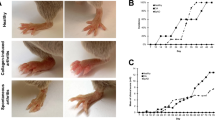
Abstract
Gene expression studies are fundamental for the understanding of complex diseases, providing new insights into the pathogenic process and new tools for diagnostic and patient stratification. Gene profiling studies by real-time PCR require the use of reference genes for normalization and an appropriate validation is essential for accurate results. We performed a comprehensive assessment of six common housekeeping genes in the K/BxN serum-induced arthritis model in mice. Classical statistics and NormFinder analyses pointed out Gapdh as the less stable and therefore unsuitable as a reference control. Gapdh was considerably down-regulated in arthritic joints and therefore produced an overestimation of transcriptional changes. Hptr, B2m, and Rpl13a showed the most constant expression. Collectively our data advise against the use of Gapdh in gene expression studies in the acute phase of the K/BxN model and adds a cautionary note on the need to validate the reference genes for reliable, comparable, and reproducible results.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C T :
-
Threshold cycle
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- RT:
-
Reverse transcription
- WT:
-
Wild type
REFERENCES
Firestein, G.S. 2003. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 423(6937): 356–361.
McInnes, I.B., and G. Schett. 2011. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. The New England Journal of Medicine 365(23): 2205–2219.
Smolen, J.S., and G. Steiner. 2003. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery 2(6): 473–488.
Isaacs, J.D., and G. Ferraccioli. 2011. The need for personalised medicine for rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 70(1): 4–7.
van der Pouw Kraan, T.C., F.A. van Gaalen, P.V. Kasperkovitz, N.L. Verbeet, T.J. Smeets, M.C. Kraan, et al. 2003. Rheumatoid arthritis is a heterogeneous disease: evidence for differences in the activation of the STAT-1 pathway between rheumatoid tissues. Arthritis and Rheumatism 48(8): 2132–2145.
Schena, M., D. Shalon, R. Heller, A. Chai, P.O. Brown, and R.W. Davis. 1996. Parallel human genome analysis: microarray-based expression monitoring of 1000 genes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 93(20): 10614–10619.
Nolan, T., R.E. Hands, and S.A. Bustin. 2006. Quantification of mRNA using real-time RT-PCR. Nature Protocols 1(3): 1559–1582.
Heid, C.A., J. Stevens, K.J. Livak, and P.M. Williams. 1996. Real time quantitative PCR. Genome Research 6(10): 986–994.
Bustin, S.A., and T. Nolan. 2004. Pitfalls of quantitative real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. Journal of Biomolecular Techniques: JBT 15(3): 155–166.
Udvardi, M.K., T. Czechowski, and W.R. Scheible. 2008. Eleven golden rules of quantitative RT-PCR. The Plant Cell 20(7): 1736–1737.
Peters, I.R., C.R. Helps, E.J. Hall, and M.J. Day. 2004. Real-time RT-PCR: considerations for efficient and sensitive assay design. Journal of Immunological Methods 286(1–2): 203–217.
Fleige, S., and M.W. Pfaffl. 2006. RNA integrity and the effect on the real-time qRT-PCR performance. Molecular Aspects of Medicine 27(2–3): 126–139.
Nolan, T., R.E. Hands, W. Ogunkolade, and S.A. Bustin. 2006. SPUD: a quantitative PCR assay for the detection of inhibitors in nucleic acid preparations. Analytical Biochemistry 351(2): 308–310.
Rieu, I., and S.J. Powers. 2009. Real-time quantitative RT-PCR: design, calculations, and statistics. The Plant Cell 21(4): 1031–1033.
Tricarico, C., P. Pinzani, S. Bianchi, M. Paglierani, V. Distante, M. Pazzagli, et al. 2002. Quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction: normalization to rRNA or single housekeeping genes is inappropriate for human tissue biopsies. Analytical Biochemistry 309(2): 293–300.
Vandesompele, J., K. De Preter, F. Pattyn, B. Poppe, N. Van Roy, A. De Paepe, et al. 2002. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biology 3(7), RESEARCH0034.
Pfaffl, M.W., A. Tichopad, C. Prgomet, and T.P. Neuvians. 2004. Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper–Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnology Letters 26(6): 509–515.
Andersen, C.L., J.L. Jensen, and T.F. Orntoft. 2004. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Research 64(15): 5245–5250.
Libus, J., and H. Storchova. 2006. Quantification of cDNA generated by reverse transcription of total RNA provides a simple alternative tool for quantitative RT-PCR normalization. BioTechniques 41(2): 156. 158, 160 passim.
Verweij, C.L. 2009. Transcript profiling towards personalised medicine in rheumatoid arthritis. The Netherlands Journal of Medicine 67(11): 364–371.
Pombo-Suarez, M., M. Calaza, J.J. Gomez-Reino, and A. Gonzalez. 2008. Reference genes for normalization of gene expression studies in human osteoarthritic articular cartilage. BMC Molecular Biology 9: 17.
Hanafy, S., and F. Jamali. 2011. Adjuvant arthritis influences expression of housekeeping genes. Inflammation Research: Official Journal of the European Histamine Research Society … [et al.] 60(6): 521–523.
Jiang, C., L. Meng, W. Zhu, M. Shahzad, X. Yang, and S. Lu. 2009. Housekeeping gene stability in pristane-induced arthritis and antigen-induced pulmonary inflammation of rats. Inflammation Research: Official Journal of the European Histamine Research Society 58(9): 601–609.
Kouskoff, V., A.S. Korganow, V. Duchatelle, C. Degott, C. Benoist, and D. Mathis. 1996. Organ-specific disease provoked by systemic autoimmunity. Cell 87(5): 811–822.
Ditzel, H.J. 2004. The K/BxN mouse: a model of human inflammatory arthritis. Trends in Molecular Medicine 10(1): 40–45.
Lee, D.M., D.S. Friend, M.F. Gurish, C. Benoist, D. Mathis, and M.B. Brenner. 2002. Mast cells: a cellular link between autoantibodies and inflammatory arthritis. Science 297(5587): 1689–1692.
Monach, P.A., P.A. Nigrovic, M. Chen, H. Hock, D.M. Lee, C. Benoist, et al. 2010. Neutrophils in a mouse model of autoantibody-mediated arthritis: Critical producers of Fc receptor gamma, the receptor for C5a, and lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1. Arthritis and Rheumatism 62(3): 753–764.
Matzelle, M.M., M.A. Gallant, K.W. Condon, N.C. Walsh, C.A. Manning, G.S. Stein, et al. 2012. Resolution of inflammation induces osteoblast function and regulates the Wnt signaling pathway. Arthritis and Rheumatism 64(5): 1540–1550.
Montero-Melendez, T., H.B. Patel, M. Seed, S. Nielsen, T.E. Jonassen, and M. Perretti. 2011. The melanocortin agonist AP214 exerts anti-inflammatory and proresolving properties. The American Journal of Pathology 179(1): 259–269.
Patel, H.B., K.N. Kornerup, A.L. Sampaio, F. D’Acquisto, M.P. Seed, A.P. Girol, et al. 2012. The impact of endogenous annexin A1 on glucocorticoid control of inflammatory arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 71(11): 1872–1880.
Savli, H., A. Karadenizli, F. Kolayli, S. Gundes, U. Ozbek, and H. Vahaboglu. 2003. Expression stability of six housekeeping genes: a proposal for resistance gene quantification studies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by real-time quantitative RT-PCR. Journal of Medical Microbiology 52(Pt 5): 403–408.
Chen, M., E. Boilard, P.A. Nigrovic, P. Clark, D. Xu, G.A. Fitzgerald, et al. 2008. Predominance of cyclooxygenase 1 over cyclooxygenase 2 in the generation of proinflammatory prostaglandins in autoantibody-driven K/BxN serum-transfer arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 58(5): 1354–1365.
Patel, H.B., M. Bombardieri, A.L. Sampaio, F. D’Acquisto, M. Gray, P. Grieco, et al. 2010. Anti-inflammatory and antiosteoclastogenesis properties of endogenous melanocortin receptor type 3 in experimental arthritis. FASEB Journal: Official Publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 24(12): 4835–4843.
Al-Kashi, A., T. Montero-Melendez, N. Moradi-Bidhendi, J.P. Gilligan, N. Mehta, and M. Perretti. 2013. The calcitonin and glucocorticoids combination: mechanistic insights into their class-effect synergy in experimental arthritis. PloS One 8(2): e54299.
Dabek, J., J. Wilczok, A. Kulach, and Z. Gasior. 2010. Altered transcriptional activity of gene encoding GAPDH in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with cardiac syndrome X—an important part in pathology of microvascular angina? Archives of Medical Science AMS 6(5): 709–712.
Della Beffa, C., F. Klawonn, J.P. Menetski, H.R. Schumacher Jr., and F. Pessler. 2011. Evaluation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, prolylpeptidyl isomerase A, and a set of stably expressed genes as reference mRNAs in urate crystal inflammation. BMC Research Notes 4: 443.
Waxman, S., and E. Wurmbach. 2007. De-regulation of common housekeeping genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Genomics 8: 243.
Glare, E.M., M. Divjak, M.J. Bailey, and E.H. Walters. 2002. beta-Actin and GAPDH housekeeping gene expression in asthmatic airways is variable and not suitable for normalising mRNA levels. Thorax 57(9): 765–770.
Wan, G., K. Yang, Q. Lim, L. Zhou, B.P. He, H.K. Wong, et al. 2010. Identification and validation of reference genes for expression studies in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 400(4): 575–580.
Foldager, C.B., S. Munir, M. Ulrik-Vinther, K. Soballe, C. Bunger, and M. Lind. 2009. Validation of suitable housekeeping genes for hypoxia-cultured human chondrocytes. BMC Molecular Biology 10: 94.
Perez, S., L.J. Royo, A. Astudillo, D. Escudero, F. Alvarez, A. Rodriguez, et al. 2007. Identifying the most suitable endogenous control for determining gene expression in hearts from organ donors. BMC Molecular Biology 8: 114.
Mori, R., Q. Wang, K.D. Danenberg, J.K. Pinski, and P.V. Danenberg. 2008. Both beta-actin and GAPDH are useful reference genes for normalization of quantitative RT-PCR in human FFPE tissue samples of prostate cancer. The Prostate 68(14): 1555–1560.
Arenas-Hernandez, M., and R. Vega-Sanchez. 2013. Housekeeping gene expression stability in reproductive tissues after mitogen stimulation. BMC Research Notes 6: 285.
Riemer, A.B., D.B. Keskin, and E.L. Reinherz. 2012. Identification and validation of reference genes for expression studies in human keratinocyte cell lines treated with and without interferon-gamma—a method for qRT-PCR reference gene determination. Experimental Dermatology 21(8): 625–629.
Quiroz, F.G., O.M. Posada, D. Gallego-Perez, N. Higuita-Castro, C. Sarassa, D.J. Hansford, et al. 2010. Housekeeping gene stability influences the quantification of osteogenic markers during stem cell differentiation to the osteogenic lineage. Cytotechnology 62(2): 109–120.
Laidlaw, A.M., B. Copeland, C.M. Ross, and J.E. Hardingham. 2006. Extent of over-expression of hepatocyte growth factor receptor in colorectal tumours is dependent on the choice of normaliser. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 341(4): 1017–1021.
Livak, K.J., and T.D. Schmittgen. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4): 402–408.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Funded by Medical Research Council, MR/K013068/1.
Conflict of Interest
Authors declare no competing interests.
Authors’ Contributions
TMM: designed the study, performed and analyzed experiments, and wrote manuscript.
MP: participated in the design of the study, helped to draft the manuscript, and provided funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montero-Melendez, T., Perretti, M. Gapdh Gene Expression Is Modulated by Inflammatory Arthritis and Is not Suitable for qPCR Normalization. Inflammation 37, 1059–1069 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9829-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9829-x