Abstract
Purpose
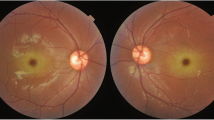
To evaluate accumulation patterns of deposits in retinal layers of type B Niemann–Pick patients by multimodal imaging.
Methods
Seven patients with type B Niemann–Pick disease were included in this study. All participants underwent a complete ophthalmologic evaluation, high-resolution digital colour imaging, spectral-domain optical coherence tomography, blue light fundus autofluorescence and optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA).
Results
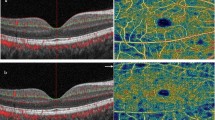
We demonstrated different accumulation patterns in the retinal ganglion cell layer, the retinal nerve fibre layer and the subfoveolar region by multimodal imaging. Local retinal capillary nonflow areas in the superficial plexus, increased vascular tortuosity and deformed foveal avascular areas were shown in OCTA scans.
Conclusion
Multimodal imaging including OCTA is a useful technique for the identification of different types of accumulation patterns, diagnosis and follow-up of type B Niemann–Pick patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Simões RG, Maia H (2014) Niemann-Pick type B in adulthood. BMJ Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2014-208286
Manshadi MD, Kamalidehghan B, Keshavarzi F, Aryani O, Dadgar S, Arastehkani A et al (2015) Four novel p. N385 K, p.V36A, c.1033–1034insT and c.1417–1418delCT mutations in the sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1 (SMPD1) gene in patients with types A and B Niemann–Pick disease. Int J Mol Sci 16:6668–6676
Schuchman EH, Desnick RJ (2017) Types A and B Niemann–Pick disease. Mol Genet Metab 120:27–33
Cogan DG, Chu FC, Barranger JA, Gregg R (1982) Macula halo syndrome. Read in part before the American Ophthalmological Society, Hot Springs, VA, 25 May 1982
Campbell JP, Zhang M, Hwang TS et al (2017) Detailed vascular anatomy of the human retina by projection-resolved optical coherence tomography angiography. Sci Rep 7:42201
Libert J, Toussaint D, Guiselings R (1975) Ocular findings in Niemann–Pick disease. Am J Ophthalmol 80:991–1002
Robb MR, Kuwabara T (1973) The ocular pathology of type A Niemann–Pick disease: a light and electron microscopic study. Invest Ophthalmol 12:366–373
Rudich DS, Curcio CA, Wasserstein M, Brodie SE (2013) Inner macular hyper-reflectivity demonstrated by optical coherence tomography in Niemann–Pick disease. JAMA Ophthalmol 131(9):1244–1246
Rochon-Duvigneaud A (1907) Recherches sur la fovea de la rétine humaine et particulièrement sur le bouquet des cônes centraux. Arch d’Anat Microsc 9:315–342
Tschulakow AV, Oltrup T, Bende T, Schmelzle S, Schraermeyer U (2018) The anatomy of the foveola reinvestigated. PeerJ. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4482
Yan X, Ma L, Hovakimyan M, Lukas J, Wree A, Frank M et al (2014) Defects in the retina of Niemann–Pick type C 1 mutant mice. BMC Neurosci 15:126
Shen C, Yan S, Du M, Zhao H, Shao L, Hu Y (2018) Assessment of capillary dropout in the superficial retinal capillary plexus by optical coherence tomography angiography in the early stage of diabetic retinopathy. BMC Ophthalmol 18:113
Motoharu T, Masako M, Yuichi T (2016) Delineation of capillary dropout in the deep retinal capillary plexus using optical coherence tomography angiography in a patient with Purtscher’s retinopathy exhibiting normal fluorescein angiography findings: a case report. BMC Ophthalmol 16:113
Wang XN, You QS, Li Q, Li Y, Mao Y et al (2018) Findings of optical coherence tomography angiography in Best vitelliform macular dystrophy. Ophthalmic Res. https://doi.org/10.1159/000487488
de Carlo TE, Chin AT, Bonini Filho MA, Adhi M, Branchini L et al (2015) Detection of microvascular changes in eyes of patients with diabetes but not clinical diabetic retinopathy using optical coherence tomography angiography. Retina 35(11):2364–2370
Thurberg BL, Wasserstein MP, Schiano T, O’Brien F, Richards S et al (2012) Liver and skin histopathology in adults with sphingomyelinase deficiency (Niemann–Pick disease type B). Am J Surg Pathol 36(8):1234–1246
San Román IS, Rodríguez ME, Caporossi O, Zoppetti C, Sodi A, Mecocci A et al (2017) Computer assisted retinal vessel tortuosity evaluation in novel mutation Fabry disease: towards new prognostic markers. Retina 37:592–603
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any financial or conflicting interests to disclose.
Ethical standard
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bolukbasi, S., Dogan, C., Kiykim, E. et al. Multimodal imaging including optical coherence tomography angiography in patients with type B Niemann–Pick disease. Int Ophthalmol 39, 2545–2552 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-019-01102-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-019-01102-y