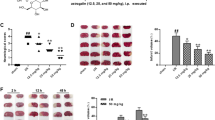
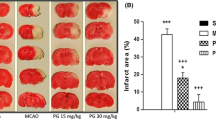
Abstract
It is well established that inflammatory reactions and oxidative stress play an imperial role in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion pathogenesis. Fisetin is a flavonoid and has an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect on various diseases. In this study, we have been working to examine the neuroprotective effect of fisetin in brain injuries triggered by cerebral ischemic-reperfusion and explore the potential role of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling. In vitro, fisetin was examined against the cell viability, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) leakage, cytokines, and apoptosis after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) induced in the cells. In vivo, I/R injury was induced in the brain via transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (2 h) and reperfusion (20 h). The infarction area, brain water content, and neurofunctional parameters were also estimated. Inflammatory cytokines and brain injury markers were scrutinized at the end of the study. Fisetin treatment alleviated cell injury and suppressed the inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-1 (IL-1), tumor necrosis factor- α (TNF-α), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), interleukin-16 (IL-6), and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)) and antioxidant parameters in a dose-dependent manner. Fisetin significantly (P < 0.001) reduced the infarct volume, brain water content. Fisetin significantly (P < 0.001) suppressed the neurological parameters and inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, TNF-α, iNOS, IL-1β, COX-2, IL-6, PGE2, and oxidative markers in a dose-dependent manner. Fisetin significantly (P < 0.001) reduced the inflammatory mediators including NF-κB and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1). Further studies also showed that fisetin significantly inhibited the NF-κB activity via inflammatory and antioxidant pathways. In conclusion, by suppressing inflammatory cytokines, fisetin protected the brain tissue against I/R injury, and this effect could be due to reduced NF-κB activity.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor kappa B
- LDH:
-
lactate dehydrogenase
- I/R:
-
ischemia/reperfusion
- IL-1:
-
interleukin-1
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor-α
- Inos:
-
inducible nitric oxide synthase
- IL-1β:
-
interleukin-1β
- COX-2:
-
cyclooxygenase-2
- IL-6:
-
interleukin-6
- PGE2 :
-
prostaglandin E2
- MMPs:
-
matric metalloproteinases
- ASIC:
-
acid-sensing ion channel
- ATP:
-
adenosine triphosphate
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- TLRs:
-
toll-like receptors
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- AlCl3 :
-
aluminum chloride
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- CO2 :
-
carbon dioxide
- PBS:
-
phosphate buffer saline
- 15-HETE:
-
15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid
- TMB:
-
3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine
- SD:
-
Sprague-Dawley
- MCAO:
-
middle cerebral artery
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- CAT:
-
catalase
- MDA:
-
malonaldehyde
- GSH:
-
glutathione
- GPx:
-
glutathione peroxidase
- GR:
-
glutathione reductase
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- K+ :
-
potassium
- Na+ :
-
sodium
- PPAR-γ:
-
peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor gamma
- STAT1:
-
signal transducer and activator of transcription factors and transcription-1
- DNA:
-
deoxyribonucleic acid
References
Song, Jungbin, Young Sik Kim, Dong Hwan Lee, Sung Hyun Lee, Hyo Jin Park, Donghun Lee, and Hocheol Kim. 2019. Neuroprotective effects of oleic acid in rodent models of cerebral ischaemia. Scientific Reports 9: 10732. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47057-z.
Huang, Lifa, Chengwei Chen, Xin Zhang, Li Xu, Zupeng Chen, Chao Yang, Xiaolong Liang, Guochong Zhu, and Xu. Zhen. 2018. Neuroprotective effect of curcumin against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion via mediating autophagy and inflammation. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience 64: 129–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-1006-x.
Fu, Chen, Xinyang Zhang, Zixiu Zeng, Tian Yang, Xianglan Jin, Fengli Wang, Zhenmin Xu, Baoxin Chen, Hong Zheng, and Xuemei Liu. 2020. Neuroprotective effects of Qingnao dripping pills against cerebral ischemia via inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome signaling pathway: in vivo and in vitro. Frontiers in Pharmacology 11: 65. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00065.
Chen, Chunxia, Chen Wan, Zhihuan Nong, Yichu Nie, Xiaoyu Chen, Xiaorong Pan, Ying Guo, Meicun Yao, and Wenbin Deng. 2020. Hyperbaric oxygen alleviated cognitive impairments in mice induced by repeated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibition of autophagy. Life Sciences 241: 117170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117170.
Li, Kang, Dun Ding, and Ming Zhang. 2016. Neuroprotection of osthole against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through an anti-apoptotic pathway in rats. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 39: 336–342. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b15-00699.
Guo, Minmin, Huiling Lu, Jian Qin, Qu Shengbiao, Wenbo Wang, Yanhong Guo, Weiyong Liao, Mengwei Song, Jian Chen, and Yong Wang. 2019. Biochanin A provides neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by Nrf2-mediated inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation signaling pathway in rats. Medical Science Monitor 25: 8975–8983. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.918665.
Gao, Jianmei, Nana Chen, Na Li, Fan Xu, Wei Wang, Yaying Lei, Jingshan Shi, and Qihai Gong. 2020. Neuroprotective effects of trilobatin, a novel naturally occurring Sirt3 agonist from Lithocarpus polystachyus Rehd., mitigate cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: involvement of TLR4/NF-κB and Nrf2/Keap-1 signaling. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling 33: 117–143. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2019.7825.
Dai, Yunyi, Haojie Zhang, Jianping Zhang, and Mingguang Yan. 2018. Isoquercetin attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis after ischemia/reperfusion injury via Nrf2-mediated inhibition of the NOX4/ROS/NF-κB pathway. Chemico-Biological Interactions 284: 32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.017.
Maurya, Khushboo, and AnandKumar Pandey. 2019. Molecular docking study for evaluation of neuroprotective potential of sericin against cerebral stroke and exploring its biomaterial properties. Biomedical Research Journal 6: 17. https://doi.org/10.4103/bmrj.bmrj_5_19.
Yaidikar, Lavanya, Bavya Byna, and Santh Rani Thakur. 2014. Neuroprotective effect of punicalagin against cerebral ischemia reperfusion-induced oxidative brain injury in rats. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 23: 2869–2878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2014.07.020.
Sinha, Kusum, Geeta Chaudhary, and Yogendra Kumar Gupta. 2002. Protective effect of resveratrol against oxidative stress in middle cerebral artery occlusion model of stroke in rats. Life Sciences 71: 655–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0024-3205(02)01691-0.
Jiang, Jun, Wei Wang, Yong Jun Sun, Mei Hu, Fei Li, and Dong Ya Zhu. 2007. Neuroprotective effect of curcumin on focal cerebral ischemic rats by preventing blood-brain barrier damage. European Journal of Pharmacology 561: 54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.12.028.
Tang, Hao, Yuping Tang, Nianguang Li, Qianping Shi, Jianming Guo, Erxin Shang, and Jin Ao Duan. 2014. Neuroprotective effects of scutellarin and scutellarein on repeatedly cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 118: 51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2014.01.003.
Qian, Lihua, Minzhe Shen, Hao Tang, Yuping Tang, Li Zhang, Fu Yifan, Qianping Shi, and Nian Guang Li. 2012. Synthesis and protective effect of scutellarein on focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Molecules 17: 10667–10674. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910667.
Sun, Lingyan, Xia Tian, Lingshan Gou, Xin Ling, Ling Wang, Yan Feng, Xiaoxing Yin, and Yi Liu. 2013. Beneficial synergistic effects of concurrent treatment with theanine and caffeine against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 91: 562–569. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2012-0309.
Tang, Hao, Ze Xi Dong, Gu Ting, Nian Guang Li, Yu Ping Tang, Qian Ping Shi, Jian Ming Guo, Peng Xuan Zhang, and Jin Ao Duan. 2015. Studies on the protective effects of scutellarein against neuronal injury by ischemia through the analysis of endogenous amino acids and Ca2+ concentration together with Ca2+-ATPase activity. Journal of Chemistry 2015: 497842–497847. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/497842.
Wang, Wenjuan, Xiaotang Ma, Jichun Han, Mingjie Zhou, Huanhuan Ren, Qunwen Pan, Chunli Zheng, and Qiusheng Zheng. 2016. Neuroprotective effect of scutellarin on ischemic cerebral injury by down-regulating the expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme and AT1 receptor. PLoS ONE 11 (1): e0146197. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146197.
Du, Shibin, Youliang Deng, Hongjie Yuan, and Yanyan Sun. 2019. Safflower Yellow B Protects brain against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury through AMPK/NF-kB pathway. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2019: 7219740–7219711. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7219740.
Liu, Xiao Jie, Zhi Gang Mei, Jing Ping Qian, Yong Bao Zeng, and Ming Zhi Wang. 2013. Puerarin partly counteracts the inflammatory response after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion via activating the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Neural Regeneration Research 8: 3203–3215. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.34.004.
Akpa, Amaka Rosita, Joseph Olusegun Ayo, Hudu Garba Mika’il, and Friday Ocheja Zakari. 2020. Protective effect of fisetin against subchronic chlorpyrifos-induced toxicity on oxidative stress biomarkers and neurobehavioral parameters in adult male albino mice. Toxicological Research. Springer Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43188-020-00049-y.
Piao, Mei Jing, Ki Cheon Kim, Sungwook Chae, Young Sam Keum, Hye Sun Kim, and Jin Won Hyun. 2013. Protective effect of fisetin (3,7,3’,4’-tetrahydroxyflavone) against γ-irradiation-induced oxidative stress and cell damage. Biomolecules and Therapeutics 21: 210–215. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2013.017.
Shin, Won Ho, Sang Joon Park, and Eun Joo Kim. 2006. Protective effect of anthocyanins in middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion model of cerebral ischemia in rats. Life Sciences 79: 130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2005.12.033.
Bora, Kundan Singh, and Anupam Sharma. 2010. Neuroprotective effect of Artemisia absinthium L. on focal ischemia and reperfusion-induced cerebral injury. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 129: 403–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2010.04.030.
Huang, Judy, Urvashi M. Upadhyay, and Rafael J. Tamargo. 2006. Inflammation in stroke and focal cerebral ischemia. Surgical Neurology 66: 232–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2005.12.028.
Pan, Jie, Angelos Aristeidis Konstas, Brian Bateman, Girolamo A. Ortolano, and John Pile-Spellman. 2007. Reperfusion injury following cerebral ischemia: pathophysiology, MR imaging, and potential therapies. Neuroradiology. 49 (2): 93–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0183-z.
Yuan, Yu, Weidong Men, Xiaosong Shan, Hexin Zhai, Xiaoxia Qiao, Lianting Geng, and Chunhui Li. 2020. Baicalein exerts neuroprotective effect against ischaemic/reperfusion injury via alteration of NF-kB and LOX and AMPK/Nrf2 pathway. Inflammopharmacology 28: 1327–1341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00714-6.
Hu, Xia Min, Mi Mei Zhou, Xian Min Hu, and Fan Dian Zeng. 2005. Neuroprotective effects of scutellarin on rat neuronal damage induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 26: 1454–1459. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2005.00239.x.
Martz, Dean, Mary Beer, and A. Lorris Betz. 1990. Dimethylthiourea reduces ischemie brain edema without affecting cerebral blood flow. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 10: 352–357. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.1990.64.
Tang, Hao, Yuping Tang, Nian Guang Li, Hang Lin, Weixia Li, Qianping Shi, Wei Zhang, Pengxuan Zhang, Zexi Dong, Minzhe Shen, Ting Gu, and Jin-Ao Duan. 2015. Comparative metabolomic analysis of the neuroprotective effects of scutellarin and scutellarein against ischemic insult. PLoS ONE 10 (7): e0131569. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0131569.
Liang, Sen, Zhaoyao Chen, Hui Li, Zhilan Cang, Kailin Yin, Minghua Wu, and Shouzhen Luo. 2020. Neuroprotective effect of umbelliferone against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion induced neurological deficits: in-vivo and in-silico studies. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics 0. Taylor & Francis: 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2020.1780153.
Yang, Tiansong, Chuwen Feng, Dongyan Wang, Yuanyuan Qu, Yan Yang, Yulin Wang, and Zhongren Sun. 2020. Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effect of tangeretin against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Inflammation 43. Inflammation: 2332–2343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01303-z.
Acknowledgments
The authors are very thankful to the Xi’an No.1 Hospital for providing the necessary facility.
Data and Materials Availability
All the data are provided on the request to the corresponding author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P. Z. performed the experimental study. J. C. designed the experimental study and interpreted the data. Both authors equally contributed to the proofreading.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The whole animal study was approved from Institute.
Consent for Publication
N/A
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Cui, J. Neuroprotective Effect of Fisetin Against the Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Damage via Suppression of Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Parameters. Inflammation 44, 1490–1506 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01434-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01434-x