Abstract
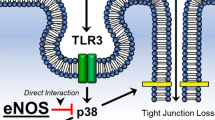
In professional immune cells, Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) induces tightly regulated inflammatory response to avoid tissue damage via the induction of “endotoxin tolerance”, which is a transient state of cell desensitization in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) restimulation after a prior LPS exposure. However, in endothelial cells, the regulation of TLR4-induced inflammation is not fully understood. In this study, we found that the gene transcripts for a lot of Toll-like receptors were expressed in various endothelial cells, including human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC), human aortic endothelial cell (HAEC), and mouse microvascular endothelial cells (bEND.3). Proteins of TLR4 and its coreceptor CD14 were also detected in HUVEC. LPS treatment significantly upregulated the expression of proinflammation cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 only in HUVEC, but not in HAEC and bEND.3, suggesting that vein endothelial cells are important source of proinflammatory cytokines in response to LPS. Unexpectedly, “endotoxin tolerance” was not induced in endothelial cell, but was induced in control glial cells, as LPS pretreatment downregulated the cytokine expression in control glial cells, but did not in endothelial cells, when the cells were restimulated with LPS. The upregulation of cytokine gene expression was dependent on NF-κB signaling, and NF-κB inhibitor repressed the induction of cytokines. Two important signal molecules MyD88 and TRIF, which are TLR4 downstream and NF-κB upstream, were upregulated in vein endothelial cells but were downregulated in control glial cells. These results suggested that vein endothelial cells may play important roles in the pathophysiology of systemic inflammation-associated diseases such as sepsis and septic cardiomyopathy.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Lindmark, E., E. Diderholm, L. Wallentin, and A. Siegbahn. 2001. Relationship between interleukin 6 and mortality in patients with unstable coronary artery disease: effects of an early invasive or noninvasive strategy. Journal of the American Medical Association 286: 2107–2113.
Peng, T., X. Lu, M. Lei, and Q. Feng. 2003. Endothelial nitric-oxide synthase enhances lipopolysaccharide-stimulated tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression via cAMP-mediated p38 MAPK pathway in cardiomyocytes. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 278: 8099–8105.
Peng, T., X. Lu, M. Lei, G.W. Moe, and Q. Feng. 2003. Inhibition of p38 MAPK decreases myocardial TNF-alpha expression and improves myocardial function and survival in endotoxemia. Cardiovascular Research 59: 893–900.
Heim, A., S. Zeuke, S. Weiss, W. Ruschewski, and I.M. Grumbach. 2000. Transient induction of cytokine production in human myocardial fibroblasts by coxsackievirus B3. Circulation Research 86: 753–759.
Zeuke, S., A.J. Ulmer, S. Kusumoto, H.A. Katus, and H. Heine. 2002. TLR4-mediated inflammatory activation of human coronary artery endothelial cells by LPS. Cardiovascular Research 56: 126–134.
Akira, S., S. Uematsu, and O. Takeuchi. 2006. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124: 783–801.
Frantz, S., G. Ertl, and J. Bauersachs. 2007. Mechanisms of disease: Toll-like receptors in cardiovascular disease. Nature Clinical Practice Cardiovascular Medicine 4: 444–454.
Nemoto, S., J.G. Vallejo, P. Knuefermann, A. Misra, G. Defreitas, B.A. Carabello, and D.L. Mann. 2002. Escherichia coli LPS-induced LV dysfunction: role of Toll-like receptor-4 in the adult heart. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology 282: H2316–H2323.
Frantz, S., L. Kobzik, Y.D. Kim, R. Fukazawa, R. Medzhitov, R.T. Lee, and R.A. Kelly. 1999. Toll4 (TLR4) expression in cardiac myocytes in normal and failing myocardium. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 104: 271–280.
Sandor, F., and M. Buc. 2005. Toll-like receptors. II. Distribution and pathways involved in TLR signalling. Folia Biologica (Praha) 51: 188–197.
Andreani, V., G. Gatti, L. Simonella, V. Rivero, and M. Maccioni. 2007. Activation of Toll-like receptor 4 on tumor cells in vitro inhibits subsequent tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Research 67: 10519–10527.
Foster, S.L., D.C. Hargreaves, and R. Medzhitov. 2007. Gene-specific control of inflammation by TLR-induced chromatin modifications. Nature 447: 972–978.
Levitt, R.J., M.M. Georgescu, and M. Pollak. 2005. PTEN-induction in U251 glioma cells decreases the expression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 336: 1056–1061.
Ning, Y., S. Chen, X. Li, Y. Ma, F. Zhao, L. Yin, and Cholesterol. 2006. LDL, and 25-hydroxycholesterol regulate expression of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein in microvascular endothelial cell line (bEnd.3). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 342: 1249–1256.
Faure, E., L. Thomas, H. Xu, A. Medvedev, O. Equils, and M. Arditi. 2001. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide and IFN-gamma induce Toll-like receptor 2 and Toll-like receptor 4 expression in human endothelial cells: role of NF-kappa B activation. Journal of Immunology 166: 2018–2024.
Akira, S., and K. Takeda. 2004. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature Reviews Immunology 4: 499–511.
Medvedev, A.E., K.M. Kopydlowski, and S.N. Vogel. 2000. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced signal transduction in endotoxin-tolerized mouse macrophages: dysregulation of cytokine, chemokine, and toll-like receptor 2 and 4 gene expression. Journal of Immunology 164: 5564–5574.
Charo, I.F., and M.B. Taubman. 2004. Chemokines in the pathogenesis of vascular disease. Circulation Research 95: 858–866.
Boisvert, W.A. 2004. Modulation of atherogenesis by chemokines. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine 14: 161–165.
Cain, B.S., D.R. Meldrum, C.A. Dinarello, X. Meng, K.S. Joo, A. Banerjee, and A.H. Harken. 1999. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta synergistically depress human myocardial function. Critical Care Medicine 27: 1309–1318.
Fujihara, M., S. Wakamoto, T. Ito, M. Muroi, T. Suzuki, H. Ikeda, and K. Ikebuchi. 2000. Lipopolysaccharide-triggered desensitization of TNF-alpha mRNA expression involves lack of phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha in a murine macrophage-like cell line, P388D1. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 68: 267–276.
Liew, F.Y., D. Xu, E.K. Brint, and L.A. O’Neill. 2005. Negative regulation of toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses. Nature Reviews Immunology 5: 446–458.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Deng, M., Liu, X. et al. TLR4 Activation Induces Nontolerant Inflammatory Response in Endothelial Cells. Inflammation 34, 509–518 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-010-9258-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-010-9258-4