Abstract
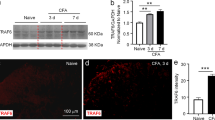
The proinflammatory and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-inducible cytokine tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) has been shown to enhance primary sensory nociceptive signaling. However, the precise cellular sites of TNF-α synthesis is still a matter of controversy. Therefore, we focused our study on TNF-α protein synthesis and expression patterns in spinal cord of controls and rats under systemic challenge with LPS. The Enzyme-linked immunosorbent (ELISA) assay showed that the protein level of TNF-α reached peak at 6 h. Double immunofluorescence revealed that LPS-induced expression of TNF-α exclusively located in a subpopulation of neurons, microglia and macrophages. These observations have demonstrated the production of this proinflammatory cytokine by spinal neurons, but the inherent mechanisms remain unknown. Further studies are needed to confirm the pathogenic role of tumor necrosis factor in the early stage of inflammation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Chaer, E. D., K. N. Westlund, and W. D. Willis. 1997. Sensitization of postsynaptic dorsal column neuron responses by colon inflammation. Neuroreport 8:3267–3273. doi:10.1097/00001756-199710200-00016.
Aldskogius, H. 2001. Microglia in neuroregeneration. Microsc. Res. Tech. 54:40–46. doi:10.1002/jemt.1119.
Alexander, H. R., G. M. Doherty, C. M. Buresh, S. J. Venzon, and D. J. Norton. 1991. A recombinant human receptor antagonist interleukin 1 improves survival after lethal endotoxemia in mice. J. Exp. Med. 173:1029–1032. doi:10.1084/jem.173.4.1029.
Andersson, P. B., V. H. Perry, and S. Gordon. 1992. The acute inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide in CNS parenchyma differs from that in other body tissues. Neuroscience 48:169–186. doi:10.1016/0306-4522(92)90347-5.
Burrell, R. 1990. Immunomodulation by bacterial endotoxin. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 17:189–208. doi:10.3109/10408419009105725.
Cheng, B., S. Christakos, and M. P. Mattson. 1994. Tumor necrosis factors protect neurons against metabolic-excitotoxic insults and promote maintenance of calcium homeostasis. Neuron. 12:139–153. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(94)90159-7.
Costelli, P., N. Carbo, L. Tessitore, G. J. Bagby, F. J. Lopez-Soriano, J. M. Argiles, et al. 1992. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates changes in tissue protein turnover in a rat cancer cachexia model. J. Clin. Invest. 92:2783–2789. doi:10.1172/JCI116897.
Coussens, L. M., and Z. Werb. 2002. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. doi:10.1038/nature01322.
Dubner, R., and M. A. Ruda. 1992. Activity dependent neuron plasticity following tissue injury and inflammation. Trends Neurosci. 15:96–103. doi:10.1016/0166-2236(92)90019-5.
Garrison, D. W., M. J. Chandler, and R. D. Foreman. 1992. Viscerosomatic convergence onto feline spinal neurons from esophagus, heart and somatic fields: effects of inflammation. Pain. 49:373–382. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(92)90245-7.
Gaur, U., and B. B. Aggarwal. 2003. Regulation of proliferation, survival and apoptosis by members of the TNF superfamily. Biochem. Pharmacol. 66:1403–1408. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(03)00490-8.
George, A., C. Schmidt, A. Weishaupt, K. V. Toyka, and C. Sommer. 1999. Serial determination of tumor necrosis factor-alpha content in rat sciatic nerve after chronic constriction injury. Exp. Neurol. 160:124–132. doi:10.1006/exnr.1999.7193.
Guth, L., Z. Zhang, N. A. DiProspero, K. Joubin, and M. T. Fitch. 1994. Spinal cord injury in the rat: treatment with bacterial lipopolysaccharide and indomethacin enhances cellular repair and locomotor function. Exp. Neurol. 126:76–87. doi:10.1006/exnr.1994.1043.
Hesse, D. G., K. J. Tracey, Y. Fong, K. R. Manogue, M. A. Palladino, A. Cerami, et al. 1988. Cytokine appearance in human endotoxemia and primate bacteremia. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 166:147–153.
Kalla, R., Z. Liu, S. Xu, A. Koppius, Y. Imai, C. U. Kloss, et al. 2001. Microglia and the early phase of immune surveillance in the axotomized facial motor nucleus: impaired microglial activation and lymphocyte recruitment but no effect on neuronal survival or axonal regeneration in macrophage-colony stimulating factor-deficient mice. J. Comp. Neurol. 436:182–201. doi:10.1002/cne.1060.
Kelley, K. W., R. M. Bluthe, R. Dantzer, J. H. Zhou, W. H. Shen, R. W. Johnson, et al. 2003. Cytokine-induced sickness behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 17:S112–S118. doi:10.1016/S0889-1591(02)00077-6.
Kirchhoff, C., S. Jung, P. W. Reeh, and H. O. Handwerker. 1990. Carageenan inflammation increases bradykinin sensitivity of rat cutaneous nocieptors. Neurosci. Lett. 111:206–210. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(90)90369-K.
Ksontini, R., S. L. MacKay, and L. L. Moldawer. 1998. Revisiting the role of tumor necrosis factor alpha and the response to surgical injury and inflammation. Arch. Surg. 133:558–567. doi:10.1001/archsurg.133.5.558.
Lazar, D. A., D. B. Ellegala, A. M. Avellino, A. T. Dailey, and K. Andrus. 1999. Modulation of macrophage and microglia responses to axonal injury in the peripheral and central nervous systems. Neurosurgery 45:593–600. doi:10.1097/00006123-199909000-00030.
Lee, S. C., W. Liu, D. W. Dickson, C. F. Brosnan, and J. W. Berman. 1993. Cytokine production by human fetal microglia and astrocytes. J. Immunol. 150:2659–2667.
Lu, X., and P. M. Richardson. 1993. Responses of macrophages in rat dorsal root ganglia following peripheral nerve injury. J. Neurocytol. 22:334–341. doi:10.1007/BF01195557.
Mathison, J. C., E. Wolfson, and R. J. Ulevitch. 1988. Participation of tumor necrosis factor in the mediation of Gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in rabbits. J. Clin. Invest. 81:1925–1937. doi:10.1172/JCI113540.
McDonald, P. P., and M. A. Cassatella. 1997. Activation of transcription factor NF-κB by phagocytic stimuli in human neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 412:583–586. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(97)00857-0.
McMahon, S. B. 1988. Neuron and behavioral consequences of chemical inflammation of the rat urinary bladder. Agents Actions 25:231–233. doi:10.1007/BF01965020.
McMahon, S. B., and C. Abel. 1987. A model for the study of visceral pain states: chronic inflammation of the chronic decerebrate rat urinary bladder by irritant chemicals. Pain. 28:109–127. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(87)91065-7.
Michie, H. R., K. R. Manogue, D. R. Spriggs, et al. 1988. Detection of circulating tumor necrosis factor after endotoxin administration. N. Engl. J. Med. 318:1481–1486.
Munoz-Fernandez, M. A., and M. Fresno. 1998. The role of tumour necrosis factor, interleukin 6, interferon-gamma and inducible nitric oxide synthase in the development and pathology of the nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 56:307–340. doi:10.1016/S0301-0082(98)00045-8.
Neumann, S., and C. J. Woolf. 1999. Regeneration of dorsal column fibres into and beyond the lesion site following adult spinal cord injury. Neuron. 23:83–91. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80755-2.
Noguchi, K., K. Kowalski, R. Traub, A. Solodkin, M. J. Iadarola, and M. A. Ruda. 1991. Dynorphin expression and fos-like immunoreactivity following inflammation-induced hyperalgesia are co-localized in spinal neurons. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 10:227–233. doi:10.1016/0169-328X(91)90065-6.
Pan, W., J. E. Zadina, R. E. Harlan, J. T. Weber, W. A. Banks, and A. J. Kastin. 1997. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha: a neuromodulator in the CNS. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 21:603–613. doi:10.1016/S0149-7634(96)00047-4.
Parada, C. A., J. J. Yeh, E. K. Joseph, and J. D. Levine. 2003. Tumor necrosis factor receptor type-1 in sensory neurons contributes to induction of chronic enhancement of inflammatory hyperalgesia in rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 17:1847–1852. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02626.x.
Prinz, M., O. Kann, H. J. Draheim, R. R. Schumann, H. Kettenmann, J. R. Weber, et al. 1999. Microglial activation by components of Gram-positive and -negative bacteria: Distinct and common routes to the induction of ion channels and cytokines. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 58:1078–1089. doi:10.1097/00005072-199910000-00006.
Raivich, G. 2002. Microglial response in the axotomised facial motor nucleus. In: Microgliak in the Rregenerating and Degenerating Central Nervous System, W.J. S. ed. New York, Springer-Verlag, pp. 166–187.
Ren Hylden, K. J. L., G. M. Williams, M. A. Ruda, and R. Dubner. 1992. The effects of a noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist MK801 on behavioral hyperalgesia and dorsal horn neuron activity in rats with unilateral inflammation. Pain. 50:331–344. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(92)90039-E.
Richardson, P. M., and X. Lu. 1994. Inflammation and axonal regeneration. J. Neurol. 242:S57–S60. doi:10.1007/BF00939244.
Schafers, M., C. Geis, D. Brors, T. L. Yaksh, and C. Sommer. 2002. Anterograde transport of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the intact and injured rat sciatic nerve. J. Neurosci. 22:536–545.
Schafers, M., C. Geis, C. I. Svensson, Z. D. Luo, and C. Sommer. 2003. Selective increase of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in injured and spared myelinated primary afferents after chronic constrictive injury of rat sciatic nerve. Eur. J. Neurosci. 17:791–804. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02504.x.
Schnell, L., S. Fearn, H. Klassen, M. E. Schwab, and V. H. Perry. 1999. Acute inflammatory responses to mechanical lesions in the CNS: differences between brain and spinal cord. Eur. J. Neurosci. 11:3648–3658. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00792.x.
Shubayev, V. I., and R. R. Myers. 2001. Axonal transport of TNF-alpha in painful neuropathy: distribution of ligand tracer and TNF receptors. J. Neuroimmunol. 114:48–56. doi:10.1016/S0165-5728(00)00453-7.
Strassmann, G., M. Fong, J. S. Kenny, and C. O. Jacob. 1992. Evidence for the involvement of interleukin 6 in experimental cancer cachexia. J. Clin. Invest. 89:1681–1684. doi:10.1172/JCI115767.
Sun, L. L., C. Cheng, H. O. Liu, C. C. Shen, F. Xiao, J. Qin, et al. 2007. Src suppressed C kinase substrate regulates the lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-alpha biosynthesis in rat astrocytes. J. Mol. Neurosci. 32:16–24. doi:10.1007/s12031-007-0003-x.
Tracey, K. J., Y. Fong, D. G. Hesse, K. R. Manogue, A. T. Lee, G. C. Kuo, et al. 1987. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature 330:662–664. doi:10.1038/330662a0.
Woolf, C. J. 1992. Excitability changes in central neurons following peripheral damage: role of central sensitization in the pathogenesis of painIn: Hyperalgesia and Allodynia, Willis, W. D. ed. New York, Raven, pp. 221–243.
Zhang, M., and K. J. Tracey. 1998. Tumor necrosis factorIn: The Cytokine Handbook, Thomson ed. San Diego, Academic Press, pp. 517–548.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China Grant (No.30300099 and No.30770488), Natural Scientific Foundation of Jiangsu Province Grant (No. BK2003035 and No. BK2006547), College and University Natural Scientific Research Programme Jiangsu Province (No. 03KJB180109 and No. 04KJB320114), Technology Guidance Plan for Social Development of Jiangsu Province Grant (BS2004526), Health Project of Jiangsu Province (H200632), the Foundation of Talented Person at the Summit of 6 Fields of Jiangsu Province. (No.2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qin Shen and Dan Zhou contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Q., Zhou, D., Ben, Z. et al. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Upregulation of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) in Rat Spinal Cord. Inflammation 31, 336–343 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-008-9083-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-008-9083-1