Abstract
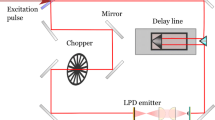
We present an electronic beam switching/steering device for operation at THz frequencies. The propagation direction of the THz beam is switched via electronic manipulation of the refractive index of a liquid crystal. The design of the steering device and the parameters of the liquid crystal are described and angle-dependent THz-TDS measurements of the beam steering are reported. This device is able to deflect the propagation direction of the THz beam by 6.3 °. This particular device approach offers a viable option for beam steering/switching in various THz applications including fiber switches, scanning imagers, and free-space communication systems in which the detector or emitter is in motion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Kleine-Ostmann and T. Nagatsuma, “A review on terahertz communications research,” J. Infrared Millim. Te., pp. 1–29, 2011.
R. Piesiewicz, T. Kleine-Ostmann, N. Krumbholz, D. Mittleman, M. Koch, J. Schoebel, and T. Kurner, “Short-range ultra-broadband terahertz communications: Concepts and perspectives,” IEEE Antenn. Propag. M., vol. 49, no. 6, pp. 24–39, 2007.
M. Theuer and J. Melinger, “High resolution waveguide terahertz time-domain spectroscopy,” J. Infrared Millim. Te., pp. 1–18, 2011.
A. True, K. Schroeck, T. French, and C. Schmuttenmaer, “Terahertz spectroscopy of histidine enantiomers and polymorphs,” J. Infrared Millim. Te., vol. 32, no. 5, pp. 691–698, 2011.
P. Jepsen and H. Merbold, “Terahertz reflection spectroscopy of aqueous NaCl and LiCl solutions,” J. Infrared Millim. Te., vol. 31, no. 4, pp. 430–440, 2010.
N. Vieweg, M. Shakfa, B. Scherger, M. Mikulics, and M. Koch, “THz Properties of Nematic Liquid Crystals,” J. Infrared Millim. Te., vol. 31, no. 11, pp. 1312–1320, 2010.
J. Laib and D. Mittleman, “Temperature-dependent terahertz spectroscopy of liquid n-alkanes,” J. Infrared Millim. Te., vol. 31, no. 9, pp. 1015–1021, 2010.
S. Katletz, M. Pfleger, H. Pühringer, N. Vieweg, B. Scherger, B. Heinen, M. Koch, and K. Wiesauer, “Efficient terahertz en-face imaging,” Opt. Express, vol. 19, no. 23, pp. 23042–23053, 2011.
T. Shibuya, T. Suzuki, K. Suizu, and K. Kawase, “Non-destructive characterization of soot in exhaust filters using millimeter-wave imaging,” J. Infrared Millim. Te., vol. 32, no. 5, pp. 716–721, 2011.
M. Scheller, J. Yarborough, J. Moloney, M. Fallahi, M. Koch, and S. Koch, “Room temperature continuous wave milliwatt terahertz source,” Opt. Express, vol. 18, no. 26, pp. 27112–27117, 2010.
W. Knap, S. Nadar, H. Videlier, S. Boubanga-Tombet, D. Coquillat, N. Dyakonova, F. Teppe, K. Karpierz, J. Lusakowski, M. Sakowicz, I. Kasalynas, D. Seliuta, G. Valusis, T. Otsuji, Y. Meziani, A. El Fatimy, S. Vandenbrouk, K. Madjour, D. Théron, and C. Gaquière, “Field effect transistors for terahertz detection and emission,” J. Infrared Millim. Te., vol. 32, pp. 618–628, 2011.
B. Scherger, C. Jördens, and M. Koch, “Variable-focus terahertz lens,” Opt. Express, vol. 19, no. 5, pp. 4528–4535, 2011.
B. Scherger, M. Scheller, C. Jansen, M. Koch, and K. Wiesauer, “Terahertz lenses made by compression molding of micropowders,” Appl. Opt., vol. 50, no. 15, pp. 2256–2262, 2011.
J. Liu, R. Mendis, and D. Mittleman, “The transition from a TEM-like mode to a plasmonic mode in parallel-plate waveguides,” Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 98, p. 231113, 2011.
C. Jördens, K. Chee, I. Al-Naib, I. Pupeza, S. Peik, G. Wenke, and M. Koch, “Dielectric fibres for low-loss transmission of millimetre waves and its application in couplers and splitters,” J. Infrared Millim. Te., vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 214–220, 2010.
S. Saha, Y. Ma, J. Grant, A. Khalid, and D. Cumming, “Low-loss terahertz artificial dielectric birefringent quarter-wave plates,” IEEE Photonic. Tech. L., vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 79–81, 2010.
B. Scherger, M. Scheller, N. Vieweg, S. T. Cundiff, and M. Koch, “Paper terahertz wave plates,” Opt. Express, vol. 19, no. 25, pp. 24884–24889, 2011.
Z. Ghattan, T. Hasek, R. Wilk, M. Shahabadi, and M. Koch, “Sub-terahertz on-off switch based on a two-dimensional photonic crystal infiltrated by liquid crystals,” Opt. Commun., vol. 281, no. 18, pp. 4623–4625, 2008.
T. Tsai, C. Chen, R. Pan, C. Pan, and X. Zhang, “Electrically controlled room temperature terahertz phase shifter with liquid crystal,” IEEE Microw. Wirel. Co., vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 77–79, 2004.
H. Chen, W. Padilla, J. Zide, A. Gossard, A. Taylor, and R. Averitt, “Active terahertz metamaterial devices,” Nat., vol. 444, no. 7119, pp. 597–600, 2006.
N. Vieweg, N. Born, I. Al-Naib, and M. Koch, “Electrically tunable terahertz notch filters,” J. Infrared Millim. Te., pp. 1–6, 2012.
H. Zhang, P. Guo, P. Chen, S. Chang, and J. Yuan, “Liquid-crystal-filled photonic crystal for terahertz switch and filter,” JOSA B, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 101–106, 2009.
R. Wilk, N. Vieweg, O. Kopschinski, and M. Koch, “Liquid crystal based electrically switchable Bragg structure for THz waves,” Opt. Express, vol. 17, no. 9, pp. 7377–7382, 2009.
D. Werner, D. Kwon, I. Khoo, A. Kildishev, and V. Shalaev, “Liquid crystal clad near-infrared metamaterials with tunable negative-zero-positive refractive indices,” Opt. Express, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 3342–3347, 2007.
R. Kersting, G. Strasser, and K. Unterrainer, “Terahertz phase modulator,” Electron. Lett., vol. 36, no. 13, pp. 1156–1158, 2000.
H. Chen, W. Padilla, M. Cich, A. Azad, R. Averitt, and A. Taylor, “A metamaterial solid-state terahertz phase modulator,” Nat. photonics, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 148–151, 2009.
T. Kleine-Ostmann, K. Pierz, G. Hein, P. Dawson, and M. Koch, “Audio signal transmission over THz communication channel using semiconductor modulator,” Electron. Lett., vol. 40, no. 2, pp. 124–126, 2004.
H. Han, H. Park, M. Cho, and J. Kim, “Terahertz pulse propagation in a plastic photonic crystal fiber,” Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 80, p. 2634, 2002.
T. Ito, Y. Matsuura, M. Miyagi, H. Minamide, and H. Ito, “Flexible terahertz fiber optics with low bend-induced losses,” JOSA B, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 1230–1235, 2007.
K. Nielsen, H. Rasmussen, A. Adam, P. Planken, O. Bang, and P. Jepsen, “Bendable, low-loss topas fibers for the terahertz frequency range,” Opt. Express, vol. 17, no. 10, pp. 8592–8601, 2009.
S. Atakaramians, S. Afshar V, H. Ebendorff-Heidepriem, M. Nagel, B. Fischer, D. Abbott, and T. Monro, “THz porous fibers: design, fabrication and experimental characterization,” Opt. Express, vol. 17, no. 16, pp. 14053–15062, 2009.
M. Naftaly and R. E. Miles, “Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy of silicate glasses and the relationship to material properties,” J. Appl. Phys., vol. 102, no. 4, p. 043517, 2007.
M. Reuter, N. Vieweg, B. M. Fischer, M. Mikulicz, M. Koch, K. Garbat, and R. Dabrowski, “Highly birefringent, low-loss liquid crystals for THz applications,” submitted for publication, 2012.
E. Nowinowski-Kruszelnicki, J. Kedzierski, Z. Raszewski, L. Jaroszewicz, R. Dabrowski, M. Kojdecki, W. Piecek, P. Perkowski, K. Garbat, M. Olifierczuk, S. M., K. Ogrodnik, P. Morawiak, and E. Miszczyk, “High birefringence liquid crystal mixtures for electro-optical devices,” Opt. Appl., vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 167–180, 2012.
N. Krumbholz, T. Hochrein, N. Vieweg, T. Hasek, K. Kretschmer, M. Bastian, M. Mikulics, and M. Koch, “Monitoring polymeric compounding processes inline with THz time-domain spectroscopy,” Polym. Test., vol. 28, no. 1, pp. 30–35, 2009.
Acknowledgments
Benedikt Scherger acknowledges financial support from the Friedrich Ebert Stiftung. Nico Vieweg likes to express his appreciation to the Studienstiftung des deutschen Volkes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scherger, B., Reuter, M., Scheller, M. et al. Discrete Terahertz Beam Steering with an Electrically Controlled Liquid Crystal Device. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves 33, 1117–1122 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-012-9927-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-012-9927-5