Abstract
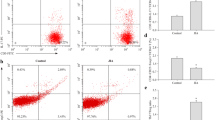
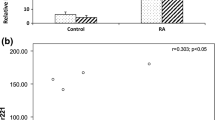
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by chronic synovial inflammation and subsequent joint destruction. Previous studies have confirmed that Th17 cells play a critical role in the pathogenesis of RA. MicroRNA (miR)-301a-3p is a regulatory factor for Th17 cells differentiation that contributes to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. The purposes of this study were to identify the alteration of Th17 cells and analyze the correlation between the expression of the miR-301a-3p and the proportion of Th17 cells in RA patients. The results showed that the frequency of Th17 cells and the expression of transcription factors (RORγt and STAT3) significantly increased in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from RA patients, and the associated proinflammatory cytokines were also upregulated. We also observed that the expression of protein inhibitor of activated STAT3 (PIAS3), the main cellular inhibitor of STAT3, was attenuated in RA patients and negatively correlated with the percentage of Th17 cells in RA. Interestingly, miR-301a-3p, an inhibitor of PIAS3 expression, was overexpressed in the PBMCs from RA patients and positively correlated with the frequency of Th17 cells in patients with RA. Taken together, these data indicated that miR-301a-3p and Th17 cells were augmented in peripheral blood, which may play an important role in the process of RA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, A.K., K.M. Murphy, and A. Sher. 1996. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature 383: 787–793.
Annunziato, F., L. Cosmi, F. Liotta, E. Maggi, and S. Romagnani. 2013. Main features of human T helper 17 cells. The Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1283: 66–70.
Harrington, L.E., R.D. Hatton, P.R. Mangan, H. Turner, T.L. Murphy, K.M. Murphy, et al. 2005. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nature Immunology 6: 1123–1132.
Liang, S.C., X.Y. Tan, D.P. Luxenberg, R. Karim, K. Dunussi-Joannopoulos, M. Collins, et al. 2006. Interleukin (IL)-22 and IL-17 are coexpressed by Th17 cells and cooperatively enhance expression of antimicrobial peptides. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 203: 2271–2279.
Aujla, S.J., P.J. Dubin, and J.K. Kolls. 2007. Th17 cells and mucosal host defense. Seminars in Immunology 19: 377–382.
Bettelli, E., M. Oukka, and V.K. Kuchroo. 2007. Th-17 cells in the circle of immunity and autoimmunity. Nature Immunology 8: 345–350.
Seiderer, J., I. Elben, J. Diegelmann, J. Glas, J. Stallhofer, C. Tillack, et al. 2008. Role of the novel Th17 cytokine IL-17F in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): upregulated colonic IL-17F expression in active Crohn’s disease and analysis of the IL17F p.His161Arg polymorphism in IBD. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases 14: 437–445.
Tang, X., X. Tian, Y. Zhang, W. Wu, J. Tian, K. Rui, et al. 2013. Correlation between the frequency of Th17 cell and the expression of microRNA-206 in patients with dermatomyositis. Clinical and Developmental Immunology 2013: 345347.
Acosta-Rodriguez, E.V., G. Napolitani, A. Lanzavecchia, and F. Sallusto. 2007. Interleukins-1β and 6 but not transforming growth factor-β are essential for the differentiation of interleukin 17–producing human T helper cells. Nature Immunology 8: 942–949.
Volpe, E., N. Servant, R. Zollinger, S.I. Bogiatzi, P. Hupé, E. Barillot, and V. Soumelis. 2008. A critical function for transforming growth factor-beta, interleukin-23 and proinflammatory cytokines in driving and modulating human TH-17 responses. Nature Immunology 9: 650–657.
Ivanov, I.I., B.S. McKenzie, L. Zhou, C.E. Tadokoro, A. Lepelley, J.J. Lafaille, et al. 2006. The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell 126: 1121–1133.
Mathur, A.N., H.C. Chang, D.G. Zisoulis, G.L. Stritesky, Q. Yu, J.T. O’Malley, et al. 2007. Stat3 and Stat4 direct development of IL-17-secreting Th cells. The Journal of Immunology 178: 4901–4907.
Yang, X.O., A.D. Panopoulos, R. Nurieva, S.H. Chang, D. Wang, S.S. Watowich, et al. 2007. STAT3 regulates cytokine-mediated generation of inflammatory helper T cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 282: 9358–9363.
Bixler, S.L., N.G. Sandler, D.C. Douek, and J.J. Mattapallil. 2013. Suppressed Th17 levels correlate with elevated PIAS3, SHP2, and SOCS3 expression in CD4 T cells during acute simian immunodeficiency virus infection. Journal of Virology 87: 7093–7101.
Firestein, G.S. 2003. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 423: 356–361.
van den Berg, W.B., and P. Miossec. 2009. IL-17 as a future therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Reviews. Rheumatology 5: 549–553.
Cascão, R., R.A. Moura, I. Perpétuo, H. Canhão, E. Vieira-Sousa, A.F. Mourão, et al. 2010. Identification of a cytokine network sustaining neutrophil and Th17 activation in untreated early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research and Therapy 12: 196–204.
Wang, S., Y. Shi, M. Yang, J. Ma, J. Tian, J. Chen, et al. 2012. GITRL exacerbates collagen-induced arthritis via enhancing the expansion of Th17 cells. The American Journal of Pathology 180: 1059–1067.
Stefani, G., and F.J. Slack. 2008. Small non-coding RNAs in animal development. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 9: 219–230.
Carlsen, A.L., A.J. Schetter, C.T. Nielsen, C. Lood, S. Knudsen, A. Voss, et al. 2013. Circulating microRNA expression profiles associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis and Rheumatism 65: 1324–1334.
Chen, J., J. Tian, X. Tang, K. Rui, J. Ma, C. Mao, et al. 2015. MiR-346 regulates CD4(+)CXCR5 (+) T cells in the pathogenesis of Graves’ disease. Endocrine 49: 752–760.
Tian, J., K. Rui, X. Tang, J. Ma, Y. Wang, X. Tian, et al. 2015. MicroRNA-9 regulates the differentiation and function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells via targeting Runx1. The Journal of Immunology 195: 1301–1311.
Mycko, M.P., M. Cichalewska, A. Machlanska, H. Cwiklinska, M. Mariasiewicz, and K.W. Selmaj. 2012. MicroRNA-301a regulation of a T-helper 17 immune response controls autoimmune demyelination. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 109: 1248–1257.
Peng, H., Y. Liu, J. Tian, J. Ma, X. Tang, J. Yang, et al. 2015. Decreased expression of microRNA-125a-3p upregulates interleukin-23 receptor in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Immunologic Research 62: 129–136.
Wang, Y., J. Tian, and S. Wang. 2015. The potential therapeutic role of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in autoimmune arthritis. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.07.003.
Farid, S.Sh., G. Azizi, and A. Mirshafiey. 2013. Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies and their clinical utility in rheumatoid arthritis. International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases 16: 379–386.
Yang, D.H., C.C. Tu, S.C. Wang, C.C. Wei, and Y.W. Cheng. 2013. Circulating anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Rheumatology International 34: 971–977.
Suzuki, M., M. Hashizume, H. Yoshida, and M. Mihara. 2010. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of tocilizumab, a humanized anti-IL-6R antibody: effect on the expression of chemokine and adhesion molecule. Rheumatology International 30: 309–315.
Darrieutort-Laffite, C., M.-A. Boutet, M. Chatelais, R. Brion, F. Blanchard, D. Heymann, et al. 2014. IL-1β and TNFα promote monocyte viability through the induction of GM-CSF expression by rheumatoid arthritis synovial Fibroblasts. Mediators of Inflammation 2014: 241840.
Aggarwal, S., N. Ghilardi, M.H. Xie, F.J. de Sauvage, and A.L. Gurney. 2003. Interleukin-23 promotes a distinct CD4 T cell activation state characterized by the production of interleukin-17. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 278: 1910–1914.
Tang X, Tian J, Ma J, Wang J, Qi C, Rui K, et al. 2015. GITRL modulates the activities of p38 MAPK and STAT3 to promote Th17 cell differentiation in autoimmune arthritis. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.6535.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported through grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 31170849, 31470881), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher School (grant no. 20133227110008), Health Department Foundation of Jiangsu Province (grant no. Z201312), Jiangsu Province “333” Project (grant no. BRA2015197), Summit of the Six Top Talents Program of Jiangsu Province (grant no. 2015-WSN-116), Jiangsu University Science Foundation (grant nos. 15JDG070, 11JDG093, FCJJ2015022), Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Laboratory Medicine Foundation (grant no. JSKLM-2014-010), and the Priority Academic Development Program of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Xinyi Tang, Kai Yin and Hongsheng Zhu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X., Yin, K., Zhu, H. et al. Correlation Between the Expression of MicroRNA-301a-3p and the Proportion of Th17 Cells in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Inflammation 39, 759–767 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0304-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0304-8