Abstract
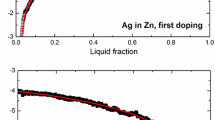
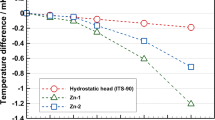
The estimation of the uncertainty component attributable to impurities remains a central and important topic of fixed-point research. Various methods are available for this estimation, depending on the extent of the available information. The sum of individual estimates method has considerable appeal where there is adequate knowledge of the sensitivity coefficients for each of the impurity elements and sufficiently low uncertainty regarding their concentrations. The overall maximum estimate (OME) forsakes the behavior of the individual elements by assuming that the cryoscopic constant adequately represents (or is an upper bound for) the sensitivity coefficients of the individual impurities. Validation of these methods using melting and/or freezing curves is recommended to provide confidence. Recent investigations of indium, tin, and zinc fixed points are reported. Glow discharge mass spectrometry was used to determine the impurity concentrations of the metals used to fill the cells. Melting curves were analyzed to derive an experimental overall impurity concentration (assuming that all impurities have a sensitivity coefficient equivalent to that of the cryoscopic constant). The two values (chemical and experimental) for the overall impurity concentrations were then compared. Based on the data obtained, the pragmatic approach of choosing the larger of the chemical and experimentally derived quantities as the best estimate of the influence of impurities on the temperature of the freezing point is suggested rather than relying solely on the chemical analysis and the OME method to derive the uncertainty component attributable to impurities.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Preston-Thomas, Metrologia 27, 3 (1990); Erratum. Metrologia 27, 107 (1990)
S. Rudtsch, T. Gusarova, A. Aulich, M. Fahr, J. Fischer, H. Klipphardt, R. Matschat, U. Panne, Int. J. Thermophys. 32, 293 (2011)
G. Failleau, N. Fleurence, R. Morice, E. Gaviot, E. Rénaot, Int. J. Thermophys. 31, 1608 (2010)
B. Fellmuth, K.D. Hill, Metrologia 43, 71 (2006)
K. Yamazawa, J.V. Widiatmo, M. Arai, Int. J. Thermophys. 28, 1941 (2007)
S.F. Tsai, in Temperature: Its Measurement and Control in Science and Industry, vol. 8, ed. by C. W. Meyer (AIP Publishing, Melville, NY, 2013), pp. 255–258. doi:10.1063/1.4819549
J.V. Widiatmo, M. Sakai, K. Satou, K. Yamazawa, J. Tamba, M. Arai, Int. J. Thermophys. 32, 309 (2011)
G. Krapf, H. Mammen, G. Blumröder, T. Fröhlich, Meas. Sci. Technol. 23, 074022 (2012)
B. Fellmuth, K.D. Hill, P. Bloembergen, M. de Groot, Y. Hermier, M. Matveyev, A. Pokhodun, D. Ripple, P.P.M. Steur, “Methodologies for the Estimation of Uncertainties and the Correction of Fixed-Point Temperatures Attributable to the Influence of Chemical Impurities,” Consultative Committee for Thermometry Document CCT/05-08 (BIPM, Sèvres, France, 2005), http://www.bipm.org/cc/CCT/Allowed/23/CCT_05_08_rev.pdf. Accessed 19 Sept 2013
J. Ancsin, Metrologia 38, 229 (2001)
J.V. Pearce, Int. J. Thermophys. (2014). doi:10.1007/s10765-014-1585-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hill, K.D. Estimating the Contribution of Impurities to the Uncertainty of Metal Fixed-Point Temperatures. Int J Thermophys 35, 636–647 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-014-1638-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-014-1638-9