Abstract
Site-specific temporal trends in algae, benthic invertebrate, and fish assemblages were investigated in 15 streams and rivers draining basins of varying land use in the south-central United States from 1993–2007. A multivariate approach was used to identify sites with statistically significant trends in aquatic assemblages which were then tested for correlations with assemblage metrics and abiotic environmental variables (climate, water quality, streamflow, and physical habitat). Significant temporal trends in one or more of the aquatic assemblages were identified at more than half (eight of 15) of the streams in the study. Assemblage metrics and abiotic environmental variables found to be significantly correlated with aquatic assemblages differed between land use categories. For example, algal assemblages at undeveloped sites were associated with physical habitat, while algal assemblages at more anthropogenically altered sites (agricultural and urban) were associated with nutrient and streamflow metrics. In urban stream sites results indicate that streamflow metrics may act as important controls on water quality conditions, as represented by aquatic assemblage metrics. The site-specific identification of biotic trends and abiotic–biotic relations presented here will provide valuable information that can inform interpretation of continued monitoring data and the design of future studies. In addition, the subsets of abiotic variables identified as potentially important drivers of change in aquatic assemblages provide policy makers and resource managers with information that will assist in the design and implementation of monitoring programs aimed at the protection of aquatic resources.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbour, M. T., J. Gerritsen, B. D. Snyder & J. B. Stribling, 1999. Rapid bioassessment protocols for use in streams and wadeable rivers: periphyton, benthic macroinvertebrates and fish, 2nd ed. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency 841-B-99-002.
Biggs, B. J. F., 1995. The contribution of disturbance, catchment geology and land use to the habitat template of periphyton in stream ecosystems. Freshwater Biology 33: 419–438.
Black, R. W., P. W. Moran & J. D. Frankforter, 2010. Response of algal metrics to nutrients andphysical facts and identification of nutrient thresholds in agricultural streams. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1539-8.
Boulton, A. J., 2003. Parrallels and contrasts in the effects of drought on stream macroinvertebrate assemblages. Freshwater Biology 48: 1173–1185.
Cardinale, B. J., 2011. Biodiversity improves water quality through nice partitioning. Nature 472: 86–89.
Charles, D. F., C. Knowles & R. S. Davis, 2002. Protocols for the Analysis of Algal Samples Collected as Part of the U.S. Geological Survey National Water-Quality Assessment Program. Report No. 02-06. Patrick Center for Environmental Research, The Academy of Natural Sciences Report No. 02-06, Philadelphia, PA.
Clarke, K. R. & M. Anisworth, 1993. A method of linking multivariate community structure to environmental variables. Marine Ecology Progress Series 92: 205–219.
Clarke, K. R. & R. N. Gorley, 2006. PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial. Plymouth, England.
Clarke, K. R. & R. M. Warwick, 1998. Quantifying structural redundancy in ecological communities. Oecologica 113: 278–289.
Clarke, K. R. & R. M. Warwick, 2001. Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation, 2nd ed. Plymouth, England.
Clarke, K. R., P. J. Somerfield, L. Airoldi & R. M. Warwick, 2006. Exploring interactions by second-state community analysis. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 338: 179–192.
Clausen, B. & B. J. F. Biggs, 1997. Relationships between benthic biota and hydrological indices in New Zealand streams. Freshwater Biology 38: 327–342.
Collier, K. J. & J. M. Quinn, 2003. Land-use influences macroinvertebrate community response following a pulse disturbance. Freshwater Biology 48: 1462–1481.
Commission for Environmental Cooperation, 1997. Ecological Regions of North America: Toward a Common Perspective. NAFTA, Montreal.
Cuffney, T. F., 2003. User’s Manual for the National Water-Quality Assessment Program Invertebrate Data Analysis System (IDAS) Software: Version 3. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 03-172.
Cuffney, T. F., M. E. Gurtz & M. R. Meador, 1993. Methods for Collecting Benthic Invertebrate Samples as Part of the National Water-Quality Assessment Program. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 93-406.
Cuffney, T. F., H. Zappia, E. M. P. Giddings & J. F. Coles, 2005. Effects of urbanization on benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in contrasting environmental settings: Boston, Massachusetts; Birmingham, Alabama; and Salt Lake City, Utah. In Brown, L. R., R. M. Hughes, R. Gray & M. R. Meador (eds), Effects of Urbanization on Stream Ecosystems. American Fisheries Society, Symposium 47, Bethesda, Maryland: 61–407.
Cuffney, T. F., M. D. Bilger & A. M. Haigler, 2007. Ambiguous taxa: effects on the characterization and interpretation of invertebrate assemblages. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 26: 286–307.
Dewson, Z. S., A. B. W. James & R. G. Death, 2007. Invertebrate community responses to experimentally reduced discharge in small streams of different water quality. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 26: 754–766.
Elser, J. J., T. Anderson, J. S. Baron, A.-K. Bergstrom, M. Jansson, M. Kyle, K. R. Nydick, L. Steger & D. O. Hessen, 2009a. Shifts in lake N:P stoichiometry and nutrient limitation driven by atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Science 326: 835–837.
Elser, J. J., M. Kyle, L. Steger, K. R. Nydick & J. S. Baron, 2009b. Nutrient availability and phytoplankton nutrient limitation across a gradient of atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Ecology 90: 3062–3073.
Fitzpatrick, F. A., I. R. Waite, P. J. D’Arconte, M. R. Meador, M. A. Maupin & M. E.Gurtz, 1998. Revised Methods for Characterizing Stream Habitat in the National Water Quality Assessment Program. U.S. Geological Survey Water Resources Investigations Report 98-4052.
Froese, R. & D. Pauly, 2009. Fishbase [available on internet at http://www.fishbase.org]. Accessed 20 June 2009.
Gilliom, R. J., J. E. Barbash, C. G. Crawford, P. A. Hamilton, J. D. Martin, N. Nakagaki, L. H. Nowell, J. C. Scott, P. E. Stackelberg, G. P. Thelin & D. M. Wolock, 2006. The Quality of Our Nation’s Waters—Pesticides in the Nation’s Streams and Ground Water, 1992–2001. U.S. Geological Survey Circular 1291.
Goldstein, R. M. & M. R. Meador, 2004. Comparisons of fish species traits from small streams to large rivers. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 133: 971–983.
Grossman, G. D., R. E. Ratajczak, M. Crawford & M. C. Freeman, 1998. Assemblage organization in stream fishes: effects of environmental variation and interspecific interactions. Ecological Monographs 68: 395–420.
Hambrook-Berkman, J. A., B. C. Scudder, M. A. Lutz & M. A. Harris, 2010. Evaluation of Aquatic Biota in Relation to Environmental Characteristics Measured at Multiple Scales in Agricultural Streams of the Midwest: 1993–2004. U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2010-5051.
Helsel, D. R. & R. M. Hirsch, 1992. Statistical Methods in Water Resources. Elsevier, New York.
Jackson, J. K. & L. Füreder, 2006. Long-term studies of freshwater macroinvertebrates: a review of the frequency, duration and ecological significance. Freshwater Biology 51: 591–603.
Kennen, J. G., K. R. Murray & K. M. Beaulieu, 2010. Determining hydrologic factors that influence stream macroinvertebrate assemblages in the northeastern US. Ecohydrology 3: 88–106.
Köhler, J. & S. Hoeg, 2000. Phytoplankton selection in a river-lake system during two decades of changing nutrient supply. Hydrobiologia 424: 13–24.
Konrad, C. P., A. M. D. Brasher & J. T. May, 2008. Assessing streamflow characteristics as limiting factors on benthic invertebrate assemblages in streams across the western United States. Freshwater Biology 53: 1983–1998.
Lenat, D. R., 1983. Chironomid taxa richness: natural variation and use in pollution assessment. Freshwater Invertebrate Biology 2: 192–198.
Lenat, D. R., 1993. A biotic index for the southeastern United States: derivation and list of tolerance values, with criteria for assigning water-quality ratings. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 12: 279–290.
McCormick, P. V. & J. Carins, 1994. Algae as indicators of environmental change. Journal of Applied Phycology 6: 509–526.
McCormick, P. V., P. S. Rawlik, K. Lurding, E. P. Smith & F. H. Sklar, 1996. Periphyton-water quality relationships along a nutrient gradient in the northern Florida Everglades. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 15: 433–449.
McElravy, E. P., G. A. Lamberti & V. H. Resh, 1989. Year-to-year variation in the aquatic macroinvertebrate fauna of a northern California stream. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 8: 51–63.
Meador, M. R., T. F. Cuffney & M. E. Gurtz, 1993a. Methods for Sampling Fish Communities as Part of the National Water-Quality Assessment Program. U.S. geological Survey Open-File Report 93-104.
Meador, M. R., Hupp, C. R., Cuffney, T. F., Gurtz, M. E., 1993b. Methods for Characterizing Stream Habitat as Part of the National Water-Quality Assessment Program. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 93-408, Reston, VA: 48 pp.
Moulton, S. R. II, J. L. Carter, S. A. Grotheer, T. F. Cuffney & T. M. Short, 2000. Methods of Analysis by the U.S. Geological Survey National Water Quality Laboratory—Processing, Taxonomy, and Quality Control of Benthic Macroinvertebrate Samples. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 00-212.
Moulton, S. R. II, J. G. Kennen, R. M. Goldstein& J. A. Hambrook, 2002. Revised Protocols for Sampling Algal, Invertebrate, And Fish Communities as Part of the National Water-Quality Assessment Program. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 02-150.
Peterson, C. G., 1996. Response of benthic algal communities to natural physical disturbance. In Stevenson, R. J., M. L. Bothwell & R. L. Lowe (eds), Algal Ecology. Academic Press, San Diego: 375–402.
Peterson, C. G. & N. B. Grimm, 1992. Temporal variation in enrichment effects during periphyton succession in a nitrogen-limited desert stream ecosystem. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 11: 20–36.
Poff, N. L. & J. D. Allan, 1995. Functional organization of stream fish assemblages in relation to hydrological variability. Ecology 76: 606–627.
Poff, N. L., J. D. Olden, N. K. M. Vieira, D. S. Finn, M. P. Simmons & B. C. Kondratieff, 2006. Functional trait niches of North American lotic insects: traits-based ecological applications in light of phylogenetic relationships. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 25: 730–755.
Porter, S. D., T. F. Cuffney, M. E. Gurtz & M. R. Meador, 1993. Methods for Collecting Algal Samples as part of the National Water-Quality Assessment Program. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 93-409.
Porter, S. D., D. K. Mueller, N. E. Spahr, M. D. Munn & N. M. Dubrovsky, 2008. Efficacy of algal metrics for assessing nutrient and organic enrichment in flowing waters. Freshwater Biology 53: 1036–1054.
Potapova, M. G. & D. F. Charles, 2003. Distribution of benthic diatoms in U.S. rivers in relation to conductivity and ionic composition. Freshwater Biology 48: 1311–1328.
Power, M. E. & A. J. Stewart, 1987. Disturbance and recovery of an algal assemblage following flooding in an Oklahoma stream. American Midland Naturalist 117: 333–345.
Pusey, B. J., M. J. Kennard & A. H. Arthington, 2000. Discharge variability and the development of predictive models relating stream fish assemblage structure to habitat in northeastern Australia. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 9: 30–50.
Richter, B. D., J. V. Baumgartner, J. Powell & D. P. Braun, 1996. A method for assessing hydrologic alteration within ecosystems. Conservation Biology 10: 1163–1174.
Ross, S. T. & J. A. Baker, 1983. The response of fishes to periodic spring floods in a southeastern stream. American Midland Naturalist 109: 1–14.
Roth, N. E., J. D. Allan & D. L. Erickson, 1996. Landscape influences on stream biotic integrity assessed at multiple spatial scales. Landscape Ecology 11: 141–156.
Roy, A. H., A. D. Rosemond, M. J. Paul, D. S. Leigh & J. B. Wallace, 2003. Stream macroinvertebrate response to catchment urbanisation (Georgia, USA). Freshwater Biology 48: 329–346.
Runkel, R. L., C. G. Crawford & T. A. Cohn, 2004. Load Estimator (LOADEST): A FORTRAN Program for Estimating Constituent Loads in Streams and Rivers. U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods Book 4, Chapter A5.
Scarsbrook, M. R., 2002. Persistence and stability of lotic invertebrate communities in New Zealand. Freshwater Biology 47: 417–431.
Scarsbrook, M. R. & C. R. Townsend, 1993. Stream community structure in relation to spatial and temporal variation: a habitat templet study of two contrasting New Zealand streams. Freshwater Biology 29: 395–410.
Sickman, J. O., J. L. Stoddard & J. M. Melack, 2002. Regional analysis of inorganic nitrogen yield and retention in high-elevation ecosystems of the Sierra Nevada and Rocky Mountains. Biogeochemistry 57(58): 341–374.
U.S. Census Bureau, 1991. Census of Population aAnd Housing, 1990. U.S. Census Bureau Technical Documentation Public Law 84-71.
U.S. Census Bureau, 2000. Census 2000 Redistricting Data Summary File. U.S. Census Bureau Technical Documentation Public Law 94-171.
Wallace, J. B., J. W. Grubaugh & M. R. Whiles, 1996. Biotic indices and stream ecosystem processes: results from an experimental study. Ecological Applications 6: 140–151.
Ward, J. V. & J. A. Stanford, 1983. The intermediate disturbance hypothesis: an explanation for biotic diversity patterns in lotic ecosystems. In Fontaine, T. D. & S. M. Bartell (eds), Dynamics of Lotic Ecosystems. Ann Arbor Science, Ann Arbor: 347–356.
Williams, M. W., J. S. Baron, N. Caine, R. Sommerfield & R. Sanford, 1996. Nitrogen Saturation in the Rocky Mountains. Envrionmental Science and Technology 30: 640–646.
Acknowledgments
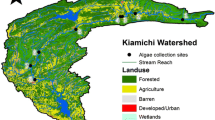
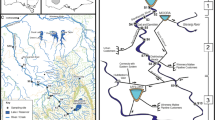
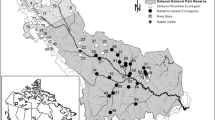
We thank the many dedicated United States Geological Survey colleagues who acquired the samples that were used in this study. Reviews by A. Brasher, D. Sullivan, and two anonymous reviewers provided many helpful suggestions that greatly improved this manuscript. S. Boyack provided assistance with the generation of Figure 1. This work was funded by the U.S. Geological Survey National Water Quality Assessment Program. The use of trade, product, or firm names in this report is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Geological Survey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Judit Padisak
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, M.P., Kennen, J.G., Mabe, J.A. et al. Temporal trends in algae, benthic invertebrate, and fish assemblages in streams and rivers draining basins of varying land use in the south-central United States, 1993–2007. Hydrobiologia 684, 15–33 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-011-0950-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-011-0950-7