagnostic interview—Revised. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services.
Schaaf, C. P., Gonzalez-Garay, M. L., Xia, F., Potocki, L., Gripp, K. W., Zhang, B., … Yang, Y. (2013). Truncating mutations of MAGEL2 cause Prader-Willi phenotypes and autism. Nature Genetics, 45(11), 1405–1408.
Skokauskas, N., Sweeny, E., Meehan, J., & Gallagher, L. (2011). Mental health problems in children with Prader-Willi syndrome. Journal of the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 21(3), 194–203.
Soden, S. E., Saunders, C. J., & Willig, L. K. (2014). Effectiveness of exome and genome sequencing guided by acuity of illness for diagnosis of neurodevelopmental disorders. Science Translational Medicine, 6(265), 265ra168.
Whittington, J., Holland, A., Webb, T., Butler, J., Clarke, D., & Boer, H. (2004). Cognitive abilities and genotype in a population-based sample of people with Prader-Willi syndrome. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 48(2), 172–187.
Funding
This study was funded by the Foundation for Prader-Willi Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CPS conceived of the study and participated in its design and coordination. LNB and RPGK performed neurobehavioral assessments. LRD assisted with neurobehavioral assessments, scoring, and data collection. JM helped with patient recruitment and data collection. MMT drafted the manuscript, performed statistical analyses, and created figures presented in the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
R.P.G.-K. would like to disclose that she recently entered into an agreement with Yamo Pharmaceuticals, LLC, to provide consulting services in clinical trial development. This relationship is unrelated to the current project and was initiated following completion of data collection. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in the study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomason, M.M., McCarthy, J., Goin-Kochel, R.P. et al. Neurocognitive and Neurobehavioral Phenotype of Youth with Schaaf-Yang Syndrome. J Autism Dev Disord 50, 2491–2500 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-018-3775-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-018-3775-7