Abstract
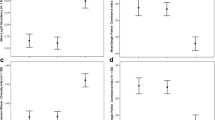
This article presents an evaluation of two sampling methods for assessing the biodiversity of heavily vegetated wetlands. The aim was to establish an effective sampling regime to maximise total taxon richness and minimise sampling effort. Three Integrated Constructed Wetland (ICW) systems in Annetown Valley, Co. Waterford, SE of the Republic of Ireland, were sampled during spring and summer 2005. The two methods that were evaluated were pond netting and two types of horizontal activity traps, namely “horizontal activity traps” (HATs) and modified “horizontal activity traps” (modified HATs). The activity traps provided a one-way funnel system and were constructed from 2 l plastic bottles, allowing for the passive collection of taxa. HATs were designed to capture macroinvertebrates in open water and modified HATs, which were designed specifically for this study, were used to sample within stands of dense emergent vegetation. Results show that a combination of pond netting and activity traps will yield a more complete estimate of taxon richness. The performance of Modified HATs was not significantly different from that of the HATs in dense vegetation. Tests on the sampling effort required for each method are also discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biggs, J., G. Fox, P. Nicolet, D. Walker, M. M. Whitfield & P. Williams, 1998. A Guide to the Methods of the National Pond Survey. Pond Action, Oxford.
Brose, U., N. D. Martínez & R. J. Williams, 2003. Estimating species richness: sensitivity to sample coverage and insensitivity to spatial patterns. Ecology 84: 2364–2377.
Chapin, F. S., E. S. Zavaleta, V. T. Eviner, R. L. Naylor, P. M. Vitousek, H. L. Reynolds, D. U. Hooper, S. Lavorel, E. O. Sala, S. E. Hobbie, M. C. Mack & S. Díaz, 2000. Consequences of changing biodiversity. Nature 405: 234–242.
Edington, J. M. & A. G. Hildrew, 1995. A Revised Key to the Caseless Caddis Larvae of the British Isles with Notes on Their Ecology. Freshwater Biological Association, Scientific Publication No. 53, Ambleside.
Elliott, J. M. & K. H. Mann, 1979. A Key to the British Freshwater Leeches. Freshwater Biological Association, Scientific Publication No. 40, Ambleside.
Elliott, J. M., U. H. Humpesch & T. T. Macan, 1988. Larvae of the British Ephemeroptera. Freshwater Biological Association, Scientific Publication No. 49, Ambleside.
Elmberg, J., P. Nummi, H. Pöysä & K. Sjöberg, 1992. Do introducing predators affect the reliability of catches in activity traps? Hydrobiologia 239: 187–193.
Friday, L. E., 1988. A Key to Adults of British Water Beetles. Field Studies Council Publication 189.
Foggo, A., S. D. Rundle & D. T. Bilton, 2003. The net result: evaluating species richness extrapolation techniques for littoral pond invertebrates. Freshwater Biology 48: 1756–1764.
García-Criado, F. & C. Trigal, 2005. Comparison of several techniques for sampling macroinvertebrates in different habitats of a North Iberian pond. Hydrobiologia 545: 103–115.
Hanson, M. A., C. C. Roy, N. H. Euliss Jr., K. D. Zimmer, M. R. Riggs & M. G. Butler, 2000. A surface-associated activity trap for capturing water-surface and aquatic invertebrates in wetlands. Wetlands 20: 205–212.
Helgen, J. H., K. Thompson, J. P. Gathman M. Gernes, L. C. Ferrington & C. Wright, 1993. Developing an Index of Biological Integrity for 33 Depressional Wetlands in Minnesota. Minnesota Pollution Control Agency, Minnesota, USA.
Heltshe, J. & N. E. Forrester, 1983. Estimating species richness using the jackknife procedure. Biometrics 39: 1–11.
Henrikson, L. & H. Oscarson, 1978. A quantitative sampler for air-breathing aquatic insects. Freshwater Biology 8: 73–77.
Hilsenhoff, W. L., 1991. Comparison of bottle traps with a D-frame net for collecting adults and larvae of Dytiscidae and Hydrophilidae (Coleoptera). Coleopterists Bulletin 45: 143–146.
Hortal, J., P. A. V. Borges & C. Gaspar, 2006. Evaluating the performance of species richness estimators: sensitivity to sample grain size. Journal of Animal Ecology 75: 274–287.
Hyvönen, T. & P. Nummi, 2000. Activity traps and the corer: complementary methods for sampling aquatic invertebrates. Hydrobiologia 432: 121–125.
Indermuehle, N., B. Oertli, N. Menetrey & L. Sager, 2004. An overview of methods potentially suitable for pond biodiversity assessment. Archives des Sciences 57: 131–140.
Kenttämies, K., S. Haapaniemi, J. Hynynen, P. Joki-Heiskala & J. Kämäri, 1985. Biological characteristics of small acidic lakes in southern Finland. Aqua Fennica 15: 21–33.
Macan, T. T. & R. D. Cooper, 1977. A Key to the British Fresh- and Brackish-Water Gastropods. Freshwater Biological Association, Scientific Publication No. 13, Ambleside.
Mitsch, J. W. & J. G. Gosselink, 2000. Wetlands, 3rd edn. John Wiley, New York.
Murkin, H. R., P. G. Abbott & J. A. Kadlec, 1983. A comparison of activity traps and sweep nets for sampling nektonic invertebrates in wetlands. Freshwater Invertebrate Biology 2: 99–106.
Muscha, M. J., K. D. Zimmer, M. G. Butler & M. A. Hanson, 2001. A comparison of horizontally and vertically deployed aquatic invertebrate activity traps. Wetlands 21: 301–307.
Muzaffar, S. B. & M. H. Colbo, 2002. The effects of sampling technique on the ecological characterization of shallow, benthic macroinvertebrate communities in two Newfoundland ponds. Hydrobiologia 477: 31–39.
Nicolet, P., J. Biggs, G. Fox, M. J. Hodson, C. Reynolds, M. Whitfield & P. Williams, 2004. The wetland plant and macroinvertebrate assemblages of temporary ponds in England and Wales. Biological Conservation 120: 261–278.
Nilsson, A. N., 1996. Aquatic Insects of Northern Europe. A Taxonomic Handbook, Vol. 1. Apollo Books, Stenstrup.
Nilsson, A. N., 1997. Aquatic Insects of Northern Europe. A Taxonomic Handbook, Vol. 2. Apollo Books, Stenstrup.
O’Connor, A., S. Bradish, T. Reed, J. Moran, E. Regan, M. Visser, M. Gormally & M. Sheehy Skeffington, 2004. A comparison of the efficacy of pond-net and box sampling methods in turloughs—Irish ephemeral aquatic systems. Hydrobiologia 524: 133–144.
Oertli, B., J. D. Auderset, E. Castella, R. Juge, D. Cambin & J. B. Lachavanne, 2002. Does size matter? The relationship between pond area and biodiversity. Biological Conservation 104: 59–70.
Oertli, B., D. A. Joye, E. Castella, R. Juge, A. Lehmann & J. B. Lachavanne, 2005. PLOCH: a standardized method for sampling and assessing the biodiversity in ponds. Aquatic Conservation 15: 665–679.
Pieczynski, E. 1961. The trap method for capturing water mites (Hydracarina). Ekologia Polska Serie B: 111–115.
Savage, A. A., 1989. Adults of the British Aquatic Hemiptera Heteroptera: A Key with Ecological Notes. Freshwater Biological Association, Scientific Publication No. 50, Ambleside.
SIL, 2004. Conference programme of XXIX Societas Internationalis Limnologiae Congress. Lahti, Finland.
Turner, A. M. & J. C. Trexler, 1997. Sampling aquatic invertebrates from marshes: evaluating the option. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 16: 694–709.
Wallace, I. D., B. Wallace & G. N. Philipson, 1990. A Key to the Case-Bearing Caddis Larvae of Britain and Ireland. Freshwater Biological Association, Scientific Publication No. 51, Ambleside.
Williams, P., M. Whitfield, J. Biggs, S. Bray, G. Fox, P. Nicolet & D. Sear, 2004. Comparative biodiversity of rivers, streams, ditches and ponds in an agricultural landscape in Southern England. Biological Conservation 115: 329–341.
Acknowledgements
This project has been funded through the European Union programme INTERREG IIIA. We gratefully acknowledge the help and enthusiasm of Waterford County Council and the constant support of Prof. Thomas Bolger, Dr. Tasman Crowe, Dr. Jan-Robert Baars, Dr. Ronan Matson, Ciara Smith B.Sc., Dr. Robert Cruishanks, Maria Callanan, B.Sc., Siobhán McCarthy, B.Sc., Ms. Katharine Maurer and Ms. Pascale Morisset with various aspects of the project. We would also like to thank two anonymous referees for their valuable comments on a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: R. Céréghino, J. Biggs, B. Oertli and S. Declerck
The ecology of European ponds: defining the characteristics of a neglected freshwater habitat
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becerra Jurado, G., Masterson, M., Harrington, R. et al. Evaluation of sampling methods for macroinvertebrate biodiversity estimation in heavily vegetated ponds. Hydrobiologia 597, 97–107 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-9217-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-9217-8