Abstract
Purpose
To review the evidence supporting diabetic retinal neurodegeneration (DRN) as a form of diabetic retinopathy.
Method
Review of literature.
Results
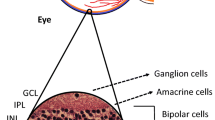
DRN is recognized to be a part of retinopathy in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM), in addition to the well-established diabetic retinal vasculopathy (DRV). DRN has been noted in the early stages of DM, before the onset of clinically evident diabetic retinopathy. The occurrence of DRN has been confirmed in animal models of DM, histopathological examination of donor’s eyes from diabetic individuals and assessment of neural structure and function in humans. DRN involves alterations in retinal ganglion cells, photoreceptors, amacrine cells and bipolar cells, and is thought to be driven by glutamate, oxidative stress and dysregulation of neuroprotective factors in the retina. Potential therapeutic options for DRN are under evaluation.
Conclusions
Literature is divided on the temporal relation between DRN and DRV, with evidence of both precedence and simultaneous occurrence. The relationship between DRN and multi-system neuropathy in DM is yet to be evaluated critically.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leasher JL, Bourne RR, Flaxman SR, Jonas JB, Keeffe J, Naidoo K, Pesudovs K, Price H, White RA, Wong TY, Resnikoff S, Taylor HR (2016) Vision Loss Expert Group of the Global Burden of Disease Study. Global estimates on the number of people blind or visually impaired by diabetic retinopathy: a meta-analysis from 1990 to 2010. Diabetes Care 39(9):1643–1649
Lee R, Wong TY, Sabanayagam C (2015) Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema and related vision loss. Eye Vis (Lond) 30(2):17
Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW, Malanda B (2018) IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 138:271–281
Wong TY, Sabanayagam C (2019) The war on diabetic retinopathy: where are we now? Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila) 8(6):448–456
Antonetti DA, Lieth E, Barber AJ, Gardner TW (1999) Molecular mechanisms of vascular permeability in diabetic retinopathy. Semin Ophthalmol 14(4):240–248
Sokol S, Moskowitz A, Skarf B, Evans R, Molitch M, Senior B (1985) Contrast sensitivity in diabetics with and without background retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 103(1):51–54
Liska V, Dostálek M (1999) Are contrast sensitivity functions impaired in insulin dependent diabetics without diabetic retinopathy? Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove) 42(4):133–138
Duh EJ, Sun JK, Stitt AW (2017) Diabetic retinopathy: current understanding, mechanisms, and treatment strategies. JCI Insight 2(14):e93751
Antonetti DA, Barber AJ, Bronson SK, Freeman WM, Gardner TW, Jefferson LS, Kester M, Kimball SR, Krady JK, LaNoue KF, Norbury CC, Quinn PG, Sandirasegarane L, Simpson IA (2006) JDRF Diabetic Retinopathy Center Group. Diabetic retinopathy: seeing beyond glucose-induced microvascular disease. Diabetes 55(9):2401–2411
Hernández C, Simó R (2012) Neuroprotection in diabetic retinopathy. Curr Diab Rep 12(4):329–337
Zhang X, Wang N, Barile GR, Bao S, Gillies M (2013) Diabetic retinopathy: neuron protection as a therapeutic target. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 45(7):1525–1529
Hernández C, Dal Monte M, Simó R, Casini G (2016) Neuroprotection as a therapeutic target for diabetic retinopathy. J Diabetes Res 2016:9508541
Ciulla TA, Amador AG, Zinman B (2003) Diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema: pathophysiology, screening, and novel therapies. Diabetes Care 26(9):2653–2664
Chou J, Rollins S, Fawzi AA (2014) Role of endothelial cell and pericyte dysfunction in diabetic retinopathy: review of techniques in rodent models. Adv Exp Med Biol 801:669–675
Cao Y, Feng B, Chen S, Chu Y, Chakrabarti S (2014) Mechanisms of endothelial to mesenchymal transition in the retina in diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 55(11):7321–7331
Hammes HP (2018) Diabetic retinopathy: hyperglycaemia, oxidative stress and beyond. Diabetologia 61(1):29–38
Hammes HP, Feng Y, Pfister F, Brownlee M (2011) Diabetic retinopathy: targeting vasoregression. Diabetes 60(1):9–16
Hamilton NB, Attwell D, Hall CN (2010) Pericyte-mediated regulation of capillary diameter: a component of neurovascular coupling in health and disease. Front Neuroenergetics 21(2):5
Pfister F, Feng Y, vom Hagen F, Hoffmann S, Molema G, Hillebrands JL, Shani M, Deutsch U, Hammes HP (2008) Pericyte migration: a novel mechanism of pericyte loss in experimental diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 57(9):2495–2502
Oshitari T, Polewski P, Chadda M, Li AF, Sato T, Roy S (2006) Effect of combined antisense oligonucleotides against high-glucose- and diabetes-induced overexpression of extracellular matrix components and increased vascular permeability. Diabetes 55(1):86–92
Stitt AW, Gardiner TA, Archer DB (1995) Histological and ultrastructural investigation of retinal microaneurysm development in diabetic patients. Br J Ophthalmol 79(4):362–367
Wilkinson CP, Ferris FL III, Klein RE, Lee PP, Agardh CD, Davis M, Dills D, Kampik A, Pararajasegaram R, Verdaguer JT (2003) Global Diabetic Retinopathy Project Group. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology 110(9):1677–1682
Pemp B, Garhofer G, Weigert G, Karl K, Resch H, Wolzt M, Schmetterer L (2009) Reduced retinal vessel response to flicker stimulation but not to exogenous nitric oxide in type 1 diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50(9):4029–4032
Campbell M, Humphries P (2013) The blood-retina barrier. In: Cheng CY (ed) Biology and regulation of blood-tissue barriers. Advances in experimental medicine and biology, vol 763. Springer, New York, pp 70–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-4711-5_3
Drzewoski J, Kasznicki J, Trojanowski Z (2009) The role of “metabolic memory” in the natural history of diabetes mellitus. Pol Arch Med Wewn 119(7–8):493–500
Misra A, Bloomgarden Z (2018) Metabolic memory: evolving concepts. J Diabetes 10(3):186–187
Testa R, Bonfigli AR, Prattichizzo F, La Sala L, De Nigris V, Ceriello A (2017) The, “metabolic memory” theory and the early treatment of hyperglycemia in prevention of diabetic complications. Nutrients 9(5):437
White NH, Sun W, Cleary PA, Danis RP, Davis MD, Hainsworth DP, Hubbard LD, Lachin JM, Nathan DM (2008) Prolonged effect of intensive therapy on the risk of retinopathy complications in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: 10 years after the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Arch Ophthalmol 126(12):1707–1715
Antonetti DA, Klein R, Gardner TW (2012) Diabetic retinopathy. N Engl J Med 366(13):1227–1239
Simó R, Hernández C (2012) European Consortium for the Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy (EUROCONDOR). Neurodegeneration is an early event in diabetic retinopathy: therapeutic implications. Br J Ophthalmol. 96(10):1285–1290
Simó R, Hernández C (2014) European Consortium for the Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy (EUROCONDOR). Neurodegeneration in the diabetic eye: new insights and therapeutic perspectives. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 25(1):23–33
Carrasco E, Hernández C, Miralles A, Huguet P, Farrés J, Simó R (2007) Lower somatostatin expression is an early event in diabetic retinopathy and is associated with retinal neurodegeneration. Diabetes Care 30(11):2902–2908
Garcia-Ramírez M, Hernández C, Villarroel M, Canals F, Alonso MA, Fortuny R, Masmiquel L, Navarro A, García-Arumí J, Simó R (2009) Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) is downregulated at early stages of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia 52(12):2633–2641
Solomon SD, Chew E, Duh EJ, Sobrin L, Sun JK, VanderBeek BL, Wykoff CC, Gardner TW (2017) Diabetic retinopathy: a position statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 40(3):412–418
Barber AJ, Lieth E, Khin SA, Antonetti DA, Buchanan AG, Gardner TW (1998) Neural apoptosis in the retina during experimental and human diabetes. Early onset and effect of insulin. J Clin Invest 102(4):783–791
Gorman AM (2008) Neuronal cell death in neurodegenerative diseases: recurring themes around protein handling. J Cell Mol Med 12(6A):2263–2280
Kadłubowska J, Malaguarnera L, Wąż P, Zorena K (2016) Neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation in diabetic retinopathy: potential approaches to delay neuronal loss. Curr Neuropharmacol 14(8):831–839
Qin Y, Xu G, Wang W (2006) Dendritic abnormalities in retinal ganglion cells of three-month diabetic rats. Curr Eye Res 31(11):967–974
Gastinger MJ, Kunselman AR, Conboy EE, Bronson SK, Barber AJ (2008) Dendrite remodeling and other abnormalities in the retinal ganglion cells of Ins2 Akita diabetic mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49(6):2635–2642
Gastinger MJ, Barber AJ, Khin SA, McRill CS, Gardner TW, Marshak DW (2001) Abnormal centrifugal axons in streptozotocin-diabetic rat retinas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 42(11):2679–2685
Gastinger MJ, Singh RS, Barber AJ (2006) Loss of cholinergic and dopaminergic amacrine cells in streptozotocin-diabetic rat and Ins2Akita-diabetic mouse retinas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47(7):3143–3150
Hammes HP, Federoff HJ, Brownlee M (1995) Nerve growth factor prevents both neuroretinal programmed cell death and capillary pathology in experimental diabetes. Mol Med 1(5):527–534
Park SH, Park JW, Park SJ, Kim KY, Chung JW, Chun MH, Oh SJ (2003) Apoptotic death of photoreceptors in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat retina. Diabetologia 46(9):1260–1268
Martin PM, Roon P, Van Ells TK, Ganapathy V, Smith SB (2004) Death of retinal neurons in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45(9):3330–3336
Tonade D, Liu H, Palczewski K, Kern TS (2017) Photoreceptor cells produce inflammatory products that contribute to retinal vascular permeability in a mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia 60(10):2111–2120
Tonade D, Liu H, Kern TS (2016) Photoreceptor cells produce inflammatory mediators that contribute to endothelial cell death in diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 57(10):4264–4271
VanGuilder HD, Brucklacher RM, Patel K, Ellis RW, Freeman WM, Barber AJ (2008) Diabetes downregulates presynaptic proteins and reduces basal synapsin I phosphorylation in rat retina. Eur J Neurosci 28(1):1–11
Valastro B, Cossette J, Lavoie N, Gagnon S, Trudeau F, Massicotte G (2002) Up-regulation of glutamate receptors is associated with LTP defects in the early stages of diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 45(5):642–650
Delyfer MN, Forster V, Neveux N, Picaud S, Léveillard T, Sahel JA (2005) Evidence for glutamate-mediated excitotoxic mechanisms during photoreceptor degeneration in the rd1 mouse retina. Mol Vis 1(11):688–696
Osborne NN, Melena J, Chidlow G, Wood JP (2001) A hypothesis to explain ganglion cell death caused by vascular insults at the optic nerve head: possible implication for the treatment of glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol 85(10):1252–1259
Cui RZ, Wang L, Qiao SN, Wang YC, Wang X, Yuan F, Weng SJ, Yang XL, Zhong YM (2019) ON-type retinal ganglion cells are preferentially affected in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 60(5):1644–1656
Pekny M, Wilhelmsson U, Pekna M (2014) The dual role of astrocyte activation and reactive gliosis. Neurosci Lett 17(565):30–38
Sardar Pasha SPB, Münch R, Schäfer P, Oertel P, Sykes AM, Zhu Y, Karl MO (2017) Retinal cell death dependent reactive proliferative gliosis in the mouse retina. Sci Rep 7(1):9517
Chang ML, Wu CH, Jiang-Shieh YF, Shieh JY, Wen CY (2007) Reactive changes of retinal astrocytes and Müller glial cells in kainate-induced neuroexcitotoxicity. J Anat 210(1):54–65
Carrasco E, Hernández C, de Torres I, Farrés J, Simó R (2008) Lowered cortistatin expression is an early event in the human diabetic retina and is associated with apoptosis and glial activation. Mol Vis 15(14):1496–1502
Mizutani M, Gerhardinger C, Lorenzi M (1998) Müller cell changes in human diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 47(3):445–449
Meyer-Rüsenberg B, Pavlidis M, Stupp T, Thanos S (2007) Pathological changes in human retinal ganglion cells associated with diabetic and hypertensive retinopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 245(7):1009–1018
Cho NC, Poulsen GL, Ver Hoeve JN, Nork TM (2000) Selective loss of S-cones in diabetic retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 118(10):1393–1400
Bharathi Devi SR, Coral K, Gayathree K, Bharathselvi M, Sivasankar S, Biswas J, Rishi P, Natarajan S, Badrinath SS, Angayarkanni N (2019) Case report on two diabetic donor eyes with no retinopathy: clinicopathological and molecular studies. Indian J Ophthalmol 67(10):1762–1765
Di Leo MA, Falsini B, Caputo S, Ghirlanda G, Porciatti V, Greco AV (1990) Spatial frequency-selective losses with pattern electroretinogram in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients without retinopathy. Diabetologia 33(12):726–730
Falsini B, Porciatti V, Scalia G, Caputo S, Minnella A, Di Leo MA, Ghirlanda G (1989) Steady-state pattern electroretinogram in insulin-dependent diabetics with no or minimal retinopathy. Doc Ophthalmol 73(2):193–200
Caputo S, Di Leo MA, Falsini B, Ghirlanda G, Porciatti V, Minella A, Greco AV (1990) Evidence for early impairment of macular function with pattern ERG in type I diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 13(4):412–418
Di Leo MA, Caputo S, Falsini B, Porciatti V, Greco AV, Ghirlanda G (1994) Presence and further development of retinal dysfunction after 3-year follow up in IDDM patients without angiographically documented vasculopathy. Diabetologia 37(9):911–916
Prager TC, Garcia CA, Mincher CA, Mishra J, Chu HH (1990) The pattern electroretinogram in diabetes. Am J Ophthalmol 109(3):279–284
Shirao Y, Kawasaki K (1998) Electrical responses from diabetic retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 17(1):59–76
van der Torren K, van Lith G (1989) Oscillatory potentials in early diabetic retinopathy. Doc Ophthalmol 71(4):375–379
Hancock HA, Kraft TW (2004) Oscillatory potential analysis and ERGs of normal and diabetic rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45(3):1002–1008
Bearse MA Jr, Han Y, Schneck ME, Adams AJ (2004) Retinal function in normal and diabetic eyes mapped with the slow flash multifocal electroretinogram. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45(1):296–304
Shimada Y, Li Y, Bearse MA Jr, Sutter EE, Fung W (2001) Assessment of early retinal changes in diabetes using a new multifocal ERG protocol. Br J Ophthalmol 85(4):414–419
Ng JS, Bearse MA Jr, Schneck ME, Barez S, Adams AJ (2008) Local diabetic retinopathy prediction by multifocal ERG delays over 3 years. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49(4):1622–1628
Han Y, Bearse MA Jr, Schneck ME, Barez S, Jacobsen CH, Adams AJ (2004) Multifocal electroretinogram delays predict sites of subsequent diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45(3):948–954
Han Y, Adams AJ, Bearse MA Jr, Schneck ME (2004) Multifocal electroretinogram and short-wavelength automated perimetry measures in diabetic eyes with little or no retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 122(12):1809–1815
Riva CE, Logean E, Falsini B (2005) Visually evoked hemodynamical response and assessment of neurovascular coupling in the optic nerve and retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 24(2):183–215
Lecleire-Collet A, Audo I, Aout M, Girmens JF, Sofroni R, Erginay A, Le Gargasson JF, Mohand-Saïd S, Meas T, Guillausseau PJ, Vicaut E, Paques M, Massin P (2011) Evaluation of retinal function and flicker light-induced retinal vascular response in normotensive patients with diabetes without retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52(6):2861–2867
Tyrberg M, Lindblad U, Melander A, Lövestam-Adrian M, Ponjavic V, Andréasson S (2011) Electrophysiological studies in newly onset type 2 diabetes without visible vascular retinopathy. Doc Ophthalmol 123(3):193–198
Tang Z, Chan MY, Leung WY, Wong HY, Ng CM, Chan VTT, Wong R, Lok J, Szeto S, Chan JCK, Tham CC, Wong TY, Cheung CY (2020) Assessment of retinal neurodegeneration with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eye (Lond). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-020-1020-z
van Dijk HW, Kok PH, Garvin M, Sonka M, Devries JH, Michels RP, van Velthoven ME, Schlingemann RO, Verbraak FD, Abràmoff MD (2009) Selective loss of inner retinal layer thickness in type 1 diabetic patients with minimal diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50(7):3404–3409
van Dijk HW, Verbraak FD, Kok PH, Garvin MK, Sonka M, Lee K, Devries JH, Michels RP, van Velthoven ME, Schlingemann RO, Abràmoff MD (2010) Decreased retinal ganglion cell layer thickness in patients with type 1 diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51(7):3660–3665
van Dijk HW, Verbraak FD, Kok PH, Stehouwer M, Garvin MK, Sonka M, DeVries JH, Schlingemann RO, Abràmoff MD (2012) Early neurodegeneration in the retina of type 2 diabetic patients. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53(6):2715–2719
Demir M, Oba E, Sensoz H, Ozdal E (2014) Retinal nerve fiber layer and ganglion cell complex thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Indian J Ophthalmol 62(6):719–720
Chhablani J, Sharma A, Goud A, Peguda HK, Rao HL, Begum VU, Barteselli G (2015) Neurodegeneration in type 2 diabetes: evidence from spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 56(11):6333–6338
Chen Y, Li J, Yan Y, Shen X (2016) Diabetic macular morphology changes may occur in the early stage of diabetes. BMC Ophthalmol 18(16):12
Santos AR, Ribeiro L, Bandello F, Lattanzio R, Egan C, Frydkjaer-Olsen U, García-Arumí J, Gibson J, Grauslund J, Harding SP, Lang GE, Massin P, Midena E, Scanlon P, Aldington SJ, Simão S, Schwartz C, Ponsati B, Porta M, Costa MÂ, Hernández C, Cunha-Vaz J, Simó R (2017) European Consortium for the Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy (EUROCONDOR). Functional and structural findings of neurodegeneration in early stages of diabetic retinopathy: cross-sectional analyses of baseline data of the EUROCONDOR project. Diabetes 66(9):2503–2510
Nagesh BN, Takkar B, Azad S, Azad R (2016) Optical coherence tomography and multifocal electroretinography in diabetic macular edema: a neurovascular relation with vision. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina 47(7):626–631
Bringmann A, Wiedemann P (2012) Müller glial cells in retinal disease. Ophthalmologica 227(1):1–19
Puro DG (2002) Diabetes-induced dysfunction of retinal Müller cells. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 100:339–352
Gerhardinger C, Costa MB, Coulombe MC, Toth I, Hoehn T, Grosu P (2005) Expression of acute-phase response proteins in retinal Müller cells in diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46(1):349–357
Li Q, Puro DG (2002) Diabetes-induced dysfunction of the glutamate transporter in retinal Müller cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43(9):3109–3116
Bergsbaken T, Fink SL, Cookson BT (2009) Pyroptosis: host cell death and inflammation. Nat Rev Microbiol 7(2):99–109
Denes A, Lopez-Castejon G, Brough D (2012) Caspase-1: is IL-1 just the tip of the ICEberg? Cell Death Dis 3(7):e338
Zeng HY, Green WR, Tso MO (2008) Microglial activation in human diabetic retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 126(2):227–232
Zhang W, Liu H, Al-Shabrawey M, Caldwell RW, Caldwell RB (2011) Inflammation and diabetic retinal microvascular complications. J Cardiovasc Dis Res 2(2):96–103
Fumagalli S, Perego C, Pischiutta F, Zanier ER, De Simoni MG (2015) The ischemic environment drives microglia and macrophage function. Front Neurol 8(6):81
Rajamani U, Jialal I (2016) Erratum to “Hyperglycemia induces toll-like receptor-2 and -4 expression and activity in human microvascular retinal endothelial cells: implications for diabetic retinopathy.” J Diabetes Res 2016:8976945
Krady JK, Basu A, Allen CM, Xu Y, LaNoue KF, Gardner TW, Levison SW (2005) Minocycline reduces proinflammatory cytokine expression, microglial activation, and caspase-3 activation in a rodent model of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 54(5):1559–1565
Zeng HY, Zhu XA, Zhang C, Yang LP, Wu LM, Tso MO (2005) Identification of sequential events and factors associated with microglial activation, migration, and cytotoxicity in retinal degeneration in rd mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46(8):2992–2999
Lai AY, Todd KG (2008) Differential regulation of trophic and proinflammatory microglial effectors is dependent on severity of neuronal injury. Glia 56(3):259–270
Zeng XX, Ng YK, Ling EA (2000) Neuronal and microglial response in the retina of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Vis Neurosci 17(3):463–471
McVicar CM, Hamilton R, Colhoun LM, Gardiner TA, Brines M, Cerami A, Stitt AW (2011) Intervention with an erythropoietin-derived peptide protects against neuroglial and vascular degeneration during diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 60(11):2995–3005
Rungger-Brändle E, Dosso AA, Leuenberger PM (2000) Glial reactivity, an early feature of diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41(7):1971–1980
Chen L, Yang P, Kijlstra A (2002) Distribution, markers, and functions of retinal microglia. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 10(1):27–39
Ozdek S, Lonneville YH, Onol M, Yetkin I, Hasanreisoğlu BB (2002) Assessment of nerve fiber layer in diabetic patients with scanning laser polarimetry. Eye (Lond) 16(6):761–765
Takahashi H, Goto T, Shoji T, Tanito M, Park M, Chihara E (2006) Diabetes-associated retinal nerve fiber damage evaluated with scanning laser polarimetry. Am J Ophthalmol 142(1):88–94
Oshitari T, Yamamoto S, Hata N, Roy S (2008) Mitochondria- and caspase-dependent cell death pathway involved in neuronal degeneration in diabetic retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol 92(4):552–556
Du Y, Veenstra A, Palczewski K, Kern TS (2013) Photoreceptor cells are major contributors to diabetes-induced oxidative stress and local inflammation in the retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(41):16586–16591
Kowluru RA, Kowluru A, Veluthakal R, Mohammad G, Syed I, Santos JM, Mishra M (2014) TIAM1-RAC1 signalling axis-mediated activation of NADPH oxidase-2 initiates mitochondrial damage in the development of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia 57(5):1047–1056
Santos JM, Tewari S, Lin JY, Kowluru RA (2013) Interrelationship between activation of matrix metalloproteinases and mitochondrial dysfunction in the development of diabetic retinopathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 438(4):760–764
Kumar B, Gupta SK, Srinivasan BP, Nag TC, Srivastava S, Saxena R, Jha KA (2013) Hesperetin rescues retinal oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and apoptosis in diabetic rats. Microvasc Res 87:65–74
Nishimura C, Kuriyama K (1985) Alterations in the retinal dopaminergic neuronal system in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Neurochem 45(2):448–455
Sánchez-Chávez G, Salceda R (2001) Acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase in normal and diabetic rat retina. Neurochem Res 26(2):153–159
Moore-Dotson JM, Beckman JJ, Mazade RE, Hoon M, Bernstein AS, Romero-Aleshire MJ, Brooks HL, Eggers ED (2016) Early retinal neuronal dysfunction in diabetic mice: reduced light-evoked inhibition increases rod pathway signaling. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 57(3):1418–1430
Lieth E, Barber AJ, Xu B, Dice C, Ratz MJ, Tanase D, Strother JM (1998) Glial reactivity and impaired glutamate metabolism in short-term experimental diabetic retinopathy. Penn State Retina Res Group Diabetes 47(5):815–820
Lieth E, LaNoue KF, Antonetti DA, Ratz M (2000) Diabetes reduces glutamate oxidation and glutamine synthesis in the retina. The Penn State Retina Research Group. Exp Eye Res 70(6):723–730
Kowluru RA, Engerman RL, Case GL, Kern TS (2001) Retinal glutamate in diabetes and effect of antioxidants. Neurochem Int 38(5):385–390
Lucas DR, Newhouse JP (1957) The toxic effect of sodium L-glutamate on the inner layers of the retina. AMA Arch Ophthalmol 58(2):193–201
Vorwerk CK, Lipton SA, Zurakowski D, Hyman BT, Sabel BA, Dreyer EB (1996) Chronic low-dose glutamate is toxic to retinal ganglion cells. Toxicity blocked by memantine. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 37(8):1618–1624
Ambati J, Chalam KV, Chawla DK, D’Angio CT, Guillet EG, Rose SJ, Vanderlinde RE, Ambati BK (1997) Elevated gamma-aminobutyric acid, glutamate, and vascular endothelial growth factor levels in the vitreous of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 115(9):1161–1166
Pulido JE, Pulido JS, Erie JC, Arroyo J, Bertram K, Lu MJ, Shippy SA (2007) A role for excitatory amino acids in diabetic eye disease. Exp Diabetes Res 2007:36150
Carvajal FJ, Mattison HA, Cerpa W (2016) Role of NMDA receptor-mediated glutamatergic signaling in chronic and acute neuropathologies. Neural Plast 2016:2701526
Xiao C, He M, Nan Y, Zhang D, Chen B, Guan Y, Pu M (2012) Physiological effects of superoxide dismutase on altered visual function of retinal ganglion cells in db/db mice. PLoS ONE 7(1):e30343
Fukumoto M, Nakaizumi A, Zhang T, Lentz SI, Shibata M, Puro DG (2012) Vulnerability of the retinal microvasculature to oxidative stress: ion channel-dependent mechanisms. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 302(9):C1413–C1420
Brownlee M (2005) The pathobiology of diabetic complications: a unifying mechanism. Diabetes 54(6):1615–1625
Nita M, Grzybowski A (2016) The role of the reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress in the pathomechanism of the age-related ocular diseases and other pathologies of the anterior and posterior eye segments in adults. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:3164734
Dyer MA, Cepko CL (2000) Control of Müller glial cell proliferation and activation following retinal injury. Nat Neurosci 3(9):873–880
Bringmann A, Pannicke T, Grosche J, Francke M, Wiedemann P, Skatchkov SN, Osborne NN, Reichenbach A (2006) Müller cells in the healthy and diseased retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 25(4):397–424
Harada T, Harada C, Kohsaka S, Wada E, Yoshida K, Ohno S, Mamada H, Tanaka K, Parada LF, Wada K (2002) Microglia-Müller glia cell interactions control neurotrophic factor production during light-induced retinal degeneration. J Neurosci 22(21):9228–9236
Zachary I (2005) Neuroprotective role of vascular endothelial growth factor: signalling mechanisms, biological function, and therapeutic potential. Neurosignals 14(5):207–221
Saint-Geniez M, Maharaj AS, Walshe TE, Tucker BA, Sekiyama E, Kurihara T, Darland DC, Young MJ, D’Amore PA (2008) Endogenous VEGF is required for visual function: evidence for a survival role on müller cells and photoreceptors. PLoS ONE 3(11):e3554
Li Y, Zhang F, Nagai N, Tang Z, Zhang S, Scotney P, Lennartsson J, Zhu C, Qu Y, Fang C, Hua J, Matsuo O, Fong GH, Ding H, Cao Y, Becker KG, Nash A, Heldin CH, Li X (2008) VEGF-B inhibits apoptosis via VEGFR-1-mediated suppression of the expression of BH3-only protein genes in mice and rats. J Clin Invest 118(3):913–923
Zhang F, Tang Z, Hou X, Lennartsson J, Li Y, Koch AW, Scotney P, Lee C, Arjunan P, Dong L, Kumar A, Rissanen TT, Wang B, Nagai N, Fons P, Fariss R, Zhang Y, Wawrousek E, Tansey G, Raber J, Fong GH, Ding H, Greenberg DA, Becker KG, Herbert JM, Nash A, Yla-Herttuala S, Cao Y, Watts RJ, Li X (2009) VEGF-B is dispensable for blood vessel growth but critical for their survival, and VEGF-B targeting inhibits pathological angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(15):6152–6157
Jin K, Mao XO, Batteur SP, McEachron E, Leahy A, Greenberg DA (2001) Caspase-3 and the regulation of hypoxic neuronal death by vascular endothelial growth factor. Neuroscience 108(2):351–358
Nishijima K, Ng YS, Zhong L, Bradley J, Schubert W, Jo N, Akita J, Samuelsson SJ, Robinson GS, Adamis AP, Shima DT (2007) Vascular endothelial growth factor-A is a survival factor for retinal neurons and a critical neuroprotectant during the adaptive response to ischemic injury. Am J Pathol 171(1):53–67
Bai Y, Ma JX, Guo J, Wang J, Zhu M, Chen Y, Le YZ (2009) Müller cell-derived VEGF is a significant contributor to retinal neovascularization. J Pathol 219(4):446–454
Li CR, Sun SG (2010) VEGF expression and cell apoptosis in NOD mouse retina. Int J Ophthalmol 3(3):224–227
Stadler K (2011) Peroxynitrite-driven mechanisms in diabetes and insulin resistance - the latest advances. Curr Med Chem 18(2):280–290
Abdelsaid MA, Pillai BA, Matragoon S, Prakash R, Al-Shabrawey M, El-Remessy AB (2010) Early intervention of tyrosine nitration prevents vaso-obliteration and neovascularization in ischemic retinopathy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 332(1):125–134
Perrin RM, Konopatskaya O, Qiu Y, Harper S, Bates DO, Churchill AJ (2005) Diabetic retinopathy is associated with a switch in splicing from anti- to pro-angiogenic isoforms of vascular endothelial growth factor. Diabetologia 48(11):2422–2427
Becerra SP, Amaral J (2002) Erythropoietin—an endogenous retinal survival factor. N Engl J Med 347(24):1968–1970
Hernández C, Fonollosa A, García-Ramírez M, Higuera M, Catalán R, Miralles A, García-Arumí J, Simó R (2006) Erythropoietin is expressed in the human retina and it is highly elevated in the vitreous fluid of patients with diabetic macular edema. Diabetes Care 29(9):2028–2033
Shen J, Wu Y, Xu JY, Zhang J, Sinclair SH, Yanoff M, Xu G, Li W, Xu GT (2010) ERK- and Akt-dependent neuroprotection by erythropoietin (EPO) against glyoxal-AGEs via modulation of Bcl-xL, Bax, and BAD. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51(1):35–46
Chen J, Connor KM, Aderman CM, Smith LE (2008) Erythropoietin deficiency decreases vascular stability in mice. J Clin Invest 118(2):526–533
Grant MB, Boulton ME, Ljubimov AV (2008) Erythropoietin: when liability becomes asset in neurovascular repair. J Clin Invest 118(2):467–470
Gupta N, Mansoor S, Sharma A, Sapkal A, Sheth J, Falatoonzadeh P, Kuppermann B, Kenney M (2013) Diabetic retinopathy and VEGF. Open Ophthalmol J 7:4–10
Kermer P, Klöcker N, Labes M, Bähr M (2000) Insulin-like growth factor-I protects axotomized rat retinal ganglion cells from secondary death via PI3-K-dependent Akt phosphorylation and inhibition of caspase-3 In vivo. J Neurosci 20(2):2–8
Morimoto T, Miyoshi T, Matsuda S, Tano Y, Fujikado T, Fukuda Y (2005) Transcorneal electrical stimulation rescues axotomized retinal ganglion cells by activating endogenous retinal IGF-1 system. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46(6):2147–2155
Barber AJ, Nakamura M, Wolpert EB, Reiter CE, Seigel GM, Antonetti DA, Gardner TW (2001) Insulin rescues retinal neurons from apoptosis by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-mediated mechanism that reduces the activation of caspase-3. J Biol Chem 276(35):32814–32821
Boulton M, Gregor Z, McLeod D, Charteris D, Jarvis-Evans J, Moriarty P, Khaliq A, Foreman D, Allamby D, Bardsley B (1997) Intravitreal growth factors in proliferative diabetic retinopathy: correlation with neovascular activity and glycaemic management. Br J Ophthalmol 81(3):228–233
Meyer-Schwickerath R, Pfeiffer A, Blum WF, Freyberger H, Klein M, Lösche C, Röllmann R, Schatz H (1993) Vitreous levels of the insulin-like growth factors I and II, and the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 2 and 3, increase in neovascular eye disease. Studies in nondiabetic and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 92(6):2620–2625
Waldbillig RJ, Jones BE, Schoen TJ, Moshayedi P, Heidersbach S, Bitar MS, van Kuijk FJ, de Juan E, Kador P, Chader GJ (1994) Vitreal insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBPs) are increased in human and animal diabetics. Curr Eye Res 13(7):539–546
Barnstable CJ, Tombran-Tink J (2004) Neuroprotective and antiangiogenic actions of PEDF in the eye: molecular targets and therapeutic potential. Prog Retin Eye Res 23(5):561–577
Tombran-Tink J, Barnstable CJ (2003) PEDF: a multifaceted neurotrophic factor. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(8):628–636
Inagaki Y, Yamagishi S, Okamoto T, Takeuchi M, Amano S (2003) Pigment epithelium-derived factor prevents advanced glycation end products-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 production in microvascular endothelial cells by suppressing intracellular reactive oxygen species generation. Diabetologia 46(2):284–287
Yamagishi S, Inagaki Y, Nakamura K, Abe R, Shimizu T, Yoshimura A, Imaizumi T (2004) Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits TNF-alpha-induced interleukin-6 expression in endothelial cells by suppressing NADPH oxidase-mediated reactive oxygen species generation. J Mol Cell Cardiol 37(2):497–506
Becerra SP (2006) Focus on molecules: pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF). Exp Eye Res 82(5):739–740
Mohamed R, El-Remessy AB (2015) Imbalance of the Nerve Growth Factor and Its Precursor: Implication in Diabetic Retinopathy. J Clin Exp Ophthalmol 6(5):483
Kummer A, Pulford BE, Ishii DN, Seigel GM (2003) Des(1–3)IGF-1 treatment normalizes type 1 IGF receptor and phospho-Akt (Thr 308) immunoreactivity in predegenerative retina of diabetic rats. Int J Exp Diabesity Res 4(1):45–57
Casaccia-Bonnefil P, Carter BD, Dobrowsky RT, Chao MV (1996) Death of oligodendrocytes mediated by the interaction of nerve growth factor with its receptor p75. Nature 383(6602):716–719
Hempstead BL (2009) Commentary: Regulating proNGF action: multiple targets for therapeutic intervention. Neurotox Res 16(3):255–260
Johnson JE, Barde YA, Schwab M, Thoenen H (1986) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor supports the survival of cultured rat retinal ganglion cells. J Neurosci 6(10):3031–3038
Seki M, Tanaka T, Nawa H, Usui T, Fukuchi T, Ikeda K, Abe H, Takei N (2004) Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in early retinal neuropathy of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats: therapeutic potential of brain-derived neurotrophic factor for dopaminergic amacrine cells. Diabetes 53(9):2412–2419
Simó R, Lecube A, Sararols L, García-Arumí J, Segura RM, Casamitjana R, Hernández C (2002) Deficit of somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in the vitreous fluid of diabetic patients: possible role in the development of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 25(12):2282–2286
Simó R, Carrasco E, Fonollosa A, García-Arumí J, Casamitjana R, Hernández C (2007) Deficit of somatostatin in the vitreous fluid of patients with diabetic macular edema. Diabetes Care 30(3):725–727
Gonzalez-Fernandez F, Ghosh D (2008) Focus on molecules: interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP). Exp Eye Res 86(2):169–170
Liou GI, Fei Y, Peachey NS, Matragoon S, Wei S, Blaner WS, Wang Y, Liu C, Gottesman ME, Ripps H (1998) Early onset photoreceptor abnormalities induced by targeted disruption of the interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein gene. J Neurosci 18(12):4511–4520
Ola MS, Alhomida AS, Ferrario CM, Ahmad S (2017) Role of tissue renin-angiotensin system and the chymase/angiotensin-(1–12) axis in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Curr Med Chem 24(28):3104–3114
Downie LE, Pianta MJ, Vingrys AJ, Wilkinson-Berka JL, Fletcher EL (2008) AT1 receptor inhibition prevents astrocyte degeneration and restores vascular growth in oxygen-induced retinopathy. Glia 56(10):1076–1090
Kurihara T, Ozawa Y, Nagai N, Shinoda K, Noda K, Imamura Y, Tsubota K, Okano H, Oike Y, Ishida S (2008) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor signaling contributes to synaptophysin degradation and neuronal dysfunction in the diabetic retina. Diabetes 57(8):2191–2198
Silva KC, Rosales MA, Biswas SK, Lopes de Faria JB, Lopes de Faria JM (2009) Diabetic retinal neurodegeneration is associated with mitochondrial oxidative stress and is improved by an angiotensin receptor blocker in a model combining hypertension and diabetes. Diabetes 58(6):1382–1390
Yoshida Y, Yamagishi S, Matsui T, Jinnouchi Y, Fukami K, Imaizumi T, Yamakawa R (2009) Protective role of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) in early phase of experimental diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 25(7):678–686
Liu Y, Tao L, Fu X, Zhao Y, Xu X (2013) BDNF protects retinal neurons from hyperglycemia through the TrkB/ERK/MAPK pathway. Mol Med Rep 7(6):1773–1778
Hernández C, Bogdanov P, Corraliza L, García-Ramírez M, Solà-Adell C, Arranz JA, Arroba AI, Valverde AM, Simó R (2016) Topical administration of GLP-1 receptor agonists prevents retinal neurodegeneration in experimental diabetes. Diabetes 65(1):172–187
Kusari J, Zhou S, Padillo E, Clarke KG, Gil DW (2007) Effect of memantine on neuroretinal function and retinal vascular changes of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48(11):5152–5159
Ghadiri Soufi F, Arbabi-Aval E, Rezaei Kanavi M, Ahmadieh H (2015) Anti-inflammatory properties of resveratrol in the retinas of type 2 diabetic rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 42(1):63–68
Soufi FG, Vardyani M, Sheervalilou R, Mohammadi M, Somi MH (2012) Long-term treatment with resveratrol attenuates oxidative stress pro-inflammatory mediators and apoptosis in streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced diabetic rats. Gen Physiol Biophys 31(4):431–438
Kumar B, Gupta SK, Nag TC, Srivastava S, Saxena R, Jha KA, Srinivasan BP (2014) Retinal neuroprotective effects of quercetin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Exp Eye Res 125:193–202
Kurihara T, Ozawa Y, Nagai N, Inoue M, Oike Y, Okano H, Tsubota K, Ishida S (2007) Neuroprotective effects of angiotensin II type 1 (AT1R) receptor blocker telmisartan on early diabetic retina. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48(13):1389
Final Report Summary—EUROCONDOR (European Consortium for the Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy). https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/278040/reporting. Accessed 24 Nov 2020
Shen X, Zhong Y, Xie B, Cheng Y, Jiao Q (2010) Pigment epithelium derived factor as an anti-inflammatory factor against decrease of glutamine synthetase expression in retinal Müller cells under high glucose conditions. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 248(8):1127–1136
Zhu XF, Zou HD (2012) PEDF in diabetic retinopathy: a protective effect of oxidative stress. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:580687
Cayouette M, Smith SB, Becerra SP, Gravel C (1999) Pigment epithelium-derived factor delays the death of photoreceptors in mouse models of inherited retinal degenerations. Neurobiol Dis 6(6):523–532
Cao W, Tombran-Tink J, Elias R, Sezate S, Mrazek D, McGinnis JF (2001) In vivo protection of photoreceptors from light damage by pigment epithelium-derived factor. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 42(7):1646–1652
Cao W, Tombran-Tink J, Chen W, Mrazek D, Elias R, McGinnis JF (1999) Pigment epithelium-derived factor protects cultured retinal neurons against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death. J Neurosci Res 57(6):789–800
Reiter CE, Wu X, Sandirasegarane L, Nakamura M, Gilbert KA, Singh RS, Fort PE, Antonetti DA, Gardner TW (2006) Diabetes reduces basal retinal insulin receptor signaling: reversal with systemic and local insulin. Diabetes 55(4):1148–1156
Bai Y, Xu J, Brahimi F, Zhuo Y, Sarunic MV, Saragovi HU (2010) An agonistic TrkB mAb causes sustained TrkB activation, delays RGC death, and protects the retinal structure in optic nerve axotomy and in glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51(9):4722–4731
Colafrancesco V, Coassin M, Rossi S, Aloe L (2011) Effect of eye NGF administration on two animal models of retinal ganglion cells degeneration. Ann Ist Super Sanita 47(3):284–289
Mayor-Torroglosa S, De la Villa P, Rodríguez ME, López-Herrera MP, Avilés-Trigueros M, García-Avilés A, de Imperial JM, Villegas-Pérez MP, Vidal-Sanz M (2005) Ischemia results 3 months later in altered ERG, degeneration of inner layers, and deafferented tectum: neuroprotection with brimonidine. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46(10):3825–3835
Sampedro J, Bogdanov P, Ramos H, Solà-Adell C, Turch M, Valeri M, Simó-Servat O, Lagunas C, Simó R, Hernández C (2019) New insights into the mechanisms of action of topical administration of GLP-1 in an experimental model of diabetic retinopathy. J Clin Med 8(3):339
Sena DF, Lindsley K (2013) Neuroprotection for treatment of glaucoma in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2(2):CD006539
Soufi FG, Mohammad-Nejad D, Ahmadieh H (2012) Resveratrol improves diabetic retinopathy possibly through oxidative stress—nuclear factor κB—apoptosis pathway. Pharmacol Rep 64(6):1505–1514
Yar AS, Menevse S, Dogan I, Alp E, Ergin V, Cumaoglu A, Aricioglu A, Ekmekci A, Menevse A (2012) Investigation of ocular neovascularization-related genes and oxidative stress in diabetic rat eye tissues after resveratrol treatment. J Med Food 15(4):391–398
Silva KC, Rosales MA, Hamassaki DE, Saito KC, Faria AM, Ribeiro PA, Faria JB, Faria JM (2013) Green tea is neuroprotective in diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54(2):1325–1336
Elgayar SA, Eltony SA, Sayed AA, Abdel-Rouf MM (2015) Genistein treatment confers protection against gliopathy and vasculopathy of the diabetic retina in rats. Ultrastruct Pathol 39(6):385–394
Ola MS, Ahmed MM, Abuohashish HM, Al-Rejaie SS, Alhomida AS (2013) Telmisartan ameliorates neurotrophic support and oxidative stress in the retina of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Neurochem Res 38(8):1572–1579
Foureaux G, Nogueira BS, Coutinho DC, Raizada MK, Nogueira JC, Ferreira AJ (2015) Activation of endogenous angiotensin converting enzyme 2 prevents early injuries induced by hyperglycemia in rat retina. Braz J Med Biol Res 48(12):1109–1114
Sohn EH, van Dijk HW, Jiao C, Kok PH, Jeong W, Demirkaya N, Garmager A, Wit F, Kucukevcilioglu M, van Velthoven ME, DeVries JH, Mullins RF, Kuehn MH, Schlingemann RO, Sonka M, Verbraak FD, Abràmoff MD (2016) Retinal neurodegeneration may precede microvascular changes characteristic of diabetic retinopathy in diabetes mellitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113(19):E2655–E2664
Roy MS, Bungay P, Collier B, Bonner R (1989) A new method in the analysis of vitreous fluorophotometry. Results in early diabetic retinopathy. Ophtalmologie 3(3):214–216
Schalnus R, Ohrloff C, Jungmann E, Maass K, Rinke S, Wagner A (1993) Permeability of the blood-retinal barrier and the blood-aqueous barrier in type I diabetes without diabetic retinopathy: simultaneous evaluation with fluorophotometry. Ger J Ophthalmol 2(4–5):202–206
Bordat B, Guirgis IR, Manderscheid JC (1990) Fluorophotometry of the vitreous body in diabetics without retinopathy or with minimal retinopathy. J Fr Ophtalmol 13(6–7):343–347
Hombrebueno JR, Chen M, Penalva RG, Xu H (2014) Loss of synaptic connectivity, particularly in second order neurons is a key feature of diabetic retinal neuropathy in the Ins2Akita mouse. PLoS ONE 9(5):e97970
Cahoon JM, Rai RR, Carroll LS, Uehara H, Zhang X, O’Neil CL, Medina RJ, Das SK, Muddana SK, Olson PR, Nielson S, Walker K, Flood MM, Messenger WB, Archer BJ, Barabas P, Krizaj D, Gibson CC, Li DY, Koh GY, Gao G, Stitt AW, Ambati BK (2015) Intravitreal AAV2.COMP-Ang1 prevents neurovascular degeneration in a murine model of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 64(12):4247–4259
Kern TS, Barber AJ (2008) Retinal ganglion cells in diabetes. J Physiol 586(18):4401–4408
Lopes de Faria JM, Russ H, Costa VP (2002) Retinal nerve fibre layer loss in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus without retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. 86(7):725–728
Phipps JA, Fletcher EL, Vingrys AJ (2004) Paired-flash identification of rod and cone dysfunction in the diabetic rat. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45(12):4592–4600
Han Y, Schneck ME, Bearse MA Jr, Barez S, Jacobsen CH, Jewell NP, Adams AJ (2004) Formulation and evaluation of a predictive model to identify the sites of future diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45(11):4106–4112
Harrison WW, Bearse MA Jr, Ng JS, Jewell NP, Barez S, Burger D, Schneck ME, Adams AJ (2011) Multifocal electroretinograms predict onset of diabetic retinopathy in adult patients with diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52(2):772–777
Bresnick GH, Palta M (1987) Predicting progression to severe proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 105(6):810–814
Simó R, Hernández C, Porta M, Bandello F, Grauslund J, Harding SP, Aldington SJ, Egan C, Frydkjaer-Olsen U, García-Arumí J, Gibson J, Lang GE, Lattanzio R, Massin P, Midena E, Ponsati B, Ribeiro L, Scanlon P, Lobo C, Costa MÂ, Cunha-Vaz J (2019) European Consortium for the Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy (EUROCONDOR). Effects of topically administered neuroprotective drugs in early stages of diabetic retinopathy: results of the EUROCONDOR clinical trial. Diabetes 68(2):457–463
Tan CS, Chew MC, Lim LW, Sadda SR (2016) Advances in retinal imaging for diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema. Indian J Ophthalmol 64(1):76–83
Ivanisević M, Stanić R (1990) Importance of fluorescein angiography in the early detection and therapy of diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmologica 201(1):9–13
Zhang B, Chou Y, Zhao X, Yang J, Chen Y (2020) Early detection of microvascular impairments with optical coherence tomography angiography in diabetic patients without clinical retinopathy: a meta-analysis. Am J Ophthalmol S0002–9394(20):30530–30534
Lombardo M, Serrao S, Devaney N, Parravano M, Lombardo G (2012) Adaptive optics technology for high-resolution retinal imaging. Sensors (Basel) 13(1):334–366
Shin YI, Nam KY, Lee SE, Lee MW, Lim HB, Jo YJ, Kim JY (2019) Peripapillary microvasculature in patients with diabetes mellitus: an optical coherence tomography angiography study. Sci Rep 9(1):15814
Huang J, Zheng B, Lu Y, Gu X, Dai H, Chen T (2020) Quantification of microvascular density of the optic nerve head in diabetic retinopathy using optical coherence tomographic angiography. J Ophthalmol 29(2020):5014035
Hafner J, Zadrazil M, Grisold A, Ricken G, Krenn M, Kitzmantl D, Pollreisz A, Gleiss A, Schmidt-Erfurth U (2020) Retinal and corneal neurodegeneration and their association with systemic signs of peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. Am J Ophthalmol 209:197–205
Takkar B, Takkar A (2020) Comment on: Retinal and corneal neurodegeneration and its association to systemic signs of peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. Am J Ophthalmol 216:286–287
Picconi F, Mataluni G, Ziccardi L, Parravano M, Di Renzo A, Ylli D, Pasqualetti P, Studer V, Chioma L, Marfia GA, Frontoni S (2018) Association between early neuroretinal dysfunction and peripheral motor unit loss in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Res 4(2018):9763507
Funding
The authors have not received grant support or research funding and do not have any proprietary interests in the materials described in the article; Dr BT gets general research support from the Hyderabad Eye Research Foundation and India Alliance CRTP grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soni, D., Sagar, P. & Takkar, B. Diabetic retinal neurodegeneration as a form of diabetic retinopathy. Int Ophthalmol 41, 3223–3248 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-021-01864-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-021-01864-4