Abstract
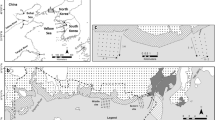
In this study, benthic decapods were sampled approximately for every three months between September 2000 and June 2002 in a heavily used subtropical lagoon and its vicinity waters in southwestern Taiwan. Seventeen shrimp species (dominated by Metapenaeus ensis and Penaeus semisulcatus) and 19 crab species (dominated by Thalamita crenata) were recorded within the lagoon, whereas a combined total of 32 shrimp species (mainly Metapenaeopsis barbata and M. palmensis) and 50 crab species (dominated by Portunus hastatoides) were recorded at 10, 20, 30, and 40-m depths outside the inlet–outlet of the lagoon. The decapod community in the lagoon varied little temporally, and was significantly different from those in the nearby waters. The results of this study document a decapod fauna in a lagoon subjected to decades of aquaculture activities and revealed that these activities benefited a distinct decapod assemblage, yet may have prevented the potential use of the lagoon by other species as a nursery or refuge. Aquaculture activities have since been prevented and dredging of the benthic sediments in the lagoon has been underway; thus the results of present study will provide a valuable and rare baseline data set to be used for future studies to determine how decapod communities shift in response to habitat change.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachelet, G., X. de Montaudouin, I. Auby & P.-J. Labourg, 2000. Seasonal changes in macrophyte and macrozoobenthos assemblages in three coastal lagoons under varying degrees of eutrophication. ICES Journal of Marine Science 57: 1495–1506.
Bishop, J. M. & M. H. Khan, 1991. Depth as a factor in abundance and size of juvenile penaeid shrimps in the absence of estuaries and marshes. Marine Biology 109: 103–114.
Blaber, S. J. M., T. Brewer & J. P. Salini, 1995. Fish communities and the nursery role of the shallow inshore waters of a tropical bay in the Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 40: 177–193.
Bomkamp, R. E., H. M. Page & J. E. Dugan, 2004. Role of food subsidies and habitat structure in influencing benthic communities of shell mounds at sites of existing and former offshore oil platforms. Marine Biology doi:10.1007/s00227-004-1413-8.
Cannicci, S., F. Dahdouh-Guebas, D. Anyona & M. Vannini, 1995. Homing in the mangrove swimming crab Thalamita crenata (Decapoda, Portunidae). Ethology 100: 242–252.
Cannicci, S., F. Dahdouh-Guebas, D. Anyona & M. Vannini, 1996. Natural diet and feeding habits of Thalamita crenata (Decapoda, Portunidae). Journal of Crustacean Biology 16: 678–683.
Carvalho, S., A. Moura, M. B. Gaspar, P. Pereira, L. C. da Fonseca, M. Falcão, T. Drago, F. Leitão & J. Regala, 2005. Spatial and inter-annual variability of the macrobenthic communities within a coastal lagoon (Óbidos lagoon) and its relationship with environmental parameters. Acta Oecologica 27: 143–159.
Chen, J. Y., 2002. Spatial & temporal variations and the ecological niche of the fish assemblage in the Dapon Bay in the Southwest Taiwan. M.S. Thesis, National Taiwan Ocean University. (in Chinese).
Chou, W. R. & L. S. Fang, 2005. The development of the decapod community at a steel-slag disposal site with disturbance from typhoon in Taiwan. Bulletin of Marine Science 76: 637–645.
Chou, W. R., S. H. Lai & L. S. Fang, 1999. Benthic crustacean communities in waters of southwestern Taiwan and their relationships to environmental characteristics. Acta Zoologica Taiwanica 10: 25–33.
Clarke, K. R. & R. M. Warwick, 1994. Changes in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation. Plymouth Marine Laboratory, UK.
Dai, A. Y., S. L. Yang, Y. Z. Song & Z. X. Chen, 1986. Crabs of the China Seas. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese).
Dall, W., B. J. Hill, P. C. Rothlisberg, D. J. Sharples, 1990. The Biology of the Penaeidae. In Blaxter J. H. S & A. J. Southward (eds), Advances in Marine Biology, Vol. 27, Academic Press, London.
Day, J. W., C. A. S. Hall, W. M. Kemp & A. Yanez-Arancibia, 1989. Estuarine Ecology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York.
Dauer, D. M., G. H. Tourtellotte & R. M. Ewing, 1982. Oyster shells and artificial worm tubes: the role of refuges in structuring benthic communities of the lower Chesapeake Bay. Internationale Revue Der Gesamten Hydrobiologie 67: 661–677.
De La Rosa, I.L., A. Rodriguez & J. E. G. Raso, 2006. Seasonal variation and structure of a decapod (Crustacea) assemblage living in a Caulerpa prolifera meadow in Cadiz Bay (SW Spain). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 66: 624–633.
Doong, R. A. & Y. T. Lin, 2004. Characterization and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminations in surface sediment and water from Gao-ping River, Taiwan. Water Research 38: 1733–1744.
Field, J. G., K. R. Clarke & R. M. Warwick, 1982. A practical strategy for analyzing multispecies distribution patterns. Marine Ecology Progress Series 8: 37–52.
Hamerlynck, O., K. Hostens, R. V. Arellano, J. Mees & P. A. Van Damme, 1993. The mobile epibenthic fauna of soft bottoms in the Dutch Delta (south-west Netherlands): spatial structure. Netherlands Journal of Aquatic Ecology 27: 343–358.
Herrnkind, W. F., M. J. Butler, J. H. Hunt & M. Childress, 1997. Role of physical refugia: implications from a mass sponge die-off in a lobster nursery in Florida. Marine and Freshwater Research 48: 759–769.
Huang, J. H., 2004. Responses of primary producers to the removal of oyster-culture pens in Tapong Bay. M. S. Thesis, National ChungHsing University, Taiwan. (in Chinese).
Hung, J. J. & P. Y. Hung, 2003. Carbon and nutrient dynamics in a hypertrophic lagoon in southwestern Taiwan. Journal of Marine Systems 42: 97–114.
Kamura, S. & H. Hashimoto, 2004. The food habits of four species of triakid sharks, Triakis scyllium, Hemitriakis japonica, Mustelus griseus and Mustelus manazo, in the central Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Fisheries Science 70: 1019–1035.
Kruskal, J. B. & M. Wish, 1978. Multidimensional Scaling. Sage Publications, Beverly Hills, London.
Kutkuhn, J. H., 1966. Dynamics of a penaeid shrimp population and management implication. Fisheries Bulletin. US Fisheries and Wildlife Service 65: 313–338.
Laroche, J., E. Baran & N. B. Rasoanandrasana, 1997. Temporal patterns in a fish assemblage of a semiarid mangrove zone in Madagascar. Journal of Fish Biology 51: 3–20.
Lo, W. T., C. L. Chung & C. T. Shih, 2004. Seasonal distribution of copepods in Tapong Bay, southwestern Taiwan. Zoological Studies 43: 464–474.
Maes, J., A. Taillieu, P. A. Van Damme, K. Cottenie & F. Ollevier, 1998. Seasonal patterns in the fish and crustacean community of a turbid temperate estuary (Zeeschelde Estuary, Belgium). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 47: 143–151.
Pérez-Castañeda, R. & O. Defeo, 2005. Growth and mortality of transient shrimp populations (Farfantepenaeus spp.) in a coastal lagoon of Mexico: role of the environment and density-dependence. ICES Journal of Marine Science 62: 14–24.
Peterson, C. H., 1979. Predation, competition, exclusion and diversity in the soft-sediment benthic communities of estuaries and lagoons. In: R. J. Livingston (ed.), Ecological Processes in Coastal and Marine Systems, Plenum Press, New York.
Peterson, C. H., 1991. Intertidal zonation of marine invertebrates in sand and mud. American Scientist 79: 236–249.
Robinson, M. & O. Tully, 2000. Spatial variability in decapod community structure and recruitment in sub-tidal habitats. Marine Ecology Progress Series 194: 133–141.
Ruiz, G. M., A. H. Hines & M. H. Posey, 1993. Shallow water as a refuge habitat for fish and crustaceans in non-vegetated estuaries: an example from Chesapeake Bay. Marine Ecology Progress Series 99: 1–16.
SPSS, 1997. SigmaStat Statistical Software. SPSS Marketing Department, Chicago, IL.
Su, M. S. & I. C. Liao, 1987. Ecological studies on commercially important prawns from the coastal waters of southwest Taiwan: I. Emigration of Penaeus monodon from Dapeng Bay. Journal of the Fisheries Society of Taiwan 14: 36–48. (in Chinese).
Su, M. S. & I. C. Liao, 1989. Community structure of penaeid prawns along the coastal waters of southwest Taiwan. Acta Oceanographica Taiwanica 24: 116–132.
Su, M. S. & I. C. Liao, 1994. Ecological studies on commercially important prawns from the coastal waters of southwest Taiwan: III. Emigration of Metapenaeus ensis from Dapeng Bay. Journal of the Fisheries Society of Taiwan 21: 183–195. (in Chinese).
Tolley, S. G. & A. K. Volety, 2005. The role of oysters in habitat use of oyster reefs by resident fishes and decapod crustaceans. Journal of Shellfish Research, 24: 1007–1012.
Wu, C. C. & Y. H. Kuo, 1999. Typhoons affecting Taiwan—current understanding and future challenges. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 80: 67–80.
Wyda, J. C., L. A. Deegan, J. E. Hughes & M. J. Weaver, 2002. The response of fishes to submerged aquatic vegetation complexity in two ecoregions of the mid-Atlantic bight: Buzzards Bay and Chesapeake Bay. Estuaries 25: 86–100.
Ye, Y. M. & H. M. A. Mohammed, 1999. An analysis of variation in catchability of green tiger prawn, Penaeus semisulcatus, in waters off Kuwait. Fishery Bulletin 97: 702–712.
Young, P. C., 1978. Moreton Bay, Queensland: A nursery area for juvenile penaeid prawns. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 29: 55–75.
Yu, H. P. & T. Y. Chan, 1986. The Illustrated Penaeid Prawns of Taiwan. Southern Materials Center, Inc., Taipei.
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to National Science Council, ROC for financial support of the research to LSF. We are also grateful to Drs. P-H. Ho for verifying the species checklist, K-T. Shao for providing samples, and D. Glover for helpful comments and suggestions on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: P. Viaroli
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tew, K.S., Chou, WR., Chuang, SF. et al. Comparison of the decapod communities in an anthropogenic impacted lagoon and its adjacent coastal waters. Hydrobiologia 607, 1–10 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-008-9328-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-008-9328-x