Abstract
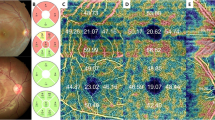
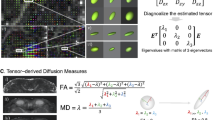
The aim of this study was to investigate whether a correlation exists between optical coherence tomography (OCT) of retina and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of the optic pathway measurements. All subjects underwent OCT measurements of optic nerve head, retinal nerve fiber layer, and macula. Fractional anisotropy (FA) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of optic pathways were analyzed using DTI. Prechiasmatic FA values were significantly decreased in unilateral amblyopic group in both affected and sound fellow eyes (p = 0.019 and 0.013), but not in bilateral amblyopic group (p = 0.221) when compared with the control group. ADC values were significantly greater in sound eye in unilateral amblyopic group in prechiasmatic and postchiasmatic regions (p = 0.001 and 0.049). ADC values were also significantly greater in bilateral amblyopic group in postchiasmatic region (p = 0.037). There were no significant differences between the affected eye and sound eye side DTI measurements. There was no significant correlation between prechiasmatic DTI and OCT measurements in affected and sound eyes of unilateral amblyopia group. DTI results demonstrated that there is a functional underdevelopment of the anterior and posterior visual pathways in both affected and sound eye of unilateral amblyopic patients. Significantly reduced FA values in prechiasmatic region where OCT values of retina were normal can be explained by possible micro-structural changes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hess RF (2001) Amblyopia: site unseen. Clin Exp Optom 84:321–336
Barnes GR, Hess RF, Dumoulin SO, Achtman RL, Pike GB (2001) The cortical deficit in humans with strabismic amblyopia. J Physiol (15) 533(Pt 1):281–297
Anderson SJ, Swettenham JB (2006) Neuroimaging in human amblyopia. Strabismus 14:21–35
Goodyear BG, Nicolle DA, Humphrey GK, Menon RS (2000) BOLD fMRI response of early visual areas to perceived contrast in human amblyopia. J Neurophysiol 84:1907–1913
Beaulieu C (2002) The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:435–455
Roebroeck A, Galuske R, Formisano E, Chiry O, Bratzke H, Ronen I, Kim D, Goebel R (2008) High-resolution diffusion tensor imaging and tractography of the human optic chiasm at 9.4 T. NeuroImage 39:157–168
Sakuma H, Nomura Y, Takeda K, Tagami T, Nakagawa T, Tamagawa Y et al (1991) Adults and neonatal human brain: diffusional anisotropy and myelination with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 180:229–233
Morriss MC, Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT, Hunter JV, Haselgrove JC (1999) Changes in brain water diffusion during childhood. Neuroradiology 41:929–934
Filippi CG, Lin DD, Tsiouris AJ, Watts R, Packard AM, Heier LA et al (2003) Diffusion Tensor MR imaging in children with developmental delay: preliminary findings. Radiology 229:44–50
Shimony JS, Burton H, Epstein AA, Mclaren DG, Sun SW, Synder AZ (2006) Diffusion tensor imaging reveals white matter reorganization in early blind humans Cereb. Cortex 16:1653–1661
Anik I, Anik Y, Koc K, Ceylan S, Genc H, Altintas O et al (2011) Evaluation of early visual recovery in pituitary macroadenomas after endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery: quantitative assessment with diffusion tensor imaging. Acta Neurochir 153(4):831–842
Xie S, Gong GL, Xiao JX, Ye JT, Liu HH, Gan XL et al (2007) Underdevelopment of optic radiation in children with amblyopia: a tractography study. Am J Ophthalmol 143(4):642–646
Yen MY, Cheng CY, Wang AG (2004) Retinal nerve fiber thickness in unilateral amblyopia. Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:2224–2230
Altintas O, Yuksel N, Ozkan B, Caglar Y (2005) Thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer, macular thickness and macular volume in patients with strabismic amblyopia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 42:216–221
Li Q, Jiang Q, Guo M et al (2013) Grey and white matter changes in children with monocular amblyopia: voxel-based morphometry and diffusion tensor imaging study. Br J Ophthalmol 97:524–529
Duan Y, Norcia AM, Yeatman JD, Mezer A (2015) The structural properties of major white matter tracts in strabismic amblyopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 56(9):5152–5160
Beaulieu C (2002) The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:435–455
Moon WJ, Provenzale JM, Sarıkaya B, Ihn YK, Morlese J, Chen S et al (2011) Diffusion-tensor imaging assessment of white matter maturation in childhood and adolescence. AJR Am J Roentgenol 197(3):704–712
Lee SK, Kim DI, Kim J, Kim DJ, Kim HD, Kim DS et al (2005) Diffusion-Tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography: a new method of describing aberrant fiber connections in developmental CNS anomalies. RadioGraphics 25:53–68
Provenzale JM, Liang L, De Long D, White LE (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging. Assessment of brain white matter maturation during the first postnatal year. AJR 189:476–486
Stieltjes B, Kaufmann WE, van Zijl PC (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging and axonal tracking in the human brainstem. Neuroimage 14:723–735
Sbardella E, Tona F, Petsas N, Pantano P (2013) DTI Measurements in Multiple Sclerosis: Evaluation of Brain Damage and Clinical Implications. MultScler Int. doi: 10.1155/2013/671730
Crawford MLJ, Von Noorden GK (1979) Concomitant strabismus and cortical eye dominance in young rhesus monkeys. Trans Ophthalmol Soc UK 99:369–374
Maehara G, Thompson B, Mansouri B, Farivar R, Hess RF (2011) The perceptual consequences of interocular suppression in amblyopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:9011–9017
Mower GD, Christen WG, Burchfiel JL, Duffy FH (1984) Microiontophoretic bicuculline restores binocular responses to visual cortical neurons in strabismic cats. Brain Res 309:168–172
Hess RF, Thompson B, Gole G, Mullen KT (2009) Deficient responses from the lateral geniculate nucleus in humans with amblyopia. Eur J Neurosci 29:1064–1070
Qi S, Mu YF, Cui LB et al (2016) Association of optic radiation integrity with cortical thickness in children with anisometropic amblyopia. Neurosci Bull 32(1):51–60
Farivar R, Thompson B, Mansouri B, Hess RF (2011) Interocular suppression in strabismic amblyopia results in an attenuated and delayed hemodynamic response function in early visual cortex. J Vis. doi:10.1167/11.14.16
Tugcu B, Araz-Ersan B, Kilic M, Erdogan ET, Yigit U, Karamursel S (2013) The morpho-functional evaluation of retina in amblyopia. Curr Eye Res 38(7):802–809
Leguire LE, Rogers GL, Bremer DL (1990) Amblyopia: the normal eye is not normal. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 27:32–38
Giaschi DE, Regan D, Kraft SP, Hong XH (1992) Defective processing of motion-defined form in the fellow eye of patients with unilateral amblyopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 33:2483–2489
Chatzistefanou KI, Theodossiadis GP, Damanakis AG, Ladas ID, Moschos MN, Chimonidou E (2005) Contrast sensitivity in amblyopia: the fellow eye of untreated and successfully treated amblyopes. JAAPOS 9:468–474
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ozgul Altintas, Sevtap Gumustas, and Ruken Cinik have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altıntaş, Ö., Gümüştaş, S., Cinik, R. et al. Correlation of the measurements of optical coherence tomography and diffuse tension imaging of optic pathways in amblyopia. Int Ophthalmol 37, 85–93 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-016-0229-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-016-0229-0