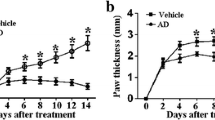
Abstract
Sinomenine (SIN) is the active principle of the Chinese medical plant Sinomenium acutum which is widely used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in China. Recently, several groups indicated that myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 (MyD88) might be associated with disease progression of RA. Here, we observed the effect of SIN on MyD88 expression and showed its therapeutic role in RA. First, immunohistochemical staining in clinical specimens showed that MyD88 was mainly located in characteristic pathological structures of RA synovial tissues. Second, we found that MyD88 was overexpressed in the synovial tissues of the rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA). Treatment with SIN markedly decreased the expression of MyD88 in AIA rats. Finally, we provided evidences that SIN suppressed inflammation response and inflammation-induced joint destructive progression and arthritis symptoms in AIA rats. Therefore, SIN is an effective therapeutic agent for RA. Targeting MyD88 signaling may provide new methods for the treatment of RA.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Choy, E.H., and G.S. Panayi. 2001. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. The New England Journal of Medicine 344: 907–916.
Sweeney, S.E., and G.S. Firestein. 2004. Rheumatoid arthritis: Regulation of synovial inflammation. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 36: 372–378.
McInnes, I.B., and G. Schett. 2007. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Reviews Immunology 7: 429–442.
Joosten, L.A., M.I. Koenders, R.L. Smeets, M. Heuvelmans-Jacobs, M.M. Helsen, K. Takeda, S. Akira, E. Lubberts, F.A. van de Loo, and W.B. van den Berg. 2003. Toll-like receptor 2 pathway drives streptococcal cell wall-induced joint inflammation: Critical role of myeloid differentiation factor 88. Journal of Immunology 171: 6145–6153.
Brown, J., H. Wang, G.N. Hajishengallis, and M. Martin. 2011. TLR-signaling networks: An integration of adaptor molecules, kinases, and cross-talk. Journal of Dental Research 90: 417–427.
Choe, J.Y., B. Crain, S.R. Wu, and M. Corr. 2003. Interleukin 1 receptor dependence of serum transferred arthritis can be circumvented by toll-like receptor 4 signaling. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 197: 537–542.
Janssens, S., and R. Beyaert. 2002. A universal role for MyD88 in TLR/IL-1R-mediated signaling. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 27: 474–482.
Kok, T.W., P.Y. Yue, N.K. Mak, T.P. Fan, L. Liu, and R.N. Wong. 2005. The anti-angiogenic effect of sinomenine. Angiogenesis 8: 3–12.
Wang, A.L., Z. Li, M. Yuan, A.C. Yu, X. Zhu, and M.O. Tso. 2007. Sinomenine inhibits activation of rat retinal microglia induced by advanced glycation end products. International Immunopharmacology 7: 1552–1558.
Chen, D.P., C.K. Wong, P.C. Leung, K.P. Fung, C.B. Lau, C.P. Lau, E.K. Li, L.S. Tam, and C.W. Lam. 2011. Anti-inflammatory activities of Chinese herbal medicine sinomenine and Liang Miao San on tumor necrosis factor-alpha-activated human fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 137: 457–468.
Liang, Y., J.Q. Fang, J.Y. Du, and J.F. Fang. 2012. Effect of electroacupuncture on activation of p38MAPK in spinal dorsal horn in rats with complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced inflammatory pain. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2012: 568273.
Gutiérrez-Cañas, I., Y. Juarranz, B. Santiago, A. Arranz, C. Martinez, M. Galindo, M. Payá, R.P. Gomariz, and J.L. Pablos. 2006. VIP down-regulates TLR4 expression and TLR4-mediated chemokine production in human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Rheumatology 45: 527–532.
Zhou, H., Y.F. Wong, J. Wang, X. Cai, and L. Liu. 2008. Sinomenine ameliorates arthritis via MMPs, TIMPs, and cytokines in rats. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 376: 352–357.
Ahmed, A.S., J. Li, M. Ahmed, L. Hua, T. Yakovleva, M.H. Ossipov, G. Bakalkin, and A. Stark. 2010. Attenuation of pain and inflammation in adjuvant-induced arthritis by the proteasome inhibitor MG132. Arthritis and Rheumatism 62: 2160–2169.
Dong, Y., J. Wang, Z. Sheng, G. Li, H. Ma, X. Wang, R. Zhang, G. Lu, Q. Hu, H. Sugimura, and X. Zhou. 2009. Downregulation of EphA1 in colorectal carcinomas correlates with invasion and metastasis. Modern Pathology 22: 151–160.
Tsubaki, T., N. Arita, T. Kawakami, T. Shiratsuchi, H. Yamamoto, N. Takubo, K. Yamada, S. Nakata, S. Yamamoto, and M. Nose. 2005. Characterization of histopathology and gene-expression profiles of synovitis in early rheumatoid arthritis using targeted biopsy specimens. Arthritis Research & Therapy 7: R825–R836.
Walsh, D.A., M. Wade, P.I. Mapp, and D.R. Blake. 1998. Focally regulated endothelial proliferation and cell death in human synovium. The American Journal of Pathology 152: 691–702.
Wang, Y., Y. Fang, W. Huang, X. Zhou, M. Wang, B. Zhong, and D. Peng. 2005. Effect of sinomenine on cytokine expression of macrophages and synoviocytes in adjuvant arthritis rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 98: 37–43.
Ju, X.D., M. Deng, Y.F. Ao, C.L. Yu, J.Q. Wang, J.K. Yu, G.Q. Cui, and Y.L. Hu. 2010. Protective effect of sinomenine on cartilage degradation and chondrocytes apoptosis. Yakugaku Zasshi: Journal of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan 130: 1053–1060.
Xu, M., L. Liu, C. Qi, B. Deng, and X. Cai. 2008. Sinomenine versus NSAIDs for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Planta Medica 74: 1423–1429.
Guerrero, A.T., T.M. Cunha, W.A. Jr Verri, R.T. Gazzinelli, M.M. Teixeira, F.Q. Cunha, and S.H. Ferreira. 2012. Toll-like receptor 2/MyD88 signaling mediates zymosan-induced joint hypernociception in mice: Participation of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and CXCL1/KC. European Journal of Pharmacology 674: 51–57.
Hutchinson, M.R., L.C. Loram, Y. Zhang, M. Shridhar, N. Rezvani, D. Berkelhammer, S. Phipps, P.S. Foster, K. Landgraf, J.J. Falke, K.C. Rice, S.F. Maier, H. Yin, and L.R. Watkins. 2010. Evidence that tricyclic small molecules may possess toll-like receptor and myeloid differentiation protein 2 activity. Neuroscience 168: 551–563.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would particularly like to thank Zi-xiang Cong who has guided us through all stages of the project. This work was supported by grants from the Jinling Hospital of Nanjing (grant no. 2012014).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, H., Yao, RB., Zhao, LJ. et al. Sinomenine Decreases MyD88 Expression and Improves Inflammation-Induced Joint Damage Progression and Symptoms in Rat Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis. Inflammation 36, 1136–1144 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9648-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9648-5