Abstract
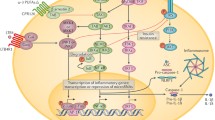
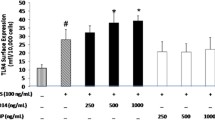
Insulin is a key regulator of metabolism and inflammation in the body. However, the mechanism of the anti-inflammatory effect of insulin is not fully understood. In the present study, we investigated the role of the class A1 scavenger receptor (SR-A1), a prototypic member of the pattern recognition receptor family, in the insulin-mediated suppression of inflammatory responses in macrophages. Our murine in vivo studies show that insulin can attenuate lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxemia in a SR-A1-dependent manner, and this was consistent with our in vitro results which demonstrate that the SR-A1 is necessary for insulin to antagonize the LPS-induced inflammatory responses in macrophages. The effect of SR-A1 on the anti-inflammatory action of insulin might be associated with the activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) signaling pathway in macrophages. Insulin could inhibit macrophage polarization to a pro-inflammatory phenotype via the SR-A1/ERK cascade. Collectively, our results suggest that SR-A1 may be a pivotal element for the anti-inflammation effect of insulin in macrophages.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taniguchi, C.M., B. Emanuelli, and C.R. Kahn. 2006. Critical nodes in signalling pathways: Insights into insulin action. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 7: 85–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1837.
Tokarz, V.L., P.E. MacDonald, and A. Klip. 2018. The cell biology of systemic insulin function. The Journal of Cell Biology 217: 2273–2289. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201802095.
Wasserman, D.H., T.J. Wang, and N.J. Brown. 2018. The vasculature in prediabetes. Circulation research. 122: 1135–1150. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.311912.
Cuschieri, J., E. Bulger, R. Grinsell, I. Garcia, and R.V. Maier. 2008. Insulin regulates macrophage activation through Activin A1. Shock 29: 285–290. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0b013e318123e4d0.
Aljada, A., H. Ghanim, R. Saadeh, and P. Dandona. 2001. Insulin inhibits NFkappaB and MCP-1 expression in human aortic endothelial cells. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 86: 450–453. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.86.1.7278.
Yu, X., H. Yi, C. Guo, D. Zuo, Y. Wang, H.L. Kim, J.R. Subjeck, and X.Y. Wang. 2011. Pattern recognition scavenger receptor CD204 attenuates Toll-like receptor 4-induced NF-kappaB activation by directly inhibiting ubiquitination of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor 6. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 286: 18795–18806. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.224345.
Kobayashi, H., N. Sakashita, T. Okuma, Y. Terasaki, K. Tsujita, H. Suzuki, T. Kodama, H. Nomori, M. Kawasuji, and M. Takeya. 2007. Class A scavenger receptor (CD204) attenuates hyperoxia-induced lung injury by reducing oxidative stress. The Journal of Pathology. 212: 38–46. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.2150.
Zhu, X., G. Zong, L. Zhu, Y. Jiang, K. Ma, H. Zhang, Y. Zhang, H. Bai, Q. Yang, J. Ben, X. Li, Y. Xu, and Q. Chen. 2014. Deletion of class A scavenger receptor deteriorates obesity-induced insulin resistance in adipose tissue. Diabetes 63: 562–577. https://doi.org/10.2337/db13-0815.
Zhu, X.D., Y. Zhuang, J.J. Ben, L.L. Qian, H.P. Huang, H. Bai, J.H. Sha, Z.G. He, and Q. Chen. 2011. Caveolae-dependent endocytosis is required for class A macrophage scavenger receptor-mediated apoptosis in macrophages. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 286: 8231–8239. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.145888.
Liang, C.P., S. Han, T. Senokuchi, and A.R. Tall. 2007. The macrophage at the crossroads of insulin resistance and atherosclerosis. Circulation Research. 100: 1546–1555. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.152165.
Lu, H., D. Huang, K. Yao, C. Li, S. Chang, Y. Dai, A. Sun, Y. Zou, J. Qian, and J. Ge. 2015. Insulin enhances dendritic cell maturation and scavenger receptor-mediated uptake of oxidised low-density lipoprotein. Journal of Diabetes and its Complications 29: 465–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.03.005.
Oh, Y.S., K.A. Cho, S.J. Ryu, L.Y. Khil, H.S. Jun, J.W. Yoon, and S.C. Park. 2006. Regulation of insulin response in skeletal muscle cell by caveolin status. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 99: 747–758. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.20943.
King, G.L., and S.M. Johnson. 1985. Receptor-mediated transport of insulin across endothelial cells. Science 227: 1583–1586.
Uhles, S., T. Moede, B. Leibiger, P.O. Berggren, and I.B. Leibiger. 2003. Isoform-specific insulin receptor signaling involves different plasma membrane domains. The Journal of Cell Biology. 163: 1327–1337. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200306093.
Fagerholm, S., U. Ortegren, M. Karlsson, I. Ruishalme, and P. Stralfors. 2009. Rapid insulin-dependent endocytosis of the insulin receptor by caveolae in primary adipocytes. PLoS One 4: e5985. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005985.
Yamamoto, M., Y. Toya, C. Schwencke, M.P. Lisanti, M.G. Myers Jr., and Y. Ishikawa. 1998. Caveolin is an activator of insulin receptor signaling. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 273: 26962–26968.
Oshikawa, J., K. Otsu, Y. Toya, T. Tsunematsu, R. Hankins, J. Kawabe, S. Minamisawa, S. Umemura, Y. Hagiwara, and Y. Ishikawa. 2004. Insulin resistance in skeletal muscles of caveolin-3-null mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 101: 12670–12675. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0402053101.
Liu, L., D. Brown, M. McKee, N.K. Lebrasseur, D. Yang, K.H. Albrecht, et al. 2008. Deletion of Cavin/PTRF causes global loss of caveolae, dyslipidemia, and glucose intolerance. Cell metabolism. 8: 310–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2008.07.008.
Vainio, S., S. Heino, J.E. Mansson, P. Fredman, E. Kuismanen, O. Vaarala, and E. Ikonen. 2002. Dynamic association of human insulin receptor with lipid rafts in cells lacking caveolae. EMBO Reports 3: 95–100. https://doi.org/10.1093/embo-reports/kvf010.
Frittitta, L., G. Grasso, M.E. Munguira, R. Vigneri, and V. Trischitta. 1993. Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity is reduced in monocytes from non-obese normoglycaemic insulin-resistant subjects. Diabetologia 36: 1163–1167.
Comi, R.J., G. Grunberger, and P. Gorden. 1987. Relationship of insulin binding and insulin-stimulated tyrosine kinase activity is altered in type II diabetes. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 79: 453–462. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI112833.
Liang, C.P., S. Han, H. Okamoto, R. Carnemolla, I. Tabas, D. Accili, and A.R. Tall. 2004. Increased CD36 protein as a response to defective insulin signaling in macrophages. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 113: 764–773. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI19528.
Han, S., C.P. Liang, T. DeVries-Seimon, M. Ranalletta, C.L. Welch, K. Collins-Fletcher, D. Accili, I. Tabas, and A.R. Tall. 2006. Macrophage insulin receptor deficiency increases ER stress-induced apoptosis and necrotic core formation in advanced atherosclerotic lesions. Cell Metabolism. 3: 257–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2006.02.008.
Avruch, J. 2007. MAP kinase pathways: The first twenty years. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1773: 1150–1160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.11.006.
Funding
This study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81830011, 81670418, and 91739304 to Qi Chen, 81870371 to Jingjing Ben, 81770417 to Xudong Zhu, 81670263 to Xiaoyu Li) and the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (18KJA310003 to Jingjing Ben, 15KJA310001 to Xiaoyu Li).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Nanjing Medical University (Permit Number: NJMU/IACUC-1601121).
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, L., Fan, L., Zhu, Y. et al. Insulin Antagonizes LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses by Activating SR-A1/ERK Axis in Macrophages. Inflammation 42, 754–762 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0933-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0933-1