Abstract
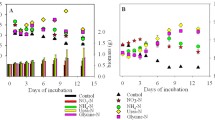
The hypothesis that nitrogen and phosphorus can have a positive effect on the bloom formation of Ulva prolifera along the southern coast of the Yellow Sea was examined. The nutrient enrichment on the growth and photosynthetic carbon assimilation of U. prolifera were investigated in laboratory. Four nitrogen and phosphorus treatments were established: high nitrogen and high phosphorus (HNHP), high nitrogen and low phosphorus, low nitrogen and high phosphorus, and low nitrogen and low phosphorus (LNLP). Fresh weights, relative growth rate (RGR), chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, photosynthetic rate, and the uptake of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) in U. prolifera were measured. The results showed that nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment significantly increased RGR of U. prolifera. The chlorophyll fluorescence parameters all reached maximum values under the HNHP treatment. The photosynthetic rate under the HNHP treatment also was the highest, which was 1.52 times that of the LNLP treatment. The DIC uptake under the HNHP treatment was 1.63 times greater than under the LNLP treatment. The photosynthesis and carbon fixation were significantly promoted by N and P enrichment. This work may further clarify the mechanisms of U. prolifera bloom formation and decline in the Yellow Sea.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- N:
-
Nitrogen
- P:
-
Phosphorus
- HNHP:
-
High nitrogen and high phosphorus
- HNLP:
-
High nitrogen and low phosphorus
- LNHP:
-
Low nitrogen and high phosphorus
- LNLP:
-
Low nitrogen and low phosphorus
- RGR:
-
Relative growth rate
- PSII:
-
Photosystem II
- F v /F m :
-
Maximum quantum yield of PSII
- Φ PSII (Yield):
-
Actual quantum yield of PSII
- NPQ:
-
Non-photochemical quenching
- F v /F 0 :
-
Potential activity of PSII
- rETR:
-
Relative electron transport rate
- α :
-
Light utilization efficiency
- DIC:
-
Dissolved inorganic carbon
- DIN:
-
Dissolved inorganic nitrogen
- DIP:
-
Dissolved inorganic phosphorus
- FW:
-
Fresh weight
- DW:
-
Dry weight
- VSE:
-
Von Stosch’s enriched
- ANOVA:
-
One-way analysis of variance
References
Cabello-Pasini, A., V. Macías-Carranza, R. Abdala, N. Korbee & F. L. Figueroa, 2011. Effect of nitrate concentration and UVR on photosynthesis, respiration, nitrate reductase activity, and phenolic compounds in Ulva rigida (Chlorophyta). Journal of Applied Phycology 23: 363–369.
Cao, J. C., Q. Wu, J. H. Zhang, H. L. Wu, Q. He, D. J. Shi, J. H. Ma & P. M. He, 2013. Studies on photosynthetic physiological characteristics and grade evaluation for free-floating algae (Ulva prolifera) along Qingdao coast. Journal Shanghai Ocean University 22: 922–927 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ding, L. P., R. X. Luan, B. X. Huang & S. J. Luan, 2008. The taxonomical study on Capsosiphonaceae (Ulvales, Chlorophyta) from Huanghai–Bohai Seas of China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 30: 169–174 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Du, R. B., L. M. Liu, A. M. Wang & Y. Q. Wang, 2013. Effects of temperature, algae biomass and ambient nutrient on the absorption of dissolved nitrogen and phosphate by Rhodophyte Gracilaria asiatica. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology 31: 353–365.
Evans, G. C., 1972. The Quantitative Analysis of Plant Growth. Blackwell Scientific Publication, Oxford, 734 pp.
Feng, Z. H., Y. Meng, W. Lu, Q. F. Chen, K. F. Yu, C. E. Cai, Y. Z. Huo, W. N. Wu, H. Wei & P. M. He, 2012. Studies on photosynthesis carbon fixation and ocean acidification prevention in Ulva prolifera I. Rate of photosynthesis carbon fixation and seawater pH increase. Acta Oceanoloogica Sinica 34: 162–168 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Fong, P., J. J. Fong & C. R. Fong, 2004. Growth, nutrient storage, and release of dissolved organic nitrogen by Enteromorpha intestinalis in response to pulses of nitrogen and phosphorus. Aquatic Botany 78: 83–95.
Gao, K. S., Y. Aruga, K. Asada, T. Ishihara, T. Akano & M. Kiyohara, 1991. Enhanced growth of the red alga Porphyra yezoensis Ueda in high CO2 concentrations. Journal of Applied Phycology 3: 355–362.
Gao, S., S. D. Shen, G. C. Wang, J. F. Niu, A. P. Lin & G. H. Pan, 2011. PSI-Driven cyclic electron flow allows intertidal macro-algae Ulva sp. (Chlorophyta) to survive in desiccated conditions. Plant and Cell Physiology 52: 885–893.
Geider, R. J., H. L. Macintyre, L. M. Graziano & R. M. L. McKay, 1998. Responses of the photosynthetic apparatus of Dunaliella tertiolecta (Chlorophyceae) to nitrogen and phosphorus limitation. European Journal of Phycology 33: 315–332.
Gómez, I., F. L. Figueroa, N. Ulloa, V. Morales, C. Lovengreen, P. Huovinen & S. Hess, 2004. Patterns of photosynthesis in 18 species of intertidal macroalgae from southern Chile. Marine Ecology Progress Series 270: 103–116.
Han, T. T., 2013. Photosynthetic physiological responses of macroalgae to different CO2 concentrations and their ecological effects: Dissertation, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
He, P. M., S. N. Xu, H. Y. Zhang, S. S. Wen, Y. J. Dai, S. J. Lin & C. Yarish, 2008. Bioremediation efficiency in the removal of dissolved inorganic nutrients by the red seaweed, Porphyra yezoensis, cultivated in the open sea. Water Research 42: 1281–1289.
Huo, Y. Z., H. L. Wu, Z. Y. Chai, S. N. Xu, F. Han, L. Dong & P. M. He, 2012. Bioremediation efficiency of Gracilaria verrucosa for an integrated multi-trophic aquaculture system with Pseudosciaena crocea in Xiangshan harbor, China. Aquaculture 326–329: 99–105.
Huo, Y. Z., J. H. Zhang, L. P. Chen, M. Hu, K. F. Yu, Q. F. Chen, Q. He & P. M. He, 2013. Green algae blooms caused by Ulva prolifera in the southern Yellow Sea: identification of the original bloom location and evaluation of biological processes occurring during the early northward floating period. Limnology and Oceanography 58: 2206–2218.
Huppe, H. C. & D. H. Turpin, 1994. Integration of carbon and nitrogen metabolism in plant and algal cells. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology 45: 577–607.
Keesing, J. K., D. Y. Liu, P. Fearns & R. Garcia, 2011. Inter- and intra-annual patterns of Ulva prolifera green tides in the Yellow Sea during 2007–2009, their origin and relationship to the expansion of coastal seaweed aquaculture in China. Marine Pollution Bulletin 62: 1169–1182.
Kittiwanich, J., T. Yamamoto, O. Kawaguchi & I. Madinabeitia, 2015. Assessing responses of the Hiroshima Bay ecosystem to increasing or decreasing phosphoru and nitrogen inputs. Marine Pollution Bulletin. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.04.003.
Kraemer, G. P., R. Carmona, T. Chopin, C. Neefus, X. R. Tang & C. Yarish, 2004. Evaluation of the bioremediatory potential of several species of the red alga Porphyra using short-term measurements of nitrogen uptake as a rapid bioassay. Journal of Applied Phycology 16: 489–497.
Li, F., D. H. Zou, Z. P. Liu, G. M. Zhao, L. W. Cheng, X. F. Zhu & W. Z. Chen, 2009. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorous levels on growth and photosynthetic traits of Gracilaria lemaneiformis (Rhodophyta). Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology 33: 1140–1147 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, J. P. & W. H. Zhao, 2011. Effects of nitrogen specification and culture method on growth of Enteromorpha prolifera. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology 29: 874–882.
Li, J. P., W. H. Zhao, M. Fu & H. Miao, 2010. Preliminary study on the effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on the growth of Enteromorpha prolifera. Marine Sciences 34: 45–48 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, S. X., K. F. Yu, Y. Z. Huo, J. H. Zhang, H. L. Wu, Q. Wu, J. J. Cui, L. H. Zhang & P. M. He, 2014. The photosynthetic physiological characteristics and evaluation of carbon fixation capacity of Ulva prolifera in Binhai sea area, Jiangsu province. Marine Fisheries 36: 306–312 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, D. Y., J. K. Keesing, Z. J. Dong, Y. Zhen, B. P. Di, Y. J. Shi, P. Fearns & P. Shi, 2010. Recurrence of the world’s largest green-tide in 2009 in Yellow Sea, China: Porphyra yezoensis aquaculture rafts confirmed as nursery for macroalgal blooms. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60: 1423–1432.
Liu, D. Y., J. K. Keesing, P. M. He, Z. L. Wang, Y. J. Shi & Y. J. Wang, 2013. The world’s largest macroalgal bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: formation and implications. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 129: 2–10.
Lobban, C. S., P. J. Harrison & M. J. Duncan, 1985. The physiological ecology of seaweeds. Cambridge University Press, New York: 11–22.
Longstaff, B. J., T. Kildea, J. W. Runcie, A. Cheshire, W. C. Dennison, C. Hurd, T. Kana, J. A. Raven & A. W. D. Larkum, 2002. An in situ study of photosynthetic oxygen exchange and electron transport rate in the marine macroalga Ulva lactuca (Chlorophyta). Photosynthesis Research 74: 281–293.
Luo, M. B., F. Liu & Z. L. Xu, 2012. Growth and nutrient uptake capacity of two co-occurring species, Ulva prolifera and Ulva linza. Aquatic Botany 100: 18–24.
Mansilla, A., M. Palacios, N. P. Navarro & M. Avila, 2008. Growth and survival performance of the gametophyte of Gigartina skottsbergii (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales) under defined nutrient conditions in laboratory culture. Journal of Applied Phycology 20: 889–896.
Marinho-Soriano, E., S. O. Nunes, M. A. A. Carneiro & D. C. Pereira, 2009. Nutrients’ removal from aquaculture wastewater using the macroalgae Gracilaria birdiae. Biomass and Bioenergy 33: 327–331.
Maxwell, K. & G. N. Johnson, 2000. Chlorophyll fluorescence – a practical guide. Journal of Experimental Biology 51: 659–668.
Mehrbach, C., C. H. Culberson, J. E. Hawley & R. M. Pytkowicz, 1973. Measurement of the apparent dissociation constants of carbonic acid in seawater at atmospheric pressure. Limnology and Oceanography 18: 897–907.
Menéndez, M., M. Martínez & F. A. Comín, 2001. A comparative study of the effect of pH and inorganic carbon resources on the photosynthesis of three floating macroalgae species of a Mediterranean coastal lagoon. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 256: 123–136.
Moazami-Goudarzi, M. & B. Colman, 2012. Changes in carbon uptake mechanisms in two green marine algae by reduced seawater pH. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 413: 94–99.
Murphy, J. & J. P. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytia Chimica Acta 27: 31–36.
Nelson, T. A., K. Haberlin, A. V. Nelson, H. Ribarich, R. Hotchkiss, K. L. Van Alstyne, L. Buckingham, D. J. Simunds & K. Fredrickson, 2003. Ecological and physiological controls of species composition in green macroalgal blooms. Ecology 89: 1287–1298.
Neori, A., I. Cohen & H. Gordin, 1991. Ulva lactuca biofilters for marine fishpond effluents II. Growth rate, yield and C:N ratio. Botanica Marina 34: 483–489.
Ott, F. D., 1965. Synthetic media and techniques for the xenic cultivation of marine algae and flagellate. Virginia Journal of Science 16: 205–218.
Packer, M., 2009. Algal capture of carbon dioxide; biomass generation as a tool for greenhouse gas mitigation with reference to New Zealand energy strategy and policy. Energy Policy 37: 3428–3437.
Pérez-lloréns, J. L., F. G. Brun, J. Andría & J. J. Vergara, 2004. Seasonal and tidal variability of environmental carbon related physico-chemical variables and inorganic C acquisition in Gracilariopsis longissima and Enteromorpha intestinalis from Los Toruños salt marsh (Cádiz Bay, Spain). Marine Biology and Ecology 304: 183–201.
Rehdanz, K., R. S. J. TOL & P. Wetzel, 2006. Ocean carbon sinks and international climate policy. Energy Policy 34: 3516–3526.
Skriptsova, A. V. & N. V. Miroshnikova, 2011. Laboratory experiment to determine the potential of two macroalgae from the Russian Far-East as biofilters for integrated multi-trophic aquaculture (IMTA). Bioresource Technology 102: 3149–3154.
State Oceanic Administration People’s Republic of China (SOA), 2011. Marine Environment Quality Status of the National Sea Waters in 2011. http://www.soa.gov.cn/soa/hygbml/hjgb/hjgb/webinfo/2012/06/1340488547097174.htm.
Terawaki, T., K. Yoshikawa, G. Yoshida, M. Uchimura & K. Iseki, 2003. Ecology and restoration techniques for Sargassum beds in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Marine Pollution Bulletin 47: 198–201.
Tsagkamilis, P., D. Danielidis, M. J. Dring & C. Katsaros, 2010. Removal of phosphate by the green seaweed Ulva lactuca in a small-scale sewage treatment plant (Ios Island, Aegean Sea, Greece). Journal of Applied Phycology 22: 331–339.
Viaroli, P., M. Bartoli, R. Azzoni, G. Giordani, C. Mucchino, M. Naldi, D. Nizzoli & L. Tajé, 2005. Nutrient and iron limitation to Ulva blooms in a eutrophic costal lagoon (Sacca di Goro, Italy). Hydrobiologia 550: 57–71.
Villares, R. & A. Carballeira, 2003. Seasonal variation in the concentrations of nutrients in two green macroalgae and nutrient levels in sediments in the Rías Baixas (NW Spain). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 58: 887–900.
Wu, H. L., Y. Z. Huo, F. Hang, Y. Y. Liu & P. M. He, 2015a. Bioremediation using Gracilaria chouae co-cultured with Sparus macrocephalus to manage the nitrogen and phosphorous balance in an IMTA system in Xiangshan Bay, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin 91: 272–279.
Wu, H. L., Y. Z. Huo, J. H. Zhang, Y. Y. Liu, Y. T. Zhao & P. M. He, 2015b. Bioremediation efficiency of the largest scale artificial Pyropia yezoensis cultivation in the open sea in China. Marine Pollution Bulletin 95: 289–296.
Wu, Q., 2015. Mechanism of floating and sinking for Ulva prolifera: Dissertation, Shanghai Ocean University (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu, C. L., W. L. Xu & C. M. Zhang, 1998. The specification for marine monitoring. Standard Press of China, Beijing: 165 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu, J. T. & K. S. Gao, 2012. Focus issue on the plant physiology of global change future CO2-induced ocean acidification mediates the physiological performance of a green tide algal. Plant Physiology 160: 1762–1769.
Xu, Z. G., D. H. Zou, X. Zhang, S. X. Liu & K. S. Gao, 2008. Effects of increased atmospheric CO2 and N supply on growth, biochemical compositions and uptake of nutrients in Gracilaria lemaneiformis (Rhodorhyta). Acta Ecologica Sinica 28: 3752–3759 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Young, E. B. & J. Beardall, 2005. Modulation of photosynthesis and inorganic carbon acquisition in a marine microalga by nitrogen, iron and light availability. Canadian Journal of Botany 83: 917–928.
Zhang, N. X., J. M. Song, C. H. Cao, R. Z. Ren, F. C. Wu, S. P. Zhang & X. Sun, 2012. The influence of macronitrogen (NO3 − and NH4 +) addition with Ulva pertusa on dissolved inorganic carbon system. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 31: 73–82.
Zhang, J. H., Y. Z. Huo, Z. L. Zhang, K. F. Yu, Q. He, L. H. Zhang, L. L. Yang, R. Xu & P. M. He, 2013. Variations of morphology and photosynthetic performances of Ulva prolifera during the whole green tide blooming process in the Yellow Sea. Marine Environmental Research 92: 35–42.
Zhang, J. H., Y. Z. Huo, H. L. Wu, K. F. Yu, J. K. Kim, C. Yarish, Y. T. Qin, C. C. Liu, R. Xu & P. M. He, 2014. The origin of the Ulva macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea in 2013. Marine Pollution Bulletin 89: 276–283.
Zou, D. H., 2005. Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 on growth, photosynthesis and nitrogen metabolism in the economic brown seaweed, Hizikia fusiforme (Sargassaceae, Phaeophyta). Aquaculture 250: 726–735.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the National Science and Technology Support Program (2012BAC07B03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Handling editor: David Philip Hamilton
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Yu, K., Huo, Y. et al. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment on growth and photosynthetic assimilation of carbon in a green tide-forming species (Ulva prolifera) in the Yellow Sea. Hydrobiologia 776, 161–171 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2749-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2749-z