Abstract
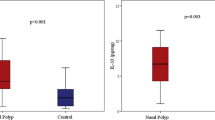
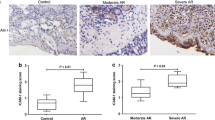
The mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) remain largely unknown. CRSwNP has garnered considerable public health concern owing to its high incidence and unsatisfactory treatment outcomes. Herbal remedies are promising candidates for the treatment of CRSwNP. We examined the utility of andrographolide, a diterpenoid lactone extracted from the Chinese herb Andrographis paniculata, an anti-inflammatory agent for CRSwNP treatment by evaluating interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-17 production and monitoring T helper 17 (Th17) differentiation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) isolated from 20 Chinese CRSwNP patients and 11 control subjects. All CRSwNP patients exhibited clinical features of CRSwNP. Andrographolide significantly inhibited IL-6 and IL-17 production, suppressed p-Stat3 expression, and inhibited Th17 differentiation of PBMCs in vitro. These findings suggested that andrographolide has useful anti-inflammatory properties and could be used for the treatment of CRSwNP.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meltzer, E.O., D.L. Hamilos, J.A. Hadley, et al. 2006. Rhinosinusitis: developing guidance for clinical trials. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 118(5 Suppl): S17–S61.
Fokkens, W.J., V.J. Lund, J. Mullol, et al. 2012. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps. Rhinology Supplement 50: 1–12.
Using topical corticosteroids in general practice. MeReC Bulletin 1999;10(6):21-24.(http://www.npc.co.uk/merec/therap/skin/resources/merec_bulletin_vol10_no06.pdf).
Aromdee, C. 2012. Modifications of andrographolide to increase some biological activities: a patent review (2006–2011). Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents 22: 169–180.
Lim, J.C., T.K. Chan, D.S. Ng, et al. 2012. Andrographolide and its analogues: versatile bioactive molecules for combating inflammation and cancer. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology 39: 300–310.
Li, J., L. Luo, X. Wang, et al. 2009. Inhibition of NF-kappaB expression and allergen-induced airway inflammation in a mouse allergic asthma model by andrographolide. Cellular and molecular immunology 6: 381–385.
Dwivedi, G., L. Fitz, M. Hegen, et al. 2014. A multiscale model of interleukin-6-mediated immune regulation in Crohn’s disease and its application in drug discovery and development. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol 8(3): e89.
Yoshida, Y., and T. Tanaka. 2014. Interleukin 6 and rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed Reseach International 2014: 698313.
Sharma, S., S. Watanabe, A. Sivam, et al. 2012. Peripheral blood and tissue T regulatory cells in chronic rhinosinusitis. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy 26: 372–379.
Ruwanpura, S.M., L. McLeod, G.D. Brooks, et al. 2014. IL-6/Stat3-driven pulmonary inflammation, but not emphysema, is dependent on interleukin-17A in mice. Respirology. doi:10.1111/resp.12243.
Ishiyama, M., H. Tominaga, M. Shiga, et al. 1996. A combined assay of cell viability and in vitro cytotoxicity with a highly water-soluble tetrazolium salt, neutral red and crystal violet. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 19: 1518–1520.
Ping, Wei, Hu. Guo-hua, Kang Hou-yong, et al. 2013. Role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Inflammation. doi:10.1007/s10753-013-9751-7.
Waldner, M.J., and M.F. Neurath. 2014. Master regulator of intestinal disease: IL-6 in chronic inflammation and cancer development. Seminars in Immunology. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2013.12.003.
Wang, Xiao-Qiang, Hu. Guo-Hua, et al. 2012. Imbalanced frequencies of Th17 and Treg cells in acute coronary syndromes are mediated by IL-6-STAT3 signaling. Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology 31: 11–19.
Shen, Y., X.Y. Tang, Y.C. Yang, et al. 2011. Impaired balance of Th17/Treg in patients with nasal polyposis. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology 74: 176–185.
Kim HY, Jhun JY, Cho ML, et al 2013 Interleukin-6 upregulates Th17 response via mTOR/STAT3 pathway in acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure. J Gastroenterol [Epub ahead of print].
Bedoya, S.K., B. Lam, K. Lau, et al. 2013. Th17 cells in immunity and autoimmunity. Clinical and Developmental Immunology 2013: 986789.
Derycke, L., N. Zhang, G. Holtappels, et al. 2012. IL-17A as a regulator of neutrophil survival in nasal polyp disease of patients with and without cystic fibrosis. Journal of Cystic Fibrosis 11: 193–200.
Peters, A.T., A. Kato, N. Zhang, et al. 2010. Evidence for altered activity of the IL-6 pathway in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 125: 397–403.
O’Connell, B.P., R.J. Schlosser, J.L. Wentzel, et al. 2014. Systemic monocyte-derived dendritic cells and associated Th2 skewing in chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 150(2): 312–320.
Ozkara, S., E. Keles, N. Ilhan, et al. 2012. The relationship between Th1/Th2 balance and 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in patients with nasal polyposis. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology 269(12): 2519–2524.
Zhang, N., T. Van Zele, C. Perez-Novo, et al. 2008. Different types of T-effector cells orchestrate mucosal inflammation in chronic sinus disease. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 122(5): 961–968.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no funding, financial relationships, or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wei Kou and Rong Sun, as the co-first authors, equally contributed to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kou, W., Sun, R., Wei, P. et al. Andrographolide Suppresses IL-6/Stat3 Signaling in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Inflammation 37, 1738–1743 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9902-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9902-5