Abstract
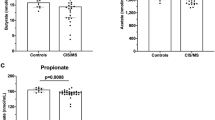
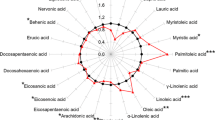
The aim of this study was to investigate whether blood cell membrane monounsaturated fatty acids were associated with inflammation and disease outcome in patients with multiple sclerosis. The fatty acid composition in peripheral blood mononuclear cell and red blood cell membranes from 26 patients and 25 controls were determined by gas chromatography. Results showed positive associations between C-reactive protein and C16:1n-7, C18:1n-7, and C24:1n-9 in membranes from controls only. In general, C18:1n-9 and C20:1n-9 showed inverse correlations, while C16:1n-7 and C18:1n-7 showed positive correlations with disease outcome. Multiple sclerosis has a known inflammatory component. There is scarcity of literature on the role of monounsaturated fatty acids in inflammation, but results from this study suggested an association in healthy subjects between monounsaturated fatty acids and C-reactive protein, even at physiologically low levels. This association was not found in the plasma from patients. Furthermore, the n-9 and n-7 fatty acids played different roles in disease outcome, and therefore warrant inclusion, together with polyunsaturated fatty acids when investigating the inflammatory aspects of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horrobin, D.F. 1999. The phospholipid concept of psychiatric disorders and its relationship to the neurodevelopmental concept of schizophrenia. In Phospholipid spectrum disorder in psychiatry, ed. M. Peet, I. Glen, and D.F. Horrobin, 3–16. Lancashire: Marius Press.
German, J.B., and C.J. Dillard. 2004. Saturated fats: what dietary intake? The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 80: 550–559.
Baker, R.W.R., R.H.S. Thompson, and K.J. Zilkha. 1964. Serum fatty acids in multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 27: 408–414.
Cherayil, G.D. 1984. Sialic acid and fatty acid concentrations in lymphocytes, red blood cells and plasma from patients with multiple sclerosis. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 63: 1–10.
Fisher, M., M.H. Johnson, A.M. Natale, and P.H. Levine. 1987. Linoleic acid levels in white blood cells, platelets, and serum of multiple sclerosis patients. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 76: 241–245.
Holman, R.T., S.B. Johnson, and E. Kokmen. 1989. Deficiencies of polyunsaturated fatty acids and replacement by nonessential fatty acids in plasma lipids in multiple sclerosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 86: 4720–4724.
Harwood, J.L., and P. Yaqoob. 2002. Nutritional and health aspects of olive oil. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology 104: 685–697.
Yaqoob, P., J.M.E. Knapper, D.H. Webb, E. Williams, A. Newsholme, and P.C. Calder. 1998. The effects of olive oil consumption on immune functions in middle-aged men. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 67: 129–135.
Linos, A., E. Kaklamanis, A. Kontomerkos, Y. Koumantaki, S. Gazi, G. Vaiopoulos, et al. 1991. The effect of olive oil and fish consumption on rheumatoid arthritis—a case control study. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 20: 419–426.
Cimmino, M.A., M. Parisi, G. Moggiana, G.S. Mela, and S. Accardo. 1998. Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in Italy, the Chivari study. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 57: 315–318.
Perez-Jimenez, F., A. Espino, F. Lopez-Segura, J. Blanco, V. Ruiz-Gutierrez, J.L. Prada, et al. 1995. Lipoprotein concentrations in normolipidemic males consuming oleic acid- rich diets from two different sources: olive oil and oleic acid-rich sunflower oil. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 62: 769–775.
Kurtzke, J.F. 1983. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33: 1444–1452.
Folch, J., M. Lees, and G.H. Sloane-Stanley. 1957. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 226: 497–509.
Van Jaarsveld, P.J., C.M. Smuts, H.Y. Tichelaar, M. Kruger, and A.J.S. Benadé. 2000. Effect of palm oil on plasma lipoprotein concentrations and plasma low-density lipoprotein composition in non-human primates. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition 51: S21–S30.
Chia, L.S., J.E. Thompson, and M.A. Moscarello. 1984. Alteration of lipid-phase behavior in multiple sclerosis myelin revealed by wide-angle x-ray diffraction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 81: 1871–1874.
Wilson, R., and D.R. Tocher. 1991. Lipid and fatty acid composition is altered in plaque tissue from multiple sclerosis brain compared with normal brain white matter. Lipids 26: 9–15.
Simopoulos, A.P. 2002. Omega-3 fatty acids in inflammation and autoimmune diseases. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 21: 495–505.
Karpuj, M.V., L. Steinman, and J.R. Oksenberg. 1997. Multiple sclerosis: a polygenic disease involving epistatic interactions, germline rearrangements and environmental effects. Neurogenetics 1: 21–28.
Willer, C.J., and G.C. Ebers. 2000. Susceptibility to multiple sclerosis: interplay between genes and environment. Current Opinion in Neurology 13: 241–247.
Moses Jr., H., and S. Sriram. 2001. An infectious basis for multiple sclerosis: perspectives on the role of Chlamydia pneumoniae and other agents. BioDrugs 15: 199–206.
Giovannoni, G., D.H. Miller, N.A. Losseff, M. Sailer, N. Lewellyn-Smith, A.J. Thompson, et al. 2001. Serum inflammatory markers and clinical/MRI markers of disease progression in multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology 248: 487–495.
Sellner, J., I. Greeve, and H.P. Mattle. 2008. Atorvastatin decreases high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis 14: 981–984.
Manzoli, F.A., S. Stefoni, L. Manzoli-Guidotti, and M. Barbieri. 1970. The fatty acids of myelin phospholipids. FEBS Letters 10: 317–320.
Acknowledgements
We would like to extend our sincere gratitude to the following: The MS Society, Western Cape Branch, South Africa, sister Treska Botha for the recruitment of patients, and Dr. Marius de Klerk for the measurement of the EDSS and FSS.
Financial Assistance/Grants
This study was funded by grants from the University Research Fund of the Cape Peninsula University of Technology, South Africa.
Conflicts of Interest
There is no conflict of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hon, G.M., Hassan, M.S., van Rensburg, S.J. et al. Monounsaturated Fatty Acids in Blood Cell Membranes from Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Inflammation 34, 681–687 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-010-9279-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-010-9279-z