Abstract
Objective
The aim of the present study was to investigate anti-inflammatory activity of Diclocor in the setting of collagen-induced osteoarthritis in rats in comparison with its active monocomponents—diclofenac sodium and quercetin.
Methods
The study was conducted on the model of collagen-induced osteoarthritis and included measurement of sialic acids, glycoproteins, C-reactive protein, prostaglandin E2, 6-keto-prostaglandin F1α, thromboxane B2, and leukotriene B4. Lastly, morphologic study with morphometry was also performed.
Results
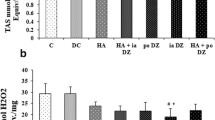
Diclocor is superior to quercetin and diclofenac sodium by the degree of pharmacological effect on some of the studied parameters. The differences between the values were statistically significant.
Conclusion
Diclocor is a promising corrector of inflammatory and destructive joint diseases. Owing to the presence of both diclofenac sodium and quercetin in its composition, Diclocor exhibits a complex mechanism of anti-inflammatory action affecting cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase ways of arachidonic acid biotransformation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aalbers J (2012) Benefit versus risk in the use of non-selective NSAIDs and selective COX-2 inhibitors. Cardiovasc J Afr 23(6):356
Bakhshaeshi M, Khaki A, Fathiazad F, Khaki AA, Ghadamkheir E (2012) Anti-oxidative role of quercetin derived from Allium cepa on aldehyde oxidase (OX-LDL) and hepatocytes apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2(7):528–531
Chernoivan NH (2010) Modulation by gastroprotective and antisecretory drugs of the antioxidant action of diclofenac sodium on a model of an oxidative modification of protein in vitro. Buk Med Herald 14(4):129–132
Chernoivan NH (2012) Using drugs with polyfunctional properties for enhancement of therapeutic effectiveness and safety of NSAIDs and perspectives for creation of a new drug. Institute of pharmacology and toxicology of NAMN Ukraine, Kiev
Chernoivan NH, Stepaniuk HI, Belenichev IF, Pavlov SV, Grib VV (2010) Modulation of antioxidative action of diclofenac sodium by combining with gastroprotective drugs in vitro. Pharmacol Med Toxicol 3(16):55–60
Comalada M, Camuesco D, Sierra S, Ballester I, Xaus J, Galvez J, Zarzuelo A (2005) In vivo quercitrin anti-inflammatory effect involves release of quercetin, which inhibits inflammation through down-regulation of the NFkappaB pathway. Eur J Immunol 35:584–592
Hauser RA (2010) The acceleration of articular cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Prolotherapy 2(1):305–322
Kamishnikov VS (2003) Clinico-biochemical laboratory diagnostics. Inter press service, Minsk
Karpishchenko AI (2002) Medical laboratory technologies. Intermedica, Saint-Petersburg
Kirkwood BR, Sterne J (2003) Essential medical statistics, 2nd edn. Blackwell Science, Oxford
Kovalenko VM (2006) NSAIDs: role and place in contemporary reumatological practice on the basis of evidence-based medicine. Ukr Reumatol J 1(23):17–29
Lader E (2013) ACP Journal Club. Review: NSAIDs increase GI and CV events; coxibs increase mortality. Ann Intern Med 159(8):JC12
Loke WM, Proudfoot JM, Stewart S, McKinley AJ, Needs PW, Kroon PA, Hodgson JM, Croft KD (2008) Metabolic transformation has a profound effect on anti-inflammatory activity of flavonoids such as quercetin: lack of association between antioxidant and lipoxygenase inhibitory activity. Biochem Pharmacol 75(5):1045–1053
Popov OS, Zupanets IA, Shebeko SK (2015) Morphological study of the effect of the drug “Diclocor” in the course of collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Morphologia 9(3):58–66. https://doaj.org/article/ca3c276dbd5c46fb83a4abd178564a4f
Rebrova OY (2006) Statistical analysis of medical data. Application of a software program STATISTICA, 3rd edn. MediaSphera, Moscow
Remmers EF, Joe B, Griffiths MM, Dobbins DE, Dracheva SV, Hashiramoto A, Furuya T, Salstrom JL, Wang J, Gulko PS, Cannon GW, Wilder RL (2002) Modulation of multiple experimental arthritis models by collagen-induced arthritis quantitative trait loci isolated in congenic rat lines. Arthritis Rheum 46(8):2225–2234
Rogerio AP (2007) Anti-inflammatory activity of quercetin and isoquercitrin in experimental murine allergic asthma. Inflamm Res 56:402–408
Stepaniuk HI, Chernoivan NH, Bezpalko LV, Shalamay AS (2009) Corvitin as a method of diclofenac-induced gastropathy prophylaxis. Patent 43359 Ukraine
Zahorodnyi MI (2003) Effect of quercetin on diclofenac sodium-induced ulceration. Lik Sprava 1:96–99
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All animal studies were performed in accordance with Directive 2010/63/EU on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. The plan of this study was approved by the Ethical Committee of National University of Pharmacy, Kharkiv, Ukraine.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zupanets, I.A., Shebeko, S.K., Popov, O.S. et al. Diclocor is superior to diclofenac sodium and quercetin in normalizing biochemical parameters in rats with collagen-induced osteoarthritis. Inflammopharmacol 24, 53–57 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-015-0258-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-015-0258-8